Podcast
Questions and Answers
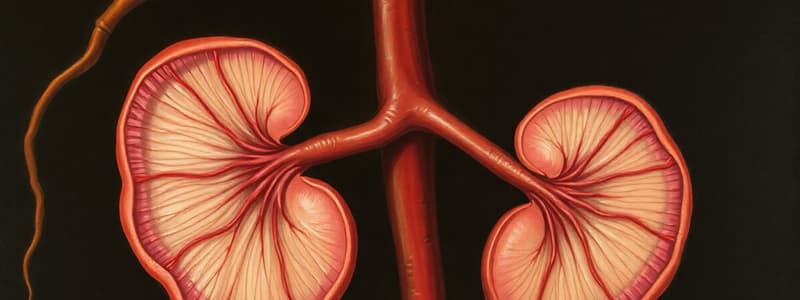
Which of the following processes is NOT directly involved in the formation of urine within the nephron?
Which of the following processes is NOT directly involved in the formation of urine within the nephron?
- Tubular reabsorption
- Glomerular filtration
- Tubular secretion
- Erythropoiesis (correct)
What primary characteristic of the glomerular filter prevents blood cells and large proteins from entering the filtrate?
What primary characteristic of the glomerular filter prevents blood cells and large proteins from entering the filtrate?
- Electrical charge of the filter
- Filter size (correct)
- Hydrostatic pressure
- Active transport mechanisms
How does increased blood pressure affect filtration rate in the glomerulus, assuming other factors remain constant?
How does increased blood pressure affect filtration rate in the glomerulus, assuming other factors remain constant?
- Initially increases, then decreases filtration rate due to glomerular damage
- Has no effect on filtration rate, as the kidney autoregulates pressure
- Decreases filtration rate by constricting afferent arterioles
- Increases filtration rate due to higher pressure pushing more fluid through the filter (correct)
During the reabsorption process, where do substances move from and to?
During the reabsorption process, where do substances move from and to?
What is the primary difference between tubular reabsorption and tubular secretion?
What is the primary difference between tubular reabsorption and tubular secretion?
In which part of the nephron is the majority of water reabsorbed?
In which part of the nephron is the majority of water reabsorbed?
What role do endocrine glands play in maintaining optimal internal balance within the kidneys?
What role do endocrine glands play in maintaining optimal internal balance within the kidneys?
How do the kidneys contribute to maintaining acid-base balance in the body?
How do the kidneys contribute to maintaining acid-base balance in the body?
What type of tissue lines the urinary bladder, allowing it to expand as it fills with urine?
What type of tissue lines the urinary bladder, allowing it to expand as it fills with urine?
What triggers the urination reflex when the bladder fills with urine?
What triggers the urination reflex when the bladder fills with urine?
Why are urinary tract infections (UTIs) more common in women than in men?
Why are urinary tract infections (UTIs) more common in women than in men?
Why is it important to promptly treat urinary infections?
Why is it important to promptly treat urinary infections?
How does the sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight) influence urine formation?
How does the sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight) influence urine formation?
What happens to the concentration of glomerular filtrate once it leaves the collecting ducts?
What happens to the concentration of glomerular filtrate once it leaves the collecting ducts?
What is the significance of the pleats called rugae in the urinary bladder?
What is the significance of the pleats called rugae in the urinary bladder?
How might a decrease in kidney function affect medication dosages in older adults?
How might a decrease in kidney function affect medication dosages in older adults?
Which of the following best describes the impact of aging on bladder function?
Which of the following best describes the impact of aging on bladder function?
Which process is primarily affected when afferent arterioles constrict due to adrenaline release?
Which process is primarily affected when afferent arterioles constrict due to adrenaline release?
A patient's urine sample reveals the presence of glucose. Which specific function of the nephron was most likely impaired, leading to this?
A patient's urine sample reveals the presence of glucose. Which specific function of the nephron was most likely impaired, leading to this?
Why might a doctor advise a patient with recurring UTIs to drink plenty of water?
Why might a doctor advise a patient with recurring UTIs to drink plenty of water?
Which of the following accurately describes the role of the uvula in the digestive process?
Which of the following accurately describes the role of the uvula in the digestive process?
How do the submandibular salivary glands contribute to the digestive process?
How do the submandibular salivary glands contribute to the digestive process?
How do the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx each contribute to the digestive or respiratory processes?
How do the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx each contribute to the digestive or respiratory processes?
What is the primary function of peristalsis in the esophagus?
What is the primary function of peristalsis in the esophagus?
Which tissue type primarily composes the mucosa layer of the alimentary canal, aiding in its function of absorption and secretion?
Which tissue type primarily composes the mucosa layer of the alimentary canal, aiding in its function of absorption and secretion?
