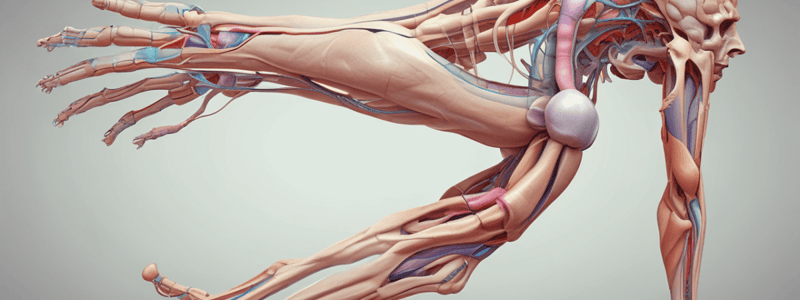
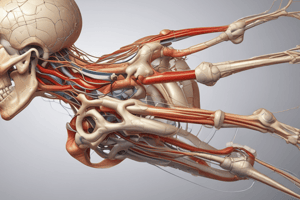
Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following nerves is responsible for holding the scapula onto the posterior part of the ribcage?
Which of the following nerves is responsible for holding the scapula onto the posterior part of the ribcage?
- Axillary nerve
- Radial nerve
- Ulnar nerve
- Long thoracic nerve (correct)
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of Erb-Duchenne Palsy?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of Erb-Duchenne Palsy?
- Claw hand paralysis (correct)
- Loss of sensation in the lateral aspect of the arm
- Paralysis of muscles of the shoulder and arm
- Adducted shoulder and medially rotated arm
Which of the following spinal nerve roots is responsible for sensation in the middle finger?
Which of the following spinal nerve roots is responsible for sensation in the middle finger?
- C6
- C5
- T1
- C7 (correct)
What is the primary function of the radial nerve in the upper limb?
What is the primary function of the radial nerve in the upper limb?
Which of the following activities is a common cause of Brachial Plexus Injuries?
Which of the following activities is a common cause of Brachial Plexus Injuries?
Which of the following nerves is responsible for extending the elbow?
Which of the following nerves is responsible for extending the elbow?
Which nerve is most commonly injured as a result of a fracture of the medial epicondyle?
Which nerve is most commonly injured as a result of a fracture of the medial epicondyle?
What is the result of paralysis of the musculocutaneous nerve?
What is the result of paralysis of the musculocutaneous nerve?
Which of the following is NOT a branch of the brachial plexus?
Which of the following is NOT a branch of the brachial plexus?
What is the result of damage to the axillary nerve?
What is the result of damage to the axillary nerve?
What is the primary function of the wrist extensors during a power grip?
What is the primary function of the wrist extensors during a power grip?
Which nerve is responsible for innervating the extensors of the posterior compartment?
Which nerve is responsible for innervating the extensors of the posterior compartment?
What is the name of the condition that occurs when the radial nerve is compressed or stretched in the armpit or upper arm?
What is the name of the condition that occurs when the radial nerve is compressed or stretched in the armpit or upper arm?
At what age is the precision grip typically developed in children?
At what age is the precision grip typically developed in children?
Which muscle group is responsible for stabilizing the medial side of the palm during a power grip?
Which muscle group is responsible for stabilizing the medial side of the palm during a power grip?
What is the main function of the interosseous membrane in the upper limb?
What is the main function of the interosseous membrane in the upper limb?
Which of the following arteries is NOT a continuation of the subclavian artery?
Which of the following arteries is NOT a continuation of the subclavian artery?
Which nerve is at risk of injury in a medial epicondyle fracture?
Which nerve is at risk of injury in a medial epicondyle fracture?
What is the main purpose of the collateral circulation around the joints?
What is the main purpose of the collateral circulation around the joints?
Which of the following is a common complication of a fractured olecranon?
Which of the following is a common complication of a fractured olecranon?
What is the origin of the posterior interosseous artery?
What is the origin of the posterior interosseous artery?
What is the main consequence of untreated compartment syndrome?
What is the main consequence of untreated compartment syndrome?
Which artery splits into the radial and ulnar arteries at the cubital fossa?
Which artery splits into the radial and ulnar arteries at the cubital fossa?
What is the treatment for compartment syndrome?
What is the treatment for compartment syndrome?
Which vein is located medial to the cubital fossa?
Which vein is located medial to the cubital fossa?
What is the primary action of the popliteus muscle in relation to the knee joint?
