Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the four basic types of tissues?
What are the four basic types of tissues?
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Neural
What is the study of tissues called?
What is the study of tissues called?
Histology
What microscopy technique can magnify over 1 million times?
What microscopy technique can magnify over 1 million times?
- Transmission electron microscope (correct)
- Ocular microscope
- Compound light microscope
- Simple microscope
Which of the following is NOT a basic type of tissue?
Which of the following is NOT a basic type of tissue?
The compound light microscope uses only one lens.
The compound light microscope uses only one lens.
What limits the resolution on a light microscope?
What limits the resolution on a light microscope?
The four basic types of tissues include epithelial, connective, muscle, and __________.
The four basic types of tissues include epithelial, connective, muscle, and __________.
What is one role of epithelial tissue?
What is one role of epithelial tissue?
What type of microscope detects visible light through a thin section of tissue?
What type of microscope detects visible light through a thin section of tissue?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
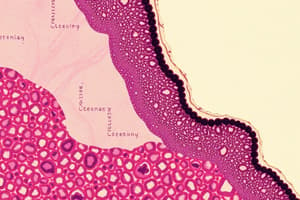
Tissue Level of Organization
- Four basic types of tissues in the body: epithelial, connective, muscle, neural.
- Epithelial tissues cover body surfaces, line cavities, and form glands.
- Study of tissues is known as histology.
Microscopy Techniques
- Microscopy began 400 years ago, enabling observation of cells and tissues.
- Simple microscopes use one lens, while compound microscopes utilize two or more lenses.
- Electron microscopes can magnify objects over 1 million times, providing greater detail.
Types of Microscopes
-
Compound Light Microscope:
- Uses visible light to illuminate the specimen.
- Comprises an objective lens and an ocular lens which magnifies the image.
- Total magnification calculated by multiplying the powers of the two lenses.
- Resolution is limited to about 200 nm due to the wavelength of light.
-
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM):
- Transmits electrons through very thin specimens.
- Employs magnets to direct an electron beam, allowing for detailed imaging.
Epithelial Tissue Characteristics
- Cell shapes: squamous (flat), cuboidal (cube-shaped), columnar (tall and column-like).
- Epithelial tissues can be classified based on the number of cell layers: simple (one layer) or stratified (multiple layers).
- Functions include absorption, secretion, and protection.
Intercellular Connections
- Epithelial cells connect through various junctions, aiding in communication and structural integrity.
- Key connections include tight junctions, adherens junctions, and gap junctions.
Exocrine Glands
- Glandular epithelia produce secretions via exocrine means, which can occur through three methods:
- Merocrine secretion (exocytosis),
- Apocrine secretion (partial cell loss),
- Holocrine secretion (complete cell lysis).
- Multicellular exocrine glands are classified by structure: tubular, acinar, or tubuloacinar.
Summary of Learning Outcomes
- Identify and describe four types of tissues in the body.
- Understand microscopy techniques for studying tissues.
- Differentiate between types of epithelial tissues based on structure and function.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.