How does the arrangement of muscle layers in the muscularis externa of the alimentary canal facilitate peristalsis?
How does the arrangement of muscle layers in the muscularis externa of the alimentary canal facilitate peristalsis?
How do the rugae in the stomach contribute to its function?
How do the rugae in the stomach contribute to its function?
What is the role of hydrochloric acid (HCl) in gastric juice within the stomach?
What is the role of hydrochloric acid (HCl) in gastric juice within the stomach?
What characteristic of chyme is important for nutrient absorption in the small intestine?
What characteristic of chyme is important for nutrient absorption in the small intestine?
How does segmentation, a type of muscular action in the small intestine, contribute to the digestive process?
How does segmentation, a type of muscular action in the small intestine, contribute to the digestive process?
What is the purpose of sodium bicarbonate secreted by the pancreas into the small intestine?
What is the purpose of sodium bicarbonate secreted by the pancreas into the small intestine?
Which of the following is a primary function of the large intestine?
Which of the following is a primary function of the large intestine?
What occurs when fecal matter remains in the large intestine for an extended period?
What occurs when fecal matter remains in the large intestine for an extended period?
How does the colon contribute to maintaining fluid balance in the body?
How does the colon contribute to maintaining fluid balance in the body?
Which quadrant of the abdomen would contain the majority of the stomach and spleen?
Which quadrant of the abdomen would contain the majority of the stomach and spleen?
How does the body prevent food from entering the trachea during swallowing?
How does the body prevent food from entering the trachea during swallowing?
What would happen if the pyloric sphincter were to malfunction and remain continuously open?
What would happen if the pyloric sphincter were to malfunction and remain continuously open?
What digestive process is most directly affected by the removal of the gallbladder?
What digestive process is most directly affected by the removal of the gallbladder?
What distinguishes the ileum from the duodenum and jejunum in terms of its function in the small intestine?
What distinguishes the ileum from the duodenum and jejunum in terms of its function in the small intestine?
What triggers the defecation reflex as part of the digestive process?
What triggers the defecation reflex as part of the digestive process?
How does the liver contribute to the digestive system as an accessory organ?
How does the liver contribute to the digestive system as an accessory organ?
What is the primary function of bile salts in the process of emulsification?
What is the primary function of bile salts in the process of emulsification?
If the hepatic duct were to become blocked, which of the following processes would be most directly affected?
If the hepatic duct were to become blocked, which of the following processes would be most directly affected?
How does the concentration of bile change as it is stored in the gallbladder?
How does the concentration of bile change as it is stored in the gallbladder?
What is the most likely consequence of having overly concentrated bile in the gallbladder?
What is the most likely consequence of having overly concentrated bile in the gallbladder?
What role do buffers secreted by the pancreas play in digestion?
What role do buffers secreted by the pancreas play in digestion?
How is the location of the pancreas beneficial for its role in digestion?
How is the location of the pancreas beneficial for its role in digestion?
Which of the following symptoms is directly related to the body's attempt to eliminate irritants from the digestive tract?
Which of the following symptoms is directly related to the body's attempt to eliminate irritants from the digestive tract?
What is the underlying cause of diarrhea as a digestive disorder?
What is the underlying cause of diarrhea as a digestive disorder?
How does constipation primarily affect the composition of feces?
How does constipation primarily affect the composition of feces?
Which of the following processes is most likely to be affected by a decrease in saliva production?
Which of the following processes is most likely to be affected by a decrease in saliva production?
How might a significant decrease in digestive juices impact nutrient absorption?
How might a significant decrease in digestive juices impact nutrient absorption?
What is the main role of the cystic duct in the digestive system?
What is the main role of the cystic duct in the digestive system?
If a patient has their gallbladder removed, what dietary adjustment is typically recommended and why?
If a patient has their gallbladder removed, what dietary adjustment is typically recommended and why?
Which of the following best describes the role of bilirubin in the digestive process?
Which of the following best describes the role of bilirubin in the digestive process?
How does the liver contribute to maintaining glucose homeostasis in the body?
How does the liver contribute to maintaining glucose homeostasis in the body?
What is the function of the liver in relation to blood clotting?
What is the function of the liver in relation to blood clotting?
How does aging affect the digestive process, specifically the production of digestive juices?
How does aging affect the digestive process, specifically the production of digestive juices?
Which function of the liver directly helps in ridding the body of harmful substances like certain drugs and alcohol?
Which function of the liver directly helps in ridding the body of harmful substances like certain drugs and alcohol?
What role does the liver play in maintaining body temperature?
What role does the liver play in maintaining body temperature?
In systemic circulation, what is the destination of blood after it leaves the heart?
