Podcast
Questions and Answers
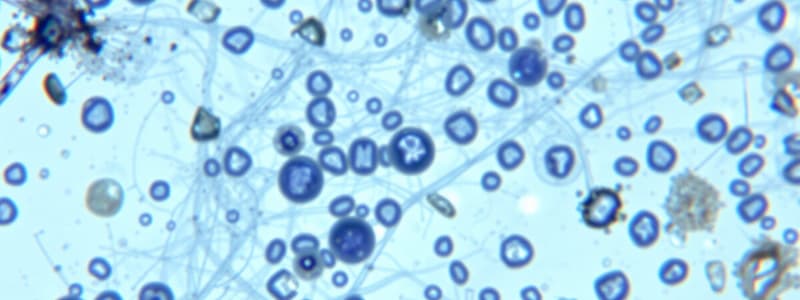
What is Staining?
What is Staining?
- A method for measuring temperature
- A way to preserve food
- A technique used to enhance color in painting
- An auxiliary technique used in microscopy to enhance contrast (correct)
What is the purpose of fixation in microscopy?
What is the purpose of fixation in microscopy?
To preserve the shape of the cells or tissue.
Bacteria are slightly negatively charged at pH 7.0.
Bacteria are slightly negatively charged at pH 7.0.
True (A)
What distinguishes Gram-positive bacteria?
What distinguishes Gram-positive bacteria?
What color do Gram-negative bacteria appear after Gram staining?
What color do Gram-negative bacteria appear after Gram staining?
What is the primary stain used in Gram staining?
What is the primary stain used in Gram staining?
What is simple staining?
What is simple staining?
What is the primary characteristic of acid-fast cells?
What is the primary characteristic of acid-fast cells?
Negative staining is used to visualize the organism itself.
Negative staining is used to visualize the organism itself.
What is used to demonstrate the presence of capsules in bacteria?
What is used to demonstrate the presence of capsules in bacteria?
What happens to endospores after staining?
What happens to endospores after staining?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Staining Overview
- Staining enhances contrast in microscopy, improving visibility of biological structures.
- Stains and dyes help highlight cellular structures in biopsies or tissue samples.
- Gram-positive bacteria retain purple dye due to high peptidoglycan levels, while Gram-negative appear pink to red.
Fixation
- Fixation preserves the morphology of cells or tissues, often using heat.
- Ensures specimens properly adhere to slides and accept staining agents.
Dye Characteristics
- Bacteria carry a slight negative charge at pH 7.0.
- Basic dyes stain bacterial cells directly, while acidic dyes stain the background.
Gram-Positive vs. Gram-Negative
- Gram-positive bacteria turn dark blue or violet with Gram staining.
- Gram-negative bacteria cannot retain the primary stain and are counterstained red or pink; they have an outer membrane and higher lipid content.
Gram Staining Technique
- Essential for distinguishing types of bacteria based on cell wall properties.
- Involves initial crystal violet application, iodine treatment, alcohol decolorization, and counterstaining.
Simple Staining
- Uses a single basic dye to enhance cell morphology studies.
- Includes methods like dilute carbol fuchsin for Vibrio cholera and polychrome methylene blue for Bacillus anthracis.
Acid-Fast Staining
- Targets Mycobacterium and Nocardia species, known for high lipid content in cell walls.
- Mycolic acid in acid-fast organisms makes them resistant to decolorization.
Negative Staining
- Useful for assessing cell size and arrangement, ideal for delicate cells.
- India ink and nigrosin stain the background, leaving microorganisms unstained.
- Highlights the capsules of bacteria, such as Cryptococcus neoformans.
Endospore Staining
- Targets Bacillus and Clostridium genera, known for forming resistant endospores.
- Endospores take up malachite green, appearing green after the process.
Capsule Staining
- Reveals the presence of negatively charged bacterial capsules around cells.
- Capsules produce a halo effect, helping to differentiate encapsulated bacteria.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.