Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main function of the respiratory system?
What is the main function of the respiratory system?
- Exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide (correct)
- Transmit nerve signals
- Digest food
- Circulate blood
Which components are part of the respiratory membrane?
Which components are part of the respiratory membrane?
- Alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, and their joined basement membrane (correct)
- Diaphragm, ribs, and sternum
- Parietal pleura, visceral pleura, and pleural cavity
- Bronchi, alveoli, and pleural membrane
Where is the apex of the lung located?
Where is the apex of the lung located?
- At the medial surface of the lung
- At the inferior part of the lung
- Slightly above the level of the middle third of the clavicle (correct)
- Near the base of the thoracic cavity
What shape is the base of the lung and where does it fit?
What shape is the base of the lung and where does it fit?
Which structure contains the hilus of the lung?
Which structure contains the hilus of the lung?
Which layer of the pleural membrane lines the wall of the thoracic cavity?
Which layer of the pleural membrane lines the wall of the thoracic cavity?
Which statement best describes the function of the serous fluid in the pleural cavity?
Which statement best describes the function of the serous fluid in the pleural cavity?
What phenomenon helps the pleural membranes adhere to one another?
What phenomenon helps the pleural membranes adhere to one another?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
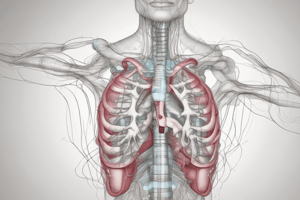
The Respiratory System
- Responsible for exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body and the environment
- Each alveolus is thin-walled and lies in contact with blood capillaries
- Millions of alveoli are present in each lung
- The respiratory membrane is the barrier across which gases are exchanged between air in alveoli and blood in pulmonary capillaries
- The respiratory membrane consists of the alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, and their joined basement membrane
Lungs
- Soft, spongy, cone-shaped organs located in the thoracic cavity
- Separated from each other by the heart and other structures in the mediastinum
- Each lung consists of four parts: apex, base, costal surface, and mediastinal (medial) surface
The Apex
- Rounded narrow superior portion that extends just slightly above the level of the middle third of the clavicle
The Base
- Broad inferior portion, concave and semilunar in shape, and fits over the convex thoracic surface of the diaphragm
The Costal Surface
- Convex surface that lies against the chest and matches the rounded curvature of the ribs
The Mediastinal (Medial) Surface
- Concave surface that contains a triangular-shaped area, the hilus, through which the bronchi, pulmonary blood vessels, lymph vessels, and nerves enter and leave
- The hilus is held together by the pleura and connective tissue and constitutes the root of the lung
The Pleural Membrane
- Two layers of serous membrane that enclose and protect each lung
- Outer layer: parietal pleura, lines the wall of the thoracic cavity
- Inner layer: visceral pleura, invests (covers) the lungs
- The space between the visceral and parietal pleura is the pleural cavity, which contains a small amount of serous fluid
- The serous fluid lubricates adjacent pleural surfaces, reducing friction during breathing, and helps the pleural membrane adhere to each other due to surface tension
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.