In systemic circulation, what is the destination of blood after it leaves the heart?
What is the functional significance of capillaries being composed of only the tunica intima?
What is the functional significance of capillaries being composed of only the tunica intima?
How do veins counteract the effects of gravity to ensure blood returns to the heart effectively?
How do veins counteract the effects of gravity to ensure blood returns to the heart effectively?
What would be the consequence if the heart's left ventricle was significantly weakened?
What would be the consequence if the heart's left ventricle was significantly weakened?
How does increased blood volume affect blood pressure, assuming other factors remain constant?
How does increased blood volume affect blood pressure, assuming other factors remain constant?
What is the role of the sinoatrial (SA) node in the heart's function?
What is the role of the sinoatrial (SA) node in the heart's function?
What is the significance of blood undergoing pulmonary circulation?
What is the significance of blood undergoing pulmonary circulation?
How does vasoconstriction contribute to the regulation of blood pressure?
How does vasoconstriction contribute to the regulation of blood pressure?
What is the function of fibrinogen, a plasma protein found in blood?
What is the function of fibrinogen, a plasma protein found in blood?
How do coronary arteries support the function of the heart?
How do coronary arteries support the function of the heart?
During the cardiac cycle, what event occurs during diastole?
During the cardiac cycle, what event occurs during diastole?
What is the immediate result of the release of chemicals from sticky platelets at a damaged site??
What is the immediate result of the release of chemicals from sticky platelets at a damaged site??
Which of the following best describes the process of phagocytosis carried out by white blood cells?
Which of the following best describes the process of phagocytosis carried out by white blood cells?
Why are individuals with atherosclerosis at a higher risk for heart attacks and strokes?
Why are individuals with atherosclerosis at a higher risk for heart attacks and strokes?
What change in blood vessel structure is characteristic of arteriosclerosis?
What change in blood vessel structure is characteristic of arteriosclerosis?
How does the pericardial cavity contribute to heart function?
How does the pericardial cavity contribute to heart function?
Which blood vessels directly deliver oxygenated blood to the left atrium?
Which blood vessels directly deliver oxygenated blood to the left atrium?
What is the function of the bicuspid valve?
What is the function of the bicuspid valve?
How does blood flow differ between the pulmonary arteries and other arteries in the body?
How does blood flow differ between the pulmonary arteries and other arteries in the body?
As people age, how would the decreased flexibility of blood vessels affect blood pressure?
As people age, how would the decreased flexibility of blood vessels affect blood pressure?
How does the respiratory system work with the cardiovascular system to maintain bodily function?
How does the respiratory system work with the cardiovascular system to maintain bodily function?
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
What is the likely result of excessive carbon dioxide buildup in the blood?
What is the likely result of excessive carbon dioxide buildup in the blood?
What are the terminal air sacs in the lungs responsible for?
What are the terminal air sacs in the lungs responsible for?
How do the upper airways contribute to the quality of air that reaches the lungs?
How do the upper airways contribute to the quality of air that reaches the lungs?
Which structure is primarily responsible for directing air into the trachea instead of the esophagus during swallowing?
Which structure is primarily responsible for directing air into the trachea instead of the esophagus during swallowing?
What is the role of cilia in the respiratory tract?
What is the role of cilia in the respiratory tract?
How do the sinuses contribute to respiratory function and overall comfort?
How do the sinuses contribute to respiratory function and overall comfort?
What is the functional difference between the nasopharynx and the oropharynx?
What is the functional difference between the nasopharynx and the oropharynx?
What structural feature primarily prevents the trachea from collapsing?
What structural feature primarily prevents the trachea from collapsing?
How does the division of the bronchi into lobar bronchi relate to lung anatomy?
How does the division of the bronchi into lobar bronchi relate to lung anatomy?
What structural changes occur as the bronchi transition into bronchioles?
What structural changes occur as the bronchi transition into bronchioles?
Where does external respiration occur?
Where does external respiration occur?
During internal respiration, what is being diffused and where is it going?
During internal respiration, what is being diffused and where is it going?
What type of cells line the airways of the respiratory system and have hair-like projections?
What type of cells line the airways of the respiratory system and have hair-like projections?
What happens to the air that passes through the oropharynx?
What happens to the air that passes through the oropharynx?
According to the content, why should mammals typically breathe through their noses instead of their mouths?
According to the content, why should mammals typically breathe through their noses instead of their mouths?
Which of the following accurately describes the role of the pharynx in respiration?
Which of the following accurately describes the role of the pharynx in respiration?
Which is the correct order of air movement through the lower respiratory tract?
Which is the correct order of air movement through the lower respiratory tract?
What is the purpose of alveolar structure?
What is the purpose of alveolar structure?
