Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of these options are correct? (Select all that apply)
Which of these options are correct? (Select all that apply)
- Hyaline cartilage (correct)
- Fibrocartilage (correct)
- Connective Tissue (correct)
- Perichondrium (correct)
- Elastic cartilage (correct)
Where is hyaline cartilage found?
Where is hyaline cartilage found?
Trachea, costal cartilage
Where is elastic cartilage found?
Where is elastic cartilage found?
Epiglottis, external ear
Where is fibrocartilage found?
Where is fibrocartilage found?
Cartilage is vascular and gets nourishment from blood vessels in the outer part of perichondrium.
Cartilage is vascular and gets nourishment from blood vessels in the outer part of perichondrium.
What is the fibrous tissue surrounding the cartilage plate called?
What is the fibrous tissue surrounding the cartilage plate called?
Hyaline cartilage fibers are demonstrable.
Hyaline cartilage fibers are demonstrable.
What are the groups of chondrocytes in the center of a hyaline cartilage plate called?
What are the groups of chondrocytes in the center of a hyaline cartilage plate called?
What stain is used to visualize elastic cartilage?
What stain is used to visualize elastic cartilage?
What are the components of elastic cartilage?
What are the components of elastic cartilage?
Elastic fibers are demonstrable by H&E stain.
Elastic fibers are demonstrable by H&E stain.
Fibrocartilage is largely composed of dense collagenous CT.
Fibrocartilage is largely composed of dense collagenous CT.
Fibrocartilage has a perichondrium.
Fibrocartilage has a perichondrium.
Fibrocartilage is avascular within the cartilage plate.
Fibrocartilage is avascular within the cartilage plate.
What are the components of fibrocartilage?
What are the components of fibrocartilage?
Bone is the least differentiated connective tissue.
Bone is the least differentiated connective tissue.
What are the two main types of bone?
What are the two main types of bone?
What is the ground substance of bone called?
What is the ground substance of bone called?
What are the cells of bone called?
What are the cells of bone called?
Compact bone binds, supports, and protects organs.
Compact bone binds, supports, and protects organs.
What are the units of compact bone tissue called?
What are the units of compact bone tissue called?
Osteons are cylindrical structures that contain only a mineral matrix.
Osteons are cylindrical structures that contain only a mineral matrix.
Bone marrow is responsible for hematopoiesis.
Bone marrow is responsible for hematopoiesis.
What are the components of bone marrow?
What are the components of bone marrow?
What is the function of blood?
What is the function of blood?
Blood is a type of connective tissue.
Blood is a type of connective tissue.
What are the main components of blood?
What are the main components of blood?
Blood is formed from the hematopoietic CT found inside the spleen.
Blood is formed from the hematopoietic CT found inside the spleen.
Which of the following blood cells are responsible for oxygen and carbon dioxide transport?
Which of the following blood cells are responsible for oxygen and carbon dioxide transport?
Lymphocytes are responsible for blood clotting during wounds.
Lymphocytes are responsible for blood clotting during wounds.
Hemopoiesis, also known as blood formation, begins in the liver.
Hemopoiesis, also known as blood formation, begins in the liver.
Which of the following is a characteristic of Marfan Syndrome?
Which of the following is a characteristic of Marfan Syndrome?
Marfan Syndrome affects only skeletal tissue.
Marfan Syndrome affects only skeletal tissue.
Flashcards
Cartilage
Cartilage
A specialized connective tissue consisting of chondrocytes and extracellular fibers embedded in a gel-like matrix.
Chondrocytes
Chondrocytes
Cells found in cartilage tissue.
Perichondrium
Perichondrium
The fibrous tissue surrounding cartilage, providing nourishment and support.
Hyaline Cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elastic Cartilage
Elastic Cartilage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cartilage Matrix
Cartilage Matrix
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vascularity
Vascularity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Nests
Cell Nests
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bone
Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteocytes
Osteocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bone Matrix
Bone Matrix
Signup and view all the flashcards
Compact Bone
Compact Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spongy Bone
Spongy Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteons (Haversian Systems)
Osteons (Haversian Systems)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Canaliculi
Canaliculi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bone Marrow
Bone Marrow
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hematopoiesis
Hematopoiesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood
Blood
Signup and view all the flashcards
Erythrocytes
Erythrocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Leukocytes
Leukocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neutrophils
Neutrophils
Signup and view all the flashcards
Eosinophils
Eosinophils
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basophils
Basophils
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Monocytes
Monocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Macrophages
Macrophages
Signup and view all the flashcards
Platelets
Platelets
Signup and view all the flashcards
Marfan Syndrome
Marfan Syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Types of Cartilage
- Hyaline cartilage is found in the trachea, costal cartilage
- Elastic cartilage is found in the epiglottis, external ear
- Fibrocartilage is found in the intervertebral disc
Cartilage
- Cartilage is a specialized connective tissue
- It consists of chondrocytes and extracellular fibers
- Embedded in an amorphous, gel-like matrix
- Chondrocytes are cells within the cartilage
Cartilage Matrix
- The matrix gives cartilage resilience
- Allows it to withstand mechanical stress without distortion
Cartilage Vascularity
- Cartilage is avascular
- Nourishment comes from blood vessels in the perichondrium
- Perichondrium surrounds the cartilage
Perichondrium
- The fibrous tissue surrounding the cartilage
- A condensation of the deeper part of the tunica propria
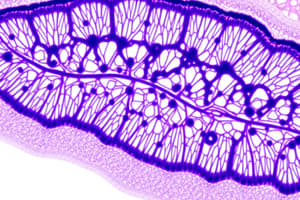
Hyaline Cartilage
- Characterized by a homogenous matrix without demonstrable fibers
- Chondrocytes within lacunae, arranged in groups (cell nests) in the center
Elastic Cartilage
- Contains elastic fibers
- Differentiated from hyaline cartilage by the presence of elastic fibers
- Typically stained with Mallory's Phosphotungstic Acid Hematoxylin
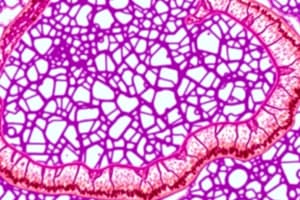
Fibrocartilage
- Dense fibrous nature
- Largely composed of dense collagenous CT
- Contains islands of hyaline cartilage matrix with spherical chondrocytes
Fibrocartilage (continued)
- Lacks perichondrium
- Avascular (no blood vessels)
- Transitions between cartilage and dense CT
Bones
- The most highly differentiated connective tissue
- Forms the skeleton
- Rigid
Types of Bones
- Compact bone
- Spongy bone
Ground Bone
- Consists of Haversian lamellae
- Osteocytes within lacunae
Compact Bone
- Supports and protects organs
- Forms the skeleton
Osteon
- Units in compact bone tissue
- Cylindrical structures
- Contain mineral matrix and living osteocytes
- Connected by canaliculi (blood transport)
Bone Marrow
- Responsible for hematopoiesis (blood cell production)
Blood
- Transports hormones, nutrients and cells throughout the body
- A fluid connective tissue
- Formed in the hematopoietic CT of bone marrow
- Contains erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets
Hematopoiesis
- Blood cell formation
- Occurs in the yolk sac, liver, and bone marrow during development
- Primarily in bone marrow after birth
Marfan Syndrome
- Inherited disorder affecting connective tissue
- Lacks connective tissue strength
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.