What is the primary action of the popliteus muscle in relation to the knee joint?
Which of the following arteries gives rise to the profunda femoris branch?
Which of the following arteries gives rise to the profunda femoris branch?
What is the level at which the abdominal aorta bifurcates?
What is the level at which the abdominal aorta bifurcates?
Which of the following muscles is NOT innervated by the femoral nerve?
Which of the following muscles is NOT innervated by the femoral nerve?
Which of the following is a branch of the internal iliac artery?
Which of the following is a branch of the internal iliac artery?
Which nerve is responsible for motor innervation of the quadriceps?
Which nerve is responsible for motor innervation of the quadriceps?
Which nerve is responsible for sensory innervation of the lateral thigh?
Which nerve is responsible for sensory innervation of the lateral thigh?
Which muscle group is innervated by the Obturator nerve?
Which muscle group is innervated by the Obturator nerve?
Which nerve is responsible for motor innervation of the gluteus maximus?
Which nerve is responsible for motor innervation of the gluteus maximus?
Which nerve is responsible for sensory innervation of the medial thigh?
Which nerve is responsible for sensory innervation of the medial thigh?
Which portion of the Sciatic nerve is responsible for motor innervation of the muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg?
Which portion of the Sciatic nerve is responsible for motor innervation of the muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg?
Which movement is allowed by the Ankle joint?
Which movement is allowed by the Ankle joint?
Which ligament is responsible for stopping the talus from moving out?
Which ligament is responsible for stopping the talus from moving out?
What is the shape of the Medial ligament?
What is the shape of the Medial ligament?
Which nerve is responsible for motor innervation of the gluteus medius and minimus?
Which nerve is responsible for motor innervation of the gluteus medius and minimus?
What is the outcome if there is paralysis of the radial nerve?
What is the outcome if there is paralysis of the radial nerve?
Which nerve is responsible for innervating the flexors in the forearm and intrinsic muscles of the hand?
Which nerve is responsible for innervating the flexors in the forearm and intrinsic muscles of the hand?
What is the outcome if there is paralysis of the musculocutaneous nerve?
What is the outcome if there is paralysis of the musculocutaneous nerve?
What is the outcome if there is damage to the axillary nerve?
What is the outcome if there is damage to the axillary nerve?
What is the outcome if there is paralysis of the median nerve?
What is the outcome if there is paralysis of the median nerve?
Which of the following spinal nerve roots is responsible for sensation in the lateral part of the arm?
Which of the following spinal nerve roots is responsible for sensation in the lateral part of the arm?
What is the main muscle affected in Klumpke Palsy?
What is the main muscle affected in Klumpke Palsy?
What is the boundary of the cubital fossa superiorly?
What is the boundary of the cubital fossa superiorly?
Which muscle is part of the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Which muscle is part of the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Which nerve is responsible for holding the scapula onto the posterior part of the ribcage?
Which nerve is responsible for holding the scapula onto the posterior part of the ribcage?
What is the typical appearance of a person with Erb-Duchenne Palsy?
What is the typical appearance of a person with Erb-Duchenne Palsy?
Which nerve is at risk of injury in a medial epicondyle fracture?
Which nerve is at risk of injury in a medial epicondyle fracture?
What is the primary role of the hypothenar muscles during a power grip?
What is the primary role of the hypothenar muscles during a power grip?
What is the origin of the axillary artery?
What is the origin of the axillary artery?
Which of the following muscles is NOT innervated by the brachial plexus?
Which of the following muscles is NOT innervated by the brachial plexus?
What is the consequence of a supracondylar fracture if the humerus moves forward?
What is the consequence of a supracondylar fracture if the humerus moves forward?
What is the clinical symptom of radial nerve injury in terms of finger movement?
What is the clinical symptom of radial nerve injury in terms of finger movement?
What is the common cause of radial nerve palsy in newborns?
What is the common cause of radial nerve palsy in newborns?
What is the main difference between power grip and precision grip?
What is the main difference between power grip and precision grip?
What is the name of the condition that occurs when the radial nerve is compressed or stretched in the armpit or upper arm?
What is the name of the condition that occurs when the radial nerve is compressed or stretched in the armpit or upper arm?
What is the main function of the quadriceps muscle group?
What is the main function of the quadriceps muscle group?
What is the origin of the femoral artery?
What is the origin of the femoral artery?
What is the function of the popliteus muscle?
What is the function of the popliteus muscle?