What structural characteristic of the alveoli directly facilitates gas exchange with pulmonary capillaries?
What structural characteristic of the alveoli directly facilitates gas exchange with pulmonary capillaries?
How does the position of the lungs within the thoracic cavity contribute to their function?
How does the position of the lungs within the thoracic cavity contribute to their function?
How does pleural fluid contribute to the mechanical process of breathing?
How does pleural fluid contribute to the mechanical process of breathing?
Why does the right lung typically sit slightly higher than the left lung within the thoracic cavity?
Why does the right lung typically sit slightly higher than the left lung within the thoracic cavity?
Which of the following best explains how the medulla oblongata responds to increased carbon dioxide levels in the blood?
Which of the following best explains how the medulla oblongata responds to increased carbon dioxide levels in the blood?
During inspiration, what mechanical change directly leads to air rushing into the lungs?
During inspiration, what mechanical change directly leads to air rushing into the lungs?
Accessory muscles become most important in which of the following scenarios?
Accessory muscles become most important in which of the following scenarios?
What is the primary mechanism that drives exhalation under normal, resting conditions?
What is the primary mechanism that drives exhalation under normal, resting conditions?
How does emphysema, a form of COPD, directly impair respiratory function?
How does emphysema, a form of COPD, directly impair respiratory function?
What physiological change is directly responsible for the bronchospasms seen in asthma?
What physiological change is directly responsible for the bronchospasms seen in asthma?
What is the significance of the hilum of the lung?
What is the significance of the hilum of the lung?
What causes the blue coloring to lips and nail beds (cyanosis)?
What causes the blue coloring to lips and nail beds (cyanosis)?
What does COPD refer to?
What does COPD refer to?
What is the effect of increased volume in the thoracic cavity?
What is the effect of increased volume in the thoracic cavity?
Which of the following muscles help pull up the rib cage to make even larger space in the thoracic cavity?
Which of the following muscles help pull up the rib cage to make even larger space in the thoracic cavity?
What is the main cause of respiratory disease?
What is the main cause of respiratory disease?
What part of the brain is the respiratory control center in?
What part of the brain is the respiratory control center in?
What is caused by the return of the diaphragm to a resting state?
What is caused by the return of the diaphragm to a resting state?
What do the accessory muscles of exhalation do?
What do the accessory muscles of exhalation do?
What causes the inflammatory process in the airways?
What causes the inflammatory process in the airways?
What role does the endocrine system play that is similar to the nervous system?
What role does the endocrine system play that is similar to the nervous system?
How do hormones exert their effects on target cells?
How do hormones exert their effects on target cells?
What is the primary mechanism by which the endocrine system maintains homeostasis after a disturbance?
What is the primary mechanism by which the endocrine system maintains homeostasis after a disturbance?
What is the relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland?
What is the relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland?
How does the posterior pituitary differ from the anterior pituitary in terms of hormone production?
How does the posterior pituitary differ from the anterior pituitary in terms of hormone production?
Under what conditions is antidiuretic hormone (ADH) released?
Under what conditions is antidiuretic hormone (ADH) released?
What is the direct effect of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) on the kidneys?
What is the direct effect of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) on the kidneys?
How does thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) regulate thyroid hormone levels?
How does thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) regulate thyroid hormone levels?
What is the role of iodine in thyroid hormone production?
What is the role of iodine in thyroid hormone production?
How do T3 and T4 affect metabolism in the body?
How do T3 and T4 affect metabolism in the body?
What is the underlying cause of Hashimoto's disease?
What is the underlying cause of Hashimoto's disease?
In Graves' disease, what is the primary abnormality?
In Graves' disease, what is the primary abnormality?
What is the main function of the pancreas in maintaining blood glucose levels?
What is the main function of the pancreas in maintaining blood glucose levels?
How does insulin affect blood glucose levels?
How does insulin affect blood glucose levels?
What is the function of glucagon?
What is the function of glucagon?
Where are the adrenal glands located?
Where are the adrenal glands located?
What are the two main regions of the adrenal glands?
What are the two main regions of the adrenal glands?
What type of hormones are released by the adrenal cortex?
What type of hormones are released by the adrenal cortex?
What hormones are released by the adrenal medulla?
What hormones are released by the adrenal medulla?
What is the primary classification of hormones?
What is the primary classification of hormones?
Which of the following is the primary function of neutrophils in the immune response?
Which of the following is the primary function of neutrophils in the immune response?
How do macrophages contribute to the later stages of an infection?
How do macrophages contribute to the later stages of an infection?
What is the main role of basophils and mast cells in the immune response?
What is the main role of basophils and mast cells in the immune response?
What is the primary mechanism by which Natural Killer (NK) cells eliminate infected or cancerous cells?
