Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is NOT a basic tissue type developed from the embryonic layers?
Which of the following is NOT a basic tissue type developed from the embryonic layers?
- Nervous tissue
- Epithelial tissue
- Connective tissue
- Muscle tissue (correct)
Epithelial tissue is avascular, meaning it contains blood vessels.
Epithelial tissue is avascular, meaning it contains blood vessels.
False (B)
What does the term 'polarity' refer to in epithelial tissue?
What does the term 'polarity' refer to in epithelial tissue?
The presence of apical, basal, and lateral surfaces.
Epithelial cells regenerate from below, mainly in __________ epithelium.
Epithelial cells regenerate from below, mainly in __________ epithelium.
Match the following classifications of epithelium with their descriptions:
Match the following classifications of epithelium with their descriptions:
What type of epithelium forms the lining of the esophagus and mouth?
What type of epithelium forms the lining of the esophagus and mouth?
What is one major function of epithelial tissue?
What is one major function of epithelial tissue?
Cuboidal epithelial cells are taller than they are wide.
Cuboidal epithelial cells are taller than they are wide.
Endocrine glands secrete their products through ducts to the exterior of the body.
Endocrine glands secrete their products through ducts to the exterior of the body.
What structural feature binds adjacent epithelial cells together?
What structural feature binds adjacent epithelial cells together?
What are goblet cells an example of?
What are goblet cells an example of?
The main function of _______ tissue is to support and move the body.
The main function of _______ tissue is to support and move the body.
Match the following types of connective tissues with their characteristics:
Match the following types of connective tissues with their characteristics:
Which method of secretion involves the cell rupturing to release its product?
Which method of secretion involves the cell rupturing to release its product?
Skeletal muscle tissue is striated and involuntary.
Skeletal muscle tissue is striated and involuntary.
Name one type of connective tissue that aids in transport.
Name one type of connective tissue that aids in transport.
Flashcards
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
A type of epithelial tissue that forms a protective barrier, often found in areas subject to abrasion.
Simple Epithelium
Simple Epithelium
A type of epithelial tissue that lines surfaces where absorption and secretion occur. It has a single layer of cells.
Endocrine Glands
Endocrine Glands
Glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream, without using ducts.
Exocrine Glands
Exocrine Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dense Connective Tissue
Dense Connective Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Smooth Muscle
Smooth Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is histology?
What is histology?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the five basic tissue types?
What are the five basic tissue types?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the characteristics of epithelial tissue?
What are the characteristics of epithelial tissue?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where is epithelial tissue found?
Where is epithelial tissue found?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the structural features of epithelial tissue?
What are the structural features of epithelial tissue?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Is epithelial tissue vascular?
Is epithelial tissue vascular?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the mitotic ability of epithelial tissue?
What is the mitotic ability of epithelial tissue?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the functions of epithelial tissue?
What are the functions of epithelial tissue?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Histology Overview
- Histology is the study of tissues in the body
- Tissues develop from the three embryonic layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
- Five basic tissue types emerge from these layers: epithelial, connective, vascular, muscular, and nervous tissue
Levels of Organization
- The levels of organization are Cells, Tissues, Organs, Organ Systems, and Organism
- Cells make up tissues
- Tissues form organs
- Organs work together in organ systems
- Organ systems combine to form an organism
Epithelial Tissue
- Characteristics: Composed mainly of cells; covers body surfaces, lines hollow organs, and forms glands (e.g., outside body surface, digestive system lining).
- Polarity: Has apical, basal, and lateral surfaces
- Basement Membrane: Rests upon this membrane
- Specialized Cell Contacts: Bind adjacent cells together
- Avascular: No blood vessels
- Mitotic Ability: Replaces lost cells through cell division
Epithelial Structure
- Apical Surface: Free surface facing outside or open space
- Basement Membrane: Underlying non-cellular layer that anchors the epithelium
Functions of Epithelia
- Protection: e.g., skin, epithelium lining the mouth
- Barrier: e.g., skin
- Passage Permitting: e.g., cells lining air sacs in lungs, nephrons in kidneys
- Secretion: e.g., pancreatic cells
- Absorption: e.g., lining of stomach and small intestine
Classifications of Epithelia
- Number of Layers: Simple (one layer), stratified (more than one layer), pseudostratified (appears stratified but all cells touch the basement membrane)
- Shape of Cells: Squamous (flat), cuboidal (equal height and width), columnar (taller than wide)
Simple Columnar Epithelium
- Description: Single layer of tall cells with oval/round nuclei, sometimes with cilia or goblet cells (mucus-secreting).
- Function: Absorption, secretion of mucus, enzymes, and other substances. Ciliated type propels mucus.