What is the branch of the femoral artery that gives blood supply to the quadriceps and hamstrings?
What is the branch of the femoral artery that gives blood supply to the quadriceps and hamstrings?
What is the level at which the abdominal aorta bifurcates?
What is the level at which the abdominal aorta bifurcates?
What is the main branch of the subclavian artery that supplies the upper limb?
What is the main branch of the subclavian artery that supplies the upper limb?
Which of the following arteries is responsible for supplying the posterior compartment of the forearm?
Which of the following arteries is responsible for supplying the posterior compartment of the forearm?
What is the result of increased pressure in a compartment due to damage to an artery or buildup of fluid?
What is the result of increased pressure in a compartment due to damage to an artery or buildup of fluid?
Which of the following veins is responsible for draining blood from the superficial tissues of the medial side of the arm?
Which of the following veins is responsible for draining blood from the superficial tissues of the medial side of the arm?
What is the treatment for compartment syndrome?
What is the treatment for compartment syndrome?
What is the main function of the Femoral nerve in relation to the quadriceps?
What is the main function of the Femoral nerve in relation to the quadriceps?
What is the main function of the Superior gluteal nerve?
What is the main function of the Superior gluteal nerve?
Which nerve is responsible for sensory innervation of the postolateral and medial surfaces of the foot?
Which nerve is responsible for sensory innervation of the postolateral and medial surfaces of the foot?
What is the main function of the Lateral Cutaneous nerve?
What is the main function of the Lateral Cutaneous nerve?
Which nerve is responsible for motor innervation of the gluteus maximus?
Which nerve is responsible for motor innervation of the gluteus maximus?
What is the primary function of the Obturator nerve?
What is the primary function of the Obturator nerve?
What is the main function of the Sciatic nerve?
What is the main function of the Sciatic nerve?
What is the main function of the Tibial nerve?
What is the main function of the Tibial nerve?
What is the primary function of the Fibular nerve?
What is the primary function of the Fibular nerve?
What is the primary function of the ankle joint?
What is the primary function of the ankle joint?
Which branch of the brachial plexus is responsible for innervating the deltoid muscle?
Which branch of the brachial plexus is responsible for innervating the deltoid muscle?
Which muscle is NOT innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve?
Which muscle is NOT innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve?
What is the consequence of long-term paralysis of the median nerve?
What is the consequence of long-term paralysis of the median nerve?
Which branch of the brachial plexus is the largest?
Which branch of the brachial plexus is the largest?
Which nerve is responsible for innervating the flexors in the forearm and intrinsic muscles of the hand?
Which nerve is responsible for innervating the flexors in the forearm and intrinsic muscles of the hand?
What is the primary function of the Long Thoracic nerve?
What is the primary function of the Long Thoracic nerve?
What is the characteristic symptom of Erb-Duchenne Palsy?
What is the characteristic symptom of Erb-Duchenne Palsy?
Which spinal nerve roots contribute to the formation of the brachial plexus?
Which spinal nerve roots contribute to the formation of the brachial plexus?
What is the result of a Klumpke Palsy?
What is the result of a Klumpke Palsy?
What is the region supplied by the C5 spinal nerve root?
What is the region supplied by the C5 spinal nerve root?
What is the primary function of the wrist extensors during a power grip?
What is the primary function of the wrist extensors during a power grip?
What is the characteristic of the radial nerve in the posterior compartment of the arm?
What is the characteristic of the radial nerve in the posterior compartment of the arm?
What is the typical consequence of radial nerve injury?
What is the typical consequence of radial nerve injury?
What is the primary function of the hypothenar muscles during a power grip?
What is the primary function of the hypothenar muscles during a power grip?
What is the typical age at which precision grip develops in humans?
What is the typical age at which precision grip develops in humans?
What is the main purpose of the deep and palmar arches in the forearm?
What is the main purpose of the deep and palmar arches in the forearm?
Which artery is responsible for supplying the humerus head?
Which artery is responsible for supplying the humerus head?
What is the origin of the posterior interosseous artery?
What is the origin of the posterior interosseous artery?
What is the consequence of increased pressure in a compartment due to damage to an artery or buildup of fluid?
What is the consequence of increased pressure in a compartment due to damage to an artery or buildup of fluid?
What is the primary function of the quadriceps muscle group?
What is the primary function of the quadriceps muscle group?
What is the level at which the abdominal aorta bifurcates?
What is the level at which the abdominal aorta bifurcates?