What is the primary mechanism by which Natural Killer (NK) cells eliminate infected or cancerous cells?
How do T lymphocytes contribute to adaptive immunity?
How do T lymphocytes contribute to adaptive immunity?
What is the function of B lymphocytes in adaptive immunity?
What is the function of B lymphocytes in adaptive immunity?
What is the main characteristic of innate immunity?
What is the main characteristic of innate immunity?
How does adaptive immunity differ from innate immunity?
How does adaptive immunity differ from innate immunity?
Which of the following events occurs during the process of inflammation?
Which of the following events occurs during the process of inflammation?
What is the initial step in the inflammatory response after tissue damage?
What is the initial step in the inflammatory response after tissue damage?
What cellular process describes how white blood cells (WBCs) destroy foreign invaders?
What cellular process describes how white blood cells (WBCs) destroy foreign invaders?
What is the role of antigens in the immune system?
What is the role of antigens in the immune system?
How do antibodies help to eliminate pathogens from the body?
How do antibodies help to eliminate pathogens from the body?
What is margination in the context of the inflammatory response?
What is margination in the context of the inflammatory response?
What is diapedesis in the context of the immune response?
What is diapedesis in the context of the immune response?
What is a common characteristic of immunodeficiency disorders?
What is a common characteristic of immunodeficiency disorders?
What is the role of histamine in allergic reactions?
What is the role of histamine in allergic reactions?
What is the life-threatening condition caused by systemic hypersensitivity?
What is the life-threatening condition caused by systemic hypersensitivity?
What is the function of cytokines in the immune system?
What is the function of cytokines in the immune system?
The redness associated with inflammation is primarily due to which of the following?
The redness associated with inflammation is primarily due to which of the following?
What is the primary role of the lymphatic system in relation to the immune system?
What is the primary role of the lymphatic system in relation to the immune system?
How do lymphatic capillaries differ from blood capillaries in terms of permeability?
How do lymphatic capillaries differ from blood capillaries in terms of permeability?
What is the specific role of lymph nodes in lymphatic function?
What is the specific role of lymph nodes in lymphatic function?
In what order does lymph flow through the lymphatic system?
In what order does lymph flow through the lymphatic system?
What is the relationship between lymphatic vessels and lymphatic trunks?
What is the relationship between lymphatic vessels and lymphatic trunks?
Considering the structure of the lymphatic system, why is the presence of lymph nodes significant in areas prone to pathogen invasion?
Considering the structure of the lymphatic system, why is the presence of lymph nodes significant in areas prone to pathogen invasion?
In addition to filtration, what other critical function does the lymphatic system perform?
In addition to filtration, what other critical function does the lymphatic system perform?
What is the primary difference in function between lymph nodes and the spleen within the lymphatic system?
What is the primary difference in function between lymph nodes and the spleen within the lymphatic system?
Why is the thymus more active and larger in children than in adults?
Why is the thymus more active and larger in children than in adults?
How do the lymphatic ducts contribute to maintaining fluid balance within the body?
How do the lymphatic ducts contribute to maintaining fluid balance within the body?
What is the role of T lymphocytes within the lymphatic system?
What is the role of T lymphocytes within the lymphatic system?
Why is it important for the lymphatic system to recycle extra fluid from the cardiovascular system?
Why is it important for the lymphatic system to recycle extra fluid from the cardiovascular system?
What is the functional significance of the spleen's location in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen?
What is the functional significance of the spleen's location in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen?
How does the filtering action of lymph nodes contribute to the activation of the adaptive immune response?
How does the filtering action of lymph nodes contribute to the activation of the adaptive immune response?
What best explains the clinical relevance of understanding the lymphatic system's role in absorbing nutrients?
What best explains the clinical relevance of understanding the lymphatic system's role in absorbing nutrients?
What is the difference between the roles of lymph nodes and T lymphocytes in the lymphatic system?
What is the difference between the roles of lymph nodes and T lymphocytes in the lymphatic system?
How does the maturation of T lymphocytes in the thymus contribute to the development of immunological competence?
How does the maturation of T lymphocytes in the thymus contribute to the development of immunological competence?
Why are there two lymphatic systems?
Why are there two lymphatic systems?
Pathogens are harmful, but why does the body allow them into the lymphatic system?
Pathogens are harmful, but why does the body allow them into the lymphatic system?
How does the spleen filter blood, allowing it to remove damaged red blood cells and pathogens?
How does the spleen filter blood, allowing it to remove damaged red blood cells and pathogens?
How does the dermis contribute to thermoregulation when the body is exposed to cold temperatures?
How does the dermis contribute to thermoregulation when the body is exposed to cold temperatures?
