Podcast
Questions and Answers
The ascending limb of the nephron loop is characterized by which permeability?
The ascending limb of the nephron loop is characterized by which permeability?
- Permeable to salts and impermeable to water. (correct)
- Permeable to both water and salts.
- Impermeable to both water and salts.
- Permeable to water and impermeable to salts.
What would happen if the vasa recta were unable to maintain the concentration gradient in the medulla?
What would happen if the vasa recta were unable to maintain the concentration gradient in the medulla?
- The kidneys would produce very concentrated urine to compensate.
- The kidneys would produce dilute urine regardless of hydration status. (correct)
- The nephron would still function effectively, as the vasa recta plays a minor role.
- The body would retain excess salt, leading to edema.
In the countercurrent exchange system, what is the primary mechanism by which water re-enters the vasa recta capillaries?
In the countercurrent exchange system, what is the primary mechanism by which water re-enters the vasa recta capillaries?
- Osmosis (correct)
- Active transport
- Facilitated diffusion
- Filtration
What would a urine sample with a specific gravity slightly higher than water indicate?
What would a urine sample with a specific gravity slightly higher than water indicate?
Which dietary change would likely result in the least acidic urine?
Which dietary change would likely result in the least acidic urine?
What is the functional significance of the muscularis layers of the ureter?
What is the functional significance of the muscularis layers of the ureter?
Why does the trigone area of the urinary bladder maintain its shape?
Why does the trigone area of the urinary bladder maintain its shape?
Which structural feature of the urinary bladder allows for significant distension as it fills with urine?
Which structural feature of the urinary bladder allows for significant distension as it fills with urine?
Damage to the detrusor muscle would directly impair which function?
Damage to the detrusor muscle would directly impair which function?
What is the initial neural signal that triggers the micturition reflex?
What is the initial neural signal that triggers the micturition reflex?
During the micturition reflex, what is the role of parasympathetic stimulation?
During the micturition reflex, what is the role of parasympathetic stimulation?
What is the primary action of sympathetic stimulation on the urinary bladder during the storage reflex?
What is the primary action of sympathetic stimulation on the urinary bladder during the storage reflex?
Why is the external urethral sphincter continuously stimulated by the pudendal nerve during the urinary bladder storage reflex?
Why is the external urethral sphincter continuously stimulated by the pudendal nerve during the urinary bladder storage reflex?
If a patient has damage to the visceral sensory neurons signaled by baroreceptors in the bladder, what is the likely outcome?
If a patient has damage to the visceral sensory neurons signaled by baroreceptors in the bladder, what is the likely outcome?
Which part of the brain is the micturition center located?
Which part of the brain is the micturition center located?
Flashcards
Descending Limb of Nephron Loop
Descending Limb of Nephron Loop
The descending limb is permeable to water but impermeable to salts, allowing water to move out.
Ascending Limb of Nephron Loop
Ascending Limb of Nephron Loop
The ascending limb is impermeable to water but permeable to salts, allowing salts to be pumped out.
Countercurrent Exchange System
Countercurrent Exchange System
Helps maintain concentration gradient. Water diffuses out of vasa recta capillaries. Salt in interstitial fluid enters vasa recta by diffusion. Increases concentration of salt in vasa recta.
Urine Composition
Urine Composition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Color of Urine
Color of Urine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ureter Function
Ureter Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary Bladder
Urinary Bladder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trigone of the Bladder
Trigone of the Bladder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Micturition Reflex
Micturition Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary Bladder Storage Reflex
Urinary Bladder Storage Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Urinary System - Part 2
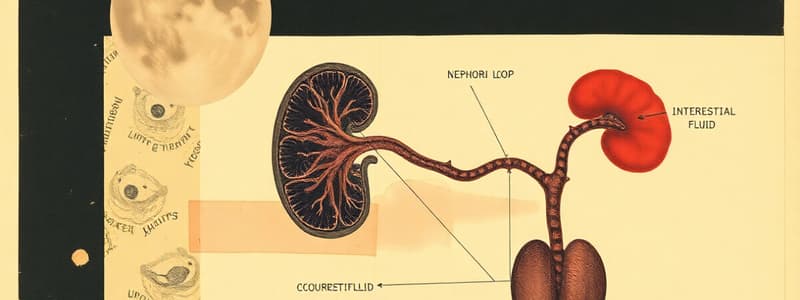
Interstitial Fluid Concentration Gradient and the Nephron Loop
- Descending limb is permeable to water but impermeable to salts.
- Water moves from the tubular fluid to the interstitial fluid.
- Salts are retained in the tubular fluid, which becomes more concentrated.
- Ascending limb is impermeable to water but permeable to salts, pumping salts out.
- The more concentrated the salts are, the more is pumped out at the beginning of the ascending limb.
- The less concentrated the salts are, the less is pumped out at the end of the ascending limb.
Countercurrent Exchange System
- The system helps maintain the concentration gradient in the nephron loop.
- Water diffuses out of vasa recta capillaries by osmosis
- Salt in the interstitial fluid enters the vasa recta via diffusion.
- Salt concentration increases in the vasa recta.
- The vasa recta runs along the descending limb of the nephron.
- Gradients are reversed, with salt diffusing out and water diffusing in.
Characteristics of Urine
- Urine is sterile unless contaminated with microbes in the kidney or urinary tract.
- Urine is composed of 95% water and 5% solutes. The solutes consist of salts, nitrogenous wastes, some hormones, drugs, and ketone bodies.
- Volume: An average of 1 to 2 liters of urine are produced per day. Variations depend on factors like fluid intake, blood pressure, temperature, diuretics, diabetes, and other fluid excretion.
- The normal pH range is between 4.5 and 8.0.
- Higher protein or wheat intake leads to a more acidic urine. A diet high in fruits and vegetables leads to less acidic urine.
- Urine pH is influenced by metabolism and infection.
- Specific gravity is slightly higher than water due to the presence of solutes.
- Urine color ranges from almost clear to dark yellow, depending on the concentration of urobilin.
- The normal smell of fresh urine is urinoid.
Urinary Tract
- The urinary tract consists of the ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra.
Ureters
- The ureters originate at the renal pelvis in each kidney.
- Muscularis layers contract to propel urine towards the urinary bladder.
Urinary Bladder
- The urinary bladder is an expandable, muscular urine reservoir.
- It has two ureter openings and one urethral opening.
- A triangular area called the trigone maintains the bladder's shape as it expands, acting as a funnel toward the urethra.
- Contains mucosal folds (rugae) to allow for greater distension.
- The bladder has three layers of muscularis, collectively called the Detrusor muscle.
Female and Male Urethra
- The female urethra is shorter than the male urethra.
Micturition Reflex
- The micturition (urination) reflex occurs when the volume of urine in the bladder is between 200 to 300 mL.
- Bladder distension activates baroreceptors, which activates bladder wall.
- Visceral sensory neurons are signaled by baroreceptors and stimulate the micturition center in the pons.
- The micturition center alters nerve signals down the spinal cord through pelvic splanchnic nerves.
- Parasympathetic stimulation causes the detrusor muscles to contract, leading to internal urethral relaxation.
Bladder Storage Reflex
- Continuous sympathetic stimulation: this causes detrusor relaxation to accommodate urine.
- Contraction of the internal urethral sphincter is stimulated so that urine is retained in the bladder.
- The external urethral sphincter is continuously stimulated by the pudendal nerve to remain contracted.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.