- Location: Lines most of the digestive tract, gallbladder, excretory ducts, small bronchi, uterine tubes, and some regions of the uterus
Stratified Epithelia
- Characteristics: Contain two or more layers of cells; regenerate from below; major role in protection; named based on apical cell shape.
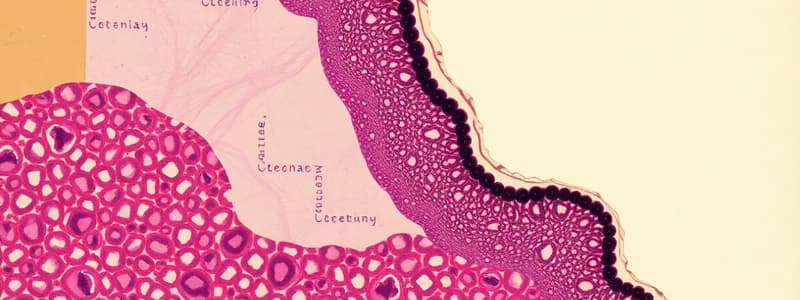
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
- Function: Protects underlying tissues in areas subject to abrasion.
- Location: Keratinized forms epidermis; non-keratinized lines esophagus and mouth.
Stratified Squamous Epithelium (detail)
- Description: Thick membrane with several cell layers; basal cells are cuboidal/columnar (metabolically active); surface cells are flattened (squamous); keratinized types are full of keratin and dead; basal cells actively multiply and produce more superficial layers.
Epithelium: Glandular
- Glands: One or more cells that makes and secretes an aqueous fluid
- Endocrine Glands: Ductless; release hormones into the bloodstream (e.g., pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, pancreas).
- Exocrine Glands: Have ducts; release secretions to the body surface or into body cavities (e.g., sweat, oil). Classified by structure (unicellular, multicellular) or method of secretion (merocrine, holocrine, apocrine).
Unicellular and Multicellular Glands (classification)
- Unicellular: Goblet cells (e.g. single cells)
- Multicellular: Classified by structure (simple tubular, simple coiled tubular, simple branched alveolar, compound tubular, simple alveolar, compound alveolar, compound tubuloalveolar)
Method of Secretion
- Merocrine: Products released by exocytosis (most glands)
- Holocrine: Cell ruptures and releases the product (sebaceous glands)
- Apocrine: Top of the cell pinches off (possibly in lactating mammary glands)
Connective Tissue
- Functions: Enclose organs, separate organs into layers, connect tissues, support and movement (bones), storage fat, insulation, transport, and protection (bone)
Structural Elements of Connective Tissue
- Ground Substance: Unstructured material fills the space between cells
- Fibers: Collagen, elastic, or reticular
- Cells: Fibroblasts, chondroblasts, osteoblasts, and others
Areolar Connective Tissue
- Description: Gel-like matrix with all three fiber types; cells include fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, and some white blood cells.
- Function: Wraps and cushions organs, macrophages phagocytize bacteria, plays a role in inflammation, and holds/conveys tissue fluid.
- Location: Widely distributed under epithelia, lamina propria of mucous membranes, around kidneys and eyeballs, within abdomen, in breasts
Adipose Tissue
- Description: Matrix is sparse; closely packed adipocytes (fat cells) with nucleus pushed to the side by large fat droplet.
- Function: Reserve fuel, insulates, supports and protects organs.
- Location: Under skin, around kidneys and eyeballs, within abdomen, breasts
Hyaline Cartilage
- Description: Amorphous matrix; collagen fibers are imperceptible; chondroblasts produce the matrix and mature into chondrocytes (in lacunae).
- Function: Supports, reinforces, has resilient cushioning properties, resists compressive stress.
- Location: Embryonic skeleton, ends of long bones, costal cartilages, nose, trachea, and larynx
Bone Tissue
- Description: Hard, calcified matrix containing collagen fibers; osteocytes lie in lacunae; very well vascularized.
- Function: Supports and protects (encloses), provides levers for muscles, stores calcium and other minerals and fat, and marrow inside bones is for blood cell formation (hematopoiesis).
- Location: Bones
Muscle Tissue
- Characteristics: Cells called fibers; contract or shorten with force when stimulated; move body and pump blood.
- Types:
- Skeletal: attached to bones
- Cardiac: muscle of the heart
- Smooth: associated with tubular structures and skin; nonstriated and involuntary.
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
- Description: Branching, striated, generally uninucleate cells with specialized junctions (intercalated discs).
- Function: As it contracts, it propels blood into the circulation; involuntary control.
- Location: Walls of the heart
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.