Why are melanomas considered to be a serious form of skin cancer?
Why are melanomas considered to be a serious form of skin cancer?
How does the subcutaneous fascia contribute to the body's ability to maintain its core temperature?
How does the subcutaneous fascia contribute to the body's ability to maintain its core temperature?
How might the loss of collagen, associated with the aging process, affect the skin's ability to heal from wounds?
How might the loss of collagen, associated with the aging process, affect the skin's ability to heal from wounds?
What is the primary role of keratin in nail health and structure?
What is the primary role of keratin in nail health and structure?
Why do individuals with chronic peripheral vascular disease sometimes experience thickening of the nails?
Why do individuals with chronic peripheral vascular disease sometimes experience thickening of the nails?
How does the integumentary system communicate with the hypothalamus to regulate body temperature?
How does the integumentary system communicate with the hypothalamus to regulate body temperature?
Which layer of the skin is responsible for generating new cells, and what specialized cells are found within it that produce skin color?
Which layer of the skin is responsible for generating new cells, and what specialized cells are found within it that produce skin color?
How does the formation of a scab contribute to skin healing after a minor wound?
How does the formation of a scab contribute to skin healing after a minor wound?
How does the absence of blood vessels in the epidermis impact its function and health?
How does the absence of blood vessels in the epidermis impact its function and health?
How do sweat glands contribute to thermoregulation when the body is overheated?
How do sweat glands contribute to thermoregulation when the body is overheated?
In the context of skin injuries, what is the primary difference between minor and severe wounds in terms of the healing process?
In the context of skin injuries, what is the primary difference between minor and severe wounds in terms of the healing process?
What triggers the signals that cause the capillaries to dilate in the skin when the body is too hot?
What triggers the signals that cause the capillaries to dilate in the skin when the body is too hot?
How does the structure of the stratum corneum contribute to its protective function?
How does the structure of the stratum corneum contribute to its protective function?
How does the arrangement of capillaries in the dermis support the skin's role in thermoregulation?
How does the arrangement of capillaries in the dermis support the skin's role in thermoregulation?
What role do nerve endings in the dermis play in protecting the body from harm?
What role do nerve endings in the dermis play in protecting the body from harm?
How does the increasing incidence of skin cancer as one ages relate to changes in the integumentary system?
How does the increasing incidence of skin cancer as one ages relate to changes in the integumentary system?
What is one of the primary functions of sebaceous glands and where do they release their secretions?
What is one of the primary functions of sebaceous glands and where do they release their secretions?
Why might damage to capillaries within the dermis lead to both bleeding and initiate the body's clotting mechanisms?
Why might damage to capillaries within the dermis lead to both bleeding and initiate the body's clotting mechanisms?
How does the aging process affect hair follicles, and what outward sign does this change commonly produce?
How does the aging process affect hair follicles, and what outward sign does this change commonly produce?
Flashcards
Filtration (kidney)
Filtration (kidney)
The process of moving fluid and chemicals from the blood into the nephron.
Filtrate
Filtrate
Fluid that moves into the nephron during filtration.
Filtration Rate
Filtration Rate
How quickly fluid passes through the filter in the nephron.
Reabsorption
Reabsorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secretion
Secretion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tubule Permeability
Tubule Permeability
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transitional Epithelium
Transitional Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
rugae
rugae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Digestive Tract
Digestive Tract
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mastication
Mastication
Signup and view all the flashcards
Digestion
Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secretion (Digestion)
Secretion (Digestion)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Absorption (Digestion)
Absorption (Digestion)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Excretion/Defecation
Excretion/Defecation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oral Cavity
Oral Cavity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uvula
Uvula
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bolus
Bolus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lingual Frenulum
Lingual Frenulum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pharynx
Pharynx
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epiglottis
Epiglottis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peristalsis
Peristalsis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mucosa
Mucosa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Submucosa
Submucosa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscularis Externa
Muscularis Externa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Serosa
Serosa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rugae (Stomach)
Rugae (Stomach)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pyloric Sphincter
Pyloric Sphincter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chyme
Chyme
Signup and view all the flashcards
Liver
Liver
Signup and view all the flashcards
Detoxification (by liver)
Detoxification (by liver)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bilirubin
Bilirubin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bile
Bile
Signup and view all the flashcards
Emulsification
Emulsification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hepatic duct
Hepatic duct
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gallbladder
Gallbladder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cystic duct
Cystic duct
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common bile duct
Common bile duct
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pancreas
Pancreas
Signup and view all the flashcards
Buffers (in pancreatic juice)
Buffers (in pancreatic juice)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vomiting
Vomiting
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diarrhea
Diarrhea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Constipation
Constipation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiovascular System
Cardiovascular System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Circulation
Circulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arteries
Arteries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arterioles
Arterioles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Capillaries
Capillaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Veins
Veins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Venules
Venules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibrous Pericardium
Fibrous Pericardium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Serous Pericardium
Serous Pericardium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pericardial Cavity
Pericardial Cavity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Base of the Heart
Base of the Heart
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apex of the Heart
Apex of the Heart
Signup and view all the flashcards
Right Side of Heart
Right Side of Heart
Signup and view all the flashcards
Left Side of Heart
Left Side of Heart
Signup and view all the flashcards
Atria
