Podcast
Questions and Answers
Based on the anatomical diagram, which muscle is located most proximally?
Based on the anatomical diagram, which muscle is located most proximally?
- Sartorius
- Rectus Femoris (correct)
- Piriformis
- Gracilis
Which of the following muscles is associated with both hip flexion and knee extension?
Which of the following muscles is associated with both hip flexion and knee extension?
- Sartorius (correct)
- Biceps Femoris
- Semimembranosus
- Gracilis
Considering the anatomical arrangement, which muscle would be directly involved in both hip abduction and external rotation?
Considering the anatomical arrangement, which muscle would be directly involved in both hip abduction and external rotation?
- Piriformis (correct)
- Semimembranosus
- Gracilis
- Rectus Femoris
If a patient has damage to the deep artery of the thigh, which compartment would be most affected by reduced blood supply?
If a patient has damage to the deep artery of the thigh, which compartment would be most affected by reduced blood supply?
Which muscle listed contributes primarily to knee flexion and is located in the posterior compartment of the thigh?
Which muscle listed contributes primarily to knee flexion and is located in the posterior compartment of the thigh?
Which of the following muscles is innervated by the tibial nerve?
Which of the following muscles is innervated by the tibial nerve?
A patient presents with an inability to plantarflex their foot. Which nerve is most likely affected?
A patient presents with an inability to plantarflex their foot. Which nerve is most likely affected?
Following a hip replacement surgery, a patient has difficulty with adduction of the thigh. Which nerve might have been affected during the procedure?
Following a hip replacement surgery, a patient has difficulty with adduction of the thigh. Which nerve might have been affected during the procedure?
A clinician assesses a patient who cannot extend their knee against resistance. Damage to which nerve is most likely the cause?
A clinician assesses a patient who cannot extend their knee against resistance. Damage to which nerve is most likely the cause?
If the sartorius and gracilis muscles are both active, what combined movements would MOST likely result?
If the sartorius and gracilis muscles are both active, what combined movements would MOST likely result?
What is the MOST likely result of damage to the common fibular nerve?
What is the MOST likely result of damage to the common fibular nerve?
If a patient is experiencing numbness along the medial aspect of their thigh, which nerve is MOST likely affected?
If a patient is experiencing numbness along the medial aspect of their thigh, which nerve is MOST likely affected?
A patient has weakness in hip extension and knee flexion. Which muscle group is MOST likely affected?
A patient has weakness in hip extension and knee flexion. Which muscle group is MOST likely affected?
Which of the following reflects the innervation pattern and action of the tibialis posterior muscle?
Which of the following reflects the innervation pattern and action of the tibialis posterior muscle?
An athlete reports pain and limited function in hip extension and knee flexion after a sprinting injury. Which group of muscles is MOST likely involved and should be assessed?
An athlete reports pain and limited function in hip extension and knee flexion after a sprinting injury. Which group of muscles is MOST likely involved and should be assessed?
Flashcards
Rectus Femoris
Rectus Femoris
Muscle located in the anterior compartment of the thigh, responsible for knee extension and hip flexion.
Sartorius
Sartorius
Long, thin muscle that originates at the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) and crosses the thigh obliquely to insert on the medial side of the tibia; involved in hip flexion, abduction, and external rotation, as well as knee flexion.
Gracilis
Gracilis
Muscle located on the medial side of the thigh, adducts the thigh, flexes and medially rotates the leg at the knee.
Hamstrings
Hamstrings
Signup and view all the flashcards
Semitendinosus
Semitendinosus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Semimembranosus
Semimembranosus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Piriformis
Piriformis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gastrocnemius
Gastrocnemius
Signup and view all the flashcards
Soleus
Soleus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flexor Digitorum Longus
Flexor Digitorum Longus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flexor Hallucis Longus
Flexor Hallucis Longus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tibialis Anterior
Tibialis Anterior
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extensor Digitorum Longus
Extensor Digitorum Longus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extensor Hallucis Longus
Extensor Hallucis Longus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Popliteus
Popliteus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
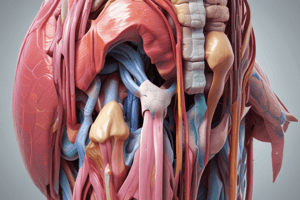
- The image provides a detailed overview of muscles, attachments, innervations, blood supply, and actions related to the thigh, leg, and gluteal regions.