Which of the following veins is responsible for draining blood from the superficial tissues of the medial side of the arm?
Which of the following veins is responsible for draining blood from the superficial tissues of the medial side of the arm?
What forms the floor of the cubital fossa?
What forms the floor of the cubital fossa?
What is the consequence of a supracondylar fracture if the humerus moves forward?
What is the consequence of a supracondylar fracture if the humerus moves forward?
Which nerve is responsible for innervating the popliteus muscle?
Which nerve is responsible for innervating the popliteus muscle?
What is the arrangement of muscles within the upper limb?
What is the arrangement of muscles within the upper limb?
What is the mechanism by which blood returns from the veins of the lower limb to the heart?
What is the mechanism by which blood returns from the veins of the lower limb to the heart?
What is the relationship between the axillary and brachial arteries?
What is the relationship between the axillary and brachial arteries?
What is the purpose of the lumbar and sacral plexi?
What is the purpose of the lumbar and sacral plexi?
What is the arrangement of the fascial compartments in the upper limb?
What is the arrangement of the fascial compartments in the upper limb?
Which nerve is responsible for motor innervation of the quadriceps?
Which nerve is responsible for motor innervation of the quadriceps?
What is the primary function of the ankle joint?
What is the primary function of the ankle joint?
Which nerve is responsible for sensory innervation of the lateral thigh?
Which nerve is responsible for sensory innervation of the lateral thigh?
What is the primary function of the Sciatic nerve?
What is the primary function of the Sciatic nerve?
What is the shape of the Medial ligament?
What is the shape of the Medial ligament?
Which nerve is responsible for motor innervation of the gluteus maximus?
Which nerve is responsible for motor innervation of the gluteus maximus?
What is the primary function of the Ankle joint?
What is the primary function of the Ankle joint?
Which nerve is responsible for sensory innervation of the postolateral and medial surfaces of the foot?
Which nerve is responsible for sensory innervation of the postolateral and medial surfaces of the foot?
What is the primary function of the Tibial nerve?
What is the primary function of the Tibial nerve?
Which nerve is responsible for motor innervation of the adductor group of muscles?
Which nerve is responsible for motor innervation of the adductor group of muscles?
What is the primary motor function of the nerve innervating serratus anterior, and what movement does it allow for?
What is the primary motor function of the nerve innervating serratus anterior, and what movement does it allow for?
Describe the symptoms of Erb-Duchenne Palsy, including the affected nerve roots and the resulting paralysis.
Describe the symptoms of Erb-Duchenne Palsy, including the affected nerve roots and the resulting paralysis.
What are the differences between Erb-Duchenne Palsy and Klumpke Palsy in terms of the affected nerve roots and resulting paralysis?
What are the differences between Erb-Duchenne Palsy and Klumpke Palsy in terms of the affected nerve roots and resulting paralysis?
What is the primary function of the Long Thoracic nerve, and how does it contribute to upper limb movement?
What is the primary function of the Long Thoracic nerve, and how does it contribute to upper limb movement?
What are the consequences of Klumpke Palsy, including the affected nerve roots and resulting paralysis?
What are the consequences of Klumpke Palsy, including the affected nerve roots and resulting paralysis?
What is the significance of the radial nerve in the posterior compartment of the upper limb, and how does injury to this nerve affect the function of the hand?
What is the significance of the radial nerve in the posterior compartment of the upper limb, and how does injury to this nerve affect the function of the hand?
What is the difference between power grip and precision grip, and what muscle groups are involved in each type of grip?
What is the difference between power grip and precision grip, and what muscle groups are involved in each type of grip?
How does median nerve palsy affect the function of the hand, and what are the possible causes of this type of palsy?
How does median nerve palsy affect the function of the hand, and what are the possible causes of this type of palsy?
What is the role of the wrist extensors during a power grip, and how do they contribute to the stabilization of the hand?
What is the role of the wrist extensors during a power grip, and how do they contribute to the stabilization of the hand?
What is the significance of the posterior interosseous artery in the upper limb, and how does it relate to the radial nerve?
What is the significance of the posterior interosseous artery in the upper limb, and how does it relate to the radial nerve?
What is the effect of damage to the suprascapular nerve, and which spinal nerves are involved in its formation?
What is the effect of damage to the suprascapular nerve, and which spinal nerves are involved in its formation?
What is the motor function of the radial nerve, and what is the effect of its paralysis on the upper limb?
What is the motor function of the radial nerve, and what is the effect of its paralysis on the upper limb?