Atria
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ventricles
Ventricles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Septum
Septum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tricuspid Valve
Tricuspid Valve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood
Blood
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hemostasis
Hemostasis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory system
Respiratory system
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ventilation
Ventilation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiration
Respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nasopharynx
Nasopharynx
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oropharynx
Oropharynx
Signup and view all the flashcards
Laryngopharynx
Laryngopharynx
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glottis
Glottis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bronchi
Bronchi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bronchioles
Bronchioles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nose functions
Nose functions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sinuses
Sinuses
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trachea
Trachea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveoli
Alveoli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar cells
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveolar Capillary Membrane
Alveolar Capillary Membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mediastinum
Mediastinum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pleura
Pleura
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pleural Fluid
Pleural Fluid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apex (of the lung)
Apex (of the lung)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Base (of the lung)
Base (of the lung)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hilum
Hilum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Right Lung Lobes
Right Lung Lobes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Left Lung Lobes
Left Lung Lobes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bony Thorax
Bony Thorax
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medulla Oblongata
Medulla Oblongata
Signup and view all the flashcards
Accessory Muscles (Inspiration)
Accessory Muscles (Inspiration)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exhalation
Exhalation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Accessory Muscles (Exhalation)
Accessory Muscles (Exhalation)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dyspnea
Dyspnea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tachypnea
Tachypnea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cyanosis
Cyanosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bronchospasm
Bronchospasm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hormones
Hormones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endocrine Glands
Endocrine Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chemical Messengers
Chemical Messengers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bloodstream
Bloodstream
Signup and view all the flashcards
Receptors
Receptors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypothalamus
Hypothalamus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH)
Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH)
Growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hormonal Control
Hormonal Control
Signup and view all the flashcards
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thyroid-stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Thyroid-stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thyroid Gland
Thyroid Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3)
Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucose
Glucose
Signup and view all the flashcards
Insulin
Insulin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucagon
Glucagon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adrenal Glands
Adrenal Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adrenal Cortex
Adrenal Cortex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Immune System
Immune System
Signup and view all the flashcards
WBCs (White Blood Cells)
WBCs (White Blood Cells)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neutrophils
Neutrophils
Signup and view all the flashcards
Macrophages
Macrophages
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basophils and Mast Cells
Basophils and Mast Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Natural Killer Cells (NK cells)
Natural Killer Cells (NK cells)
Signup and view all the flashcards
T lymphocytes (T cells)
T lymphocytes (T cells)
Signup and view all the flashcards
B lymphocytes (B cells)
B lymphocytes (B cells)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Antigens
Antigens
Signup and view all the flashcards
Antibodies
Antibodies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Innate Immunity
Innate Immunity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adaptive Immunity
Adaptive Immunity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Active Immunity
Active Immunity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Passive Immunity
Passive Immunity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inflammation
Inflammation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Histamine
Histamine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cytokines
Cytokines
Signup and view all the flashcards
Margination
Margination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diapedesis
Diapedesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pathogens
Pathogens
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lymphatic System
Lymphatic System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lymphatic System Functions
Lymphatic System Functions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lymphatic Capillaries
Lymphatic Capillaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lymph
Lymph
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lymphatic Vessels
Lymphatic Vessels
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lymph Nodes
Lymph Nodes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lymphatic Trunks
Lymphatic Trunks
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lymphatic Ducts
Lymphatic Ducts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cervical Lymph Nodes
Cervical Lymph Nodes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Axillary Lymph Nodes
Axillary Lymph Nodes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inguinal Lymph Nodes
Inguinal Lymph Nodes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spleen
Spleen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lymph Node Function
Lymph Node Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spleen Function
Spleen Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thymus
Thymus
Signup and view all the flashcards
T Lymphocytes
T Lymphocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skin
Skin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epidermis
Epidermis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Corneum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stratum Basale
Stratum Basale
Signup and view all the flashcards
Melanocytes
Melanocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Melanin
Melanin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dermis
Dermis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subcutaneous Fascia
Subcutaneous Fascia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nails
Nails
Signup and view all the flashcards
Keratin
Keratin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Melanoma
Melanoma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lesion
Lesion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Temperature regulation
Temperature regulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- The lymphatic and immune systems both protect the body from infection and harmful pathogens.
