Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the Na⁺-K⁺ pump in cellular transport?
What is the primary function of the Na⁺-K⁺ pump in cellular transport?
- Keeps high Na⁺ concentrations inside the cell
- Excretes calcium ions for metabolic processes
- Maintains membrane potential and regulates cell volume (correct)
- Facilitates passive transport of glucose
Which transport process involves the movement of molecules against their concentration gradient using energy?
Which transport process involves the movement of molecules against their concentration gradient using energy?
- Active transport (correct)
- Simple diffusion
- Passive transport
- Facilitated diffusion
What is the role of the calcium pump in a cell?
What is the role of the calcium pump in a cell?
- To export hydrogen ions to regulate pH
- To maintain high intracellular sodium levels
- To keep low intracellular calcium concentrations (correct)
- To import nutrients like glucose
Which of the following is not a characteristic of passive transport?
Which of the following is not a characteristic of passive transport?
What type of molecules can most easily permeate the plasma membrane without assistance?
What type of molecules can most easily permeate the plasma membrane without assistance?
What is one function of ABC transporters in cells?
What is one function of ABC transporters in cells?
Na⁺ ions can sometimes accumulate in cells due to the inhibition of which transporter?
Na⁺ ions can sometimes accumulate in cells due to the inhibition of which transporter?
In the process of osmosis, which of the following statements is true?
In the process of osmosis, which of the following statements is true?
Which type of transport specifically utilizes ATP to transport ions across a membrane?
Which type of transport specifically utilizes ATP to transport ions across a membrane?
What is a characteristic of symporters in cellular transport?
What is a characteristic of symporters in cellular transport?
Which of the following accurately describes facilitated diffusion?
Which of the following accurately describes facilitated diffusion?
What role does the proton pump play in stomach cells?
What role does the proton pump play in stomach cells?
What is a key feature of multidrug resistance (MDR) transporters?
What is a key feature of multidrug resistance (MDR) transporters?
Which of the following best describes the process of simple diffusion?
Which of the following best describes the process of simple diffusion?
What is the primary function of antiporters in secondary active transport?
What is the primary function of antiporters in secondary active transport?
What role do ion channels play in facilitated diffusion?
What role do ion channels play in facilitated diffusion?
Which of the following is an example of facilitated diffusion?
Which of the following is an example of facilitated diffusion?
What differentiates symporters from antiporters in coupled transport mechanisms?
What differentiates symporters from antiporters in coupled transport mechanisms?
Which type of transport directly requires ATP to function?
Which type of transport directly requires ATP to function?
What characteristic allows aquaporins to selectively facilitate the movement of water?
What characteristic allows aquaporins to selectively facilitate the movement of water?
What process describes the movement of water across a membrane down its osmotic gradient?
What process describes the movement of water across a membrane down its osmotic gradient?
What type of ion channel opens in response to specific ligands binding?
What type of ion channel opens in response to specific ligands binding?
How does the concentration gradient affect the rate of diffusion?
How does the concentration gradient affect the rate of diffusion?
Which channels are specifically selective for Na⁺ ions over K⁺ ions?
Which channels are specifically selective for Na⁺ ions over K⁺ ions?
Which of the following types of channels respond to mechanical forces?
Which of the following types of channels respond to mechanical forces?
What is the primary difference between passive and active transport mechanisms?
What is the primary difference between passive and active transport mechanisms?
What is the result of the conformational change in carrier proteins during transport?
What is the result of the conformational change in carrier proteins during transport?
Flashcards
Passive Transport
Passive Transport
Refers to the movement of molecules across a cell membrane without requiring energy. This process relies on the concentration gradient, meaning molecules move from areas of high concentration to low concentration.
Active Transport
Active Transport
The process of transporting molecules across a cell membrane against their concentration gradient, requiring energy (usually ATP). This allows cells to concentrate essential molecules inside and remove waste products.
Primary Active Transport
Primary Active Transport
A type of active transport that directly utilizes ATP (adenosine triphosphate) as the energy source to move molecules across the membrane.
Secondary Active Transport
Secondary Active Transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Na⁺-K⁺ Pump
Na⁺-K⁺ Pump
Signup and view all the flashcards
Calcium Pump
Calcium Pump
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proton Pump
Proton Pump
Signup and view all the flashcards
ABC Transporters
ABC Transporters
Signup and view all the flashcards
MDR Transporter
MDR Transporter
Signup and view all the flashcards
CFTR Transporter
CFTR Transporter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Facilitated Diffusion
Facilitated Diffusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Channel Proteins
Channel Proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carrier Proteins
Carrier Proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osmosis
Osmosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Diffusion
Simple Diffusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ion Channels
Ion Channels
Signup and view all the flashcards
Voltage-gated Ion Channels
Voltage-gated Ion Channels
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ligand-gated Ion Channels
Ligand-gated Ion Channels
Signup and view all the flashcards
Antiporters
Antiporters
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symporters
Symporters
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aquaporins
Aquaporins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sodium Channels
Sodium Channels
Signup and view all the flashcards
Potassium Channels
Potassium Channels
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Transmembrane Transport of Small Molecules and Ions
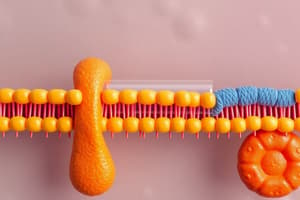
- Plasma Membrane: Semi-permeable, regulating what enters and exits the cell. Controls movement of essential nutrients, metabolites, and waste.
Passive Transport (No Energy Input)
- Simple Diffusion: Movement of small, hydrophobic molecules (e.g., O2, CO2, steroids) across the lipid bilayer without assistance. Speed depends on concentration gradient.
- Facilitated Diffusion: Movement of larger or charged molecules (e.g., glucose, amino acids) assisted by transport proteins (channels or carriers). Molecules move down their concentration gradient.
- Osmosis: Movement of water across a membrane down its osmotic gradient. Water moves through aquaporins.
Active Transport (Energy Input Required)
-
Primary Active Transport: Direct use of energy (often ATP) to move molecules against their concentration gradient.
- Na+-K+ Pump: Pumps 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ in, maintaining membrane potential and cell volume.
- Calcium Pump: Maintains low intracellular Ca2+ concentration. Essential for numerous cellular processes.
- Proton Pump: Involved in regulating acidity in stomach cells and organelles.
- ABC Transporters (ATP-binding cassette): Large family of transporters involved in importing nutrients, exporting toxins, and drugs. Overexpression is linked to drug resistance.
-
Secondary Active Transport (Coupled Transport): Uses energy from the movement of one molecule down its concentration gradient to move another molecule against its gradient.
- Symporters: Molecules move in the same direction (e.g., Na+/glucose co-transporters in intestines).
- Antiporters: Molecules move in opposite directions (e.g., Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in cardiac cells, Na+/H+ exchanger).
Ion Channels
- Types: Voltage-gated, ligand-gated, and mechanosensitive.
- Selectivity: Based on size and charge. Precise interactions within narrow pores determine selectivity (e.g., Na+ channels more selective for Na+; K+ channels more selective for K+).
- Function: Allow specific ions to rapidly pass through the membrane.
Specific Examples
- GLUT-1 (glucose transporter): Facilitated diffusion to transport glucose.
- MDR transporters (multidrug resistance): ABC transporters that export drugs and other substances.
- CFTR (Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator): ABC transporter critical for proper ion transport, especially chloride, in the lungs.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.