Attachments
- Explains the attachments of muscles to bony landmarks around the hip, thigh, and leg.
- Includes anterior and posterior thigh muscles.
- Covers medial thigh and gluteal region muscles.
- Details muscles of the posterior, lateral, and anterior leg.
Proximal Attachments
- Lumber vertebrae
- Iliac Fosa
- AIIS
- Greater Trochanter
- ASIS
- Pubic bone
- Ischial tuberosity
- Posterior Ilium
- Sacrum
Distal Attachments
- Anterior Thigh - vastus lateralis, intermedius, medialis, rectus femoris
- Posterior Thigh - biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus
- Medial Thigh- adductor longus, brevis, magnus, gracilis
- Gluteal Region - gluteus maximus, medius, minimus, piriformis, obturator internus.
- Posterior leg - gastrocnemius, soleus, flexor hallucis
- Lateral leg - fibularis longus & brevis
- Anterior leg - tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis, extensor digitorum
Innervation: Muscles
- Specifies the nerves responsible for each muscle or muscle group.
- The lumbar spinal nerve innervates the psoas major.
- The femoral nerve innervates the iliacus, sartorius, vastus medialis, intermedius and lateralis and rectus femoris.
- The obturator nerve innervates the obturator externus, adductor magnus, longus and brevis, and gracilis.
- The tibial division of the sciatic nerve innervates the semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris (long head), gastrocnemius, soleus, flexor hallucis longus, flexor digitorum longus and tibialis posterior.
- The common fibular (peroneal) nerve innervates the fibularis longus, brevis, anterior, and tertius.
- The inferior gluteal nerve innervates the gluteus maximus.
- The superior gluteal nerve innervates the gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and tensor fascia latae.
- The superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve innervates fibularis longus & brevis.
- The deep fibular nerve innervates the tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus and fibularis tertius.
Blood Supply: Muscles
- Describes the arterial supply for different muscle compartments.
- Anterior thigh muscles are supplied by the femoral artery.
- Posterior thigh muscles are supplied by the deep artery of the thigh.
- Medial thigh muscles are supplied by the obturator artery.
- Posterior leg muscles are supplied by the posterior tibial artery.
- Anterior leg muscles are supplied by the anterior tibial artery.
- Lateral leg muscles are supplied by the fibular artery.
Muscle Actions At Hip
- Hip flexion is performed by the iliacus, psoas major, sartorius, and rectus femoris.
- Hip extension is mainly done by the gluteus maximus (especially when flexed).
- Hip abduction is facilitated by the gluteus medius, minimus, and tensor fascia latae.
- Hip adduction is completed by the adductor longus, brevis, magnus, pectineus and gracilis.
- External rotation is by the piriformis, superior gemellus, inferior gemellus and obturator internus.
- Medial rotation is done by the gluteus medius and gluteus minimus.
Muscle Actions At Knee
- Knee extension is completed by the vastus medialis, intermedius, lateralis, and rectus femoris.
- Knee flexion is facilitated by the semimembranosus, semitendinosus and popliteus.
- Gracilis and Sartorius are antagonists to Gluteus maximus.
Ankle and Foot
- Plantarflexion involves the gastrocnemius, soleus and fibularis longus & brevis.
- Dorsiflexion involves the tibialis anterior.
- Inversion is done by the tibialis posterior and anterior.
- Eversion is done by the fibularis longus, brevis, and tertius.
- Flexion of digit 1 (big toe) is done by the flexor hallucis longus.
- Flexion of digits 2-5 is done by the flexor digitorum longus.
- Extension of digit 1 is done by the extensor hallucis longus.
- The extensor digitorum longus extends digits 2-5.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.