- The lymphatic system is a filtration system that keeps everything clean and balanced, while the immune system is a defense system.
- The lymphatic system is intertwined with the cardiovascular system where lymphatic capillaries intertwine with blood capillaries.
- Lymphatic capillaries are more permeable than blood capillaries, allowing extra fluid to pass easily into the lymphatic system.
- Lymphatic fluid, also known as lymph, flows through the lymph capillaries and the lymphatic system.
Functions of the Lymphatic System
- Recycles extra fluid from the cardiovascular system.
- Transports pathogens to the lymph nodes for destruction.
- Stores some white blood cells (WBCs).
- Aids in the absorption of some nutrients from the digestive system.
Network of the Lymphatic System
- Lymph capillaries collect fluid.
- Lymphatic vessels transport the fluid.
- Lymph nodes filter the fluid.
- Lymphatic vessels carry fluid away from nodes.
- Lymph then flows into lymphatic trunks.
- The lymphatic trunks empty into one of two ducts: the thoracic duct or the right lymphatic duct.
- Ducts empty the cleaned lymph fluid back into the larger blood vessels.
Lymph Nodes
- Lymph nodes are located in areas where they are most likely to catch invading pathogens.
- Lymph nodes filter fluid, and the fluid leaves nodes via lymphatic vessels.
- Lymphatic vessels empty into lymphatic trunks.
- The lymphatic trunks empty into one of two ducts.
Organs of the Lymphatic System
- The spleen and thymus are part of the lymphatic system and made of lymphatic tissue.
Spleen
- The spleen is located in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) of the abdomen.
- The spleen cleans up waste and debris.
- The spleen filters out and destroys damaged red blood cells (RBCs) from the blood and gets rid of pathogens from the blood.
Thymus
- The thymus is located just above the heart.
- The thymus is large in children and gets smaller with age.
- The thymus contains lymphocytes that mature to become T lymphocytes.
The Integumentary System
- The skin is the largest organ in the body.
- The skin has three main layers: epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous fascia.
Epidermis
- The epidermis is the superficial layer of the skin and is made of multiple layers of stratified squamous epithelium.
- The most superficial layer of the epidermis is the stratum corneum or the "horny layer" which is made of dead cells that shed and are replaced.
- The first layer of the epidermis is the stratum basale (basal layer) where new cells originate.
- Melanocytes are specialized cells in the stratum basale that produce melanin, which makes skin color.
- There are no blood vessels in the epidermis.
Dermis
- The dermis is inferior to the epidermis, much thicker, and made of connective tissue.
- The dermis contains capillaries, involuntary muscles, nerve endings, hair follicles, elastic fibers, sweat glands, and sebaceous (oil) glands.
Subcutaneous Fascia
- The subcutaneous fascia is the deepest layer of skin made of elastic connective tissue and fatty tissue.
- Fat cells make the fat that pads and protects the organs underneath.
Skin Healing
- When skin is punctured and blood vessels are damaged, the wound fills with blood.
- Blood contains substances that cause clotting; the top part of the clot exposed to air hardens to form a scab, preventing pathogens from entering.
- In minor wounds, the dermis regenerates, but in severe wounds, scar tissue replaces the dermis, which is thicker and less elastic.
Nails
- Nails are specialized cells that originate from the nail root.
- As nails grow out and over the nail bed, they become keratinized, drying and shrinking, and filling with keratin.
- Nails are also known as the nail body (finger and toe nails).
- Thickening nails can be a process of aging or caused by chronic peripheral vascular disease.
- Pink nail beds indicate normal peripheral perfusion.
- Blue nail beds indicate a decreased level of oxygen in the tissue.
- Peripheral perfusion indicates the amount of blood in the extremities.
Temperature Regulation
- The integumentary system maintains body temperature, regulated by the temperature control center in the hypothalamus.
- The hypothalamus sends messages to the integumentary system to regulate temperature.
- When hot, signals are sent to capillaries in the skin to enlarge vessels, exposing more blood to cooler air, while sweat glands release water to cool the skin's surface.
- When cold, signals are sent to capillaries to become smaller, keeping blood near the warm core of the body.
Common Disorders
- Melanoma is skin cancer caused by too much sun exposure and tanning and is a malignant tumor of melanocytes.
- A lesion means an area of tissue that has been altered.
- Common lesions include macules (freckles), papules (pimples), and erosions (pressure ulcers).
Changes Related to Aging
- Decreased collagen results in loss of skin elasticity.
- Wound healing takes longer.
- Hair loss occurs.
- Nails thicken.
- Rates of skin cancer increase.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.