What is the difference between the anterior and posterior chords of the brachial plexus, and which nerves are formed from each?
What is the difference between the anterior and posterior chords of the brachial plexus, and which nerves are formed from each?
What is the effect of damage to the ulnar nerve, and which muscles are affected?
What is the effect of damage to the ulnar nerve, and which muscles are affected?
What is the difference between the median and musculocutaneous nerves, and which muscles are innervated by each?
What is the difference between the median and musculocutaneous nerves, and which muscles are innervated by each?
What is the significance of the collateral circulation around the joints in the upper limb?
What is the significance of the collateral circulation around the joints in the upper limb?
What is the result of a supracondylar fracture if the humerus moves forward, and which nerve is at risk of damage?
What is the result of a supracondylar fracture if the humerus moves forward, and which nerve is at risk of damage?
What is the difference between the anterior and posterior compartments of the upper limb, and how do they relate to muscle function?
What is the difference between the anterior and posterior compartments of the upper limb, and how do they relate to muscle function?
What are the two main compartments of the upper limb, and what is the interosseous membrane's role in separating them?
What are the two main compartments of the upper limb, and what is the interosseous membrane's role in separating them?
What is the consequence of damage to the axillary nerve, and which muscle is affected?
What is the consequence of damage to the axillary nerve, and which muscle is affected?
Describe the course of the major arteries in the lower limb, including their bifurcation points and key branches.
Describe the course of the major arteries in the lower limb, including their bifurcation points and key branches.
What is the functional significance of the popliteus muscle in knee movement, and which nerve innervates it?
What is the functional significance of the popliteus muscle in knee movement, and which nerve innervates it?
What are the consequences of damage to the nerves in the lower limb and the lumbar and sacral plexi, and how do they impact functional movements?
What are the consequences of damage to the nerves in the lower limb and the lumbar and sacral plexi, and how do they impact functional movements?
Describe the mechanisms by which blood returns from the veins of the lower limb to the heart, and the significance of this process.
Describe the mechanisms by which blood returns from the veins of the lower limb to the heart, and the significance of this process.
Compare and contrast the functional problems arising from damage to the lumbar and sacral plexi, and how they impact lower limb movements.
Compare and contrast the functional problems arising from damage to the lumbar and sacral plexi, and how they impact lower limb movements.
What is the origin of the circumflex humeral artery, and what structure does it supply?
What is the origin of the circumflex humeral artery, and what structure does it supply?
What is the consequence of increased pressure in a compartment due to damage to an artery or buildup of fluid, and what is the treatment for this condition?
What is the consequence of increased pressure in a compartment due to damage to an artery or buildup of fluid, and what is the treatment for this condition?
What is the significance of the radial and ulnar arteries in the forearm, and how do they contribute to the blood supply of the hand?
What is the significance of the radial and ulnar arteries in the forearm, and how do they contribute to the blood supply of the hand?
What is the significance of the interosseous membrane in the forearm, and how does it relate to the posterior interosseous artery?
What is the significance of the interosseous membrane in the forearm, and how does it relate to the posterior interosseous artery?
What is the relationship between the brachial artery and its branches, including the radial and ulnar arteries, and how do they contribute to the blood supply of the forearm and hand?
What is the relationship between the brachial artery and its branches, including the radial and ulnar arteries, and how do they contribute to the blood supply of the forearm and hand?
What is the primary function of the Obturator nerve?
What is the primary function of the Obturator nerve?
What is the difference between the two portions of the Sciatic nerve?
What is the difference between the two portions of the Sciatic nerve?
Which nerve is responsible for motor innervation of the gluteus maximus?
Which nerve is responsible for motor innervation of the gluteus maximus?
What is the primary function of the Lateral Cutaneous nerve?
What is the primary function of the Lateral Cutaneous nerve?
What is the primary function of the Femoral nerve?
What is the primary function of the Femoral nerve?
What is the primary function of the Superior gluteal nerve?
What is the primary function of the Superior gluteal nerve?
Which nerve is responsible for sensory innervation of the postolateral and medial surfaces of the foot?
Which nerve is responsible for sensory innervation of the postolateral and medial surfaces of the foot?
What is the primary function of the Tibial nerve?
What is the primary function of the Tibial nerve?
What is the primary function of the Fibular (common peroneal) nerve?
What is the primary function of the Fibular (common peroneal) nerve?
What is the primary function of the ankle joint?
What is the primary function of the ankle joint?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying