Podcast
Questions and Answers
What part of the nephron is responsible for the filtration of plasma?
What part of the nephron is responsible for the filtration of plasma?
- Renal tubule
- Glomerulus (correct)
- Collecting duct
- Proximal convoluted tubule
Which part of the renal tubule dips down into the medulla?
Which part of the renal tubule dips down into the medulla?
- Distal convoluted tubule
- Collecting duct
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Loop of Henle (correct)
Which nephron type has its renal corpuscles located close to the medulla?
Which nephron type has its renal corpuscles located close to the medulla?
- Cortical nephron
- Proximal nephron
- Juxtamedullary nephron (correct)
- Distal nephron
What percentage of nephrons are categorized as cortical nephrons?
What percentage of nephrons are categorized as cortical nephrons?
What type of cells form the visceral layer of the glomerular capsule?
What type of cells form the visceral layer of the glomerular capsule?
What percentage of resting cardiac output do the kidneys receive via renal arteries?
What percentage of resting cardiac output do the kidneys receive via renal arteries?
What type of epithelium makes up the outer wall of the glomerular capsule?
What type of epithelium makes up the outer wall of the glomerular capsule?
Which capillary bed in the kidney is responsible for filtration of blood?
Which capillary bed in the kidney is responsible for filtration of blood?
Where do the collecting ducts drain urine?
Where do the collecting ducts drain urine?
What is the main function of the renal corpuscle?
What is the main function of the renal corpuscle?
What controls the blood flow and renal resistance by altering arterioles?
What controls the blood flow and renal resistance by altering arterioles?
Which part of the nephron is responsible for filtering fluid?
Which part of the nephron is responsible for filtering fluid?
Where are efferent arterioles formed in the kidney?
Where are efferent arterioles formed in the kidney?
What is primarily carried away by peritubular capillaries?
What is primarily carried away by peritubular capillaries?
Which nephron type has a long loop of Henle that stretches through the medulla?
Which nephron type has a long loop of Henle that stretches through the medulla?
What process occurs in the glomerular capillaries of the renal corpuscle?
What process occurs in the glomerular capillaries of the renal corpuscle?
Which branch of medicine deals with the structure, function, and diseases of the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system?
Which branch of medicine deals with the structure, function, and diseases of the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system?
Which part of the kidney's anatomy points towards the center of the kidney?
Which part of the kidney's anatomy points towards the center of the kidney?
What is the role of renin secreted by the kidneys?
What is the role of renin secreted by the kidneys?
Which structures collect urine from the renal papillae and empty into the renal pelvis?
Which structures collect urine from the renal papillae and empty into the renal pelvis?
Which component of the kidney filters blood and returns most of the water and solutes to the bloodstream?
Which component of the kidney filters blood and returns most of the water and solutes to the bloodstream?
Where are the kidneys located in the body?
Where are the kidneys located in the body?
What term describes the inferior displacement of the kidneys?
What term describes the inferior displacement of the kidneys?
What does the parenchyma of the kidney consist of?
What does the parenchyma of the kidney consist of?
What type of epithelium is found in the proximal convoluted tubule?
What type of epithelium is found in the proximal convoluted tubule?
Which structure in the nephron is involved in glomerular filtration?
Which structure in the nephron is involved in glomerular filtration?
What is the main function of the descending limb of the loop of Henle?
What is the main function of the descending limb of the loop of Henle?
Which cells are part of the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
Which cells are part of the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
What is the significance of the small size of the efferent arteriole?
What is the significance of the small size of the efferent arteriole?
What type of epithelium lines the descending limb of the loop of Henle?
What type of epithelium lines the descending limb of the loop of Henle?
What cells are found in the distal convoluted tubule and collecting ducts?
What cells are found in the distal convoluted tubule and collecting ducts?
What happens if the glomerular blood hydrostatic pressure (GBHP) drops to 45mm Hg?
What happens if the glomerular blood hydrostatic pressure (GBHP) drops to 45mm Hg?
At what mean arterial pressure range do the kidneys function normally?
At what mean arterial pressure range do the kidneys function normally?
What is the average glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in an adult male?
What is the average glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in an adult male?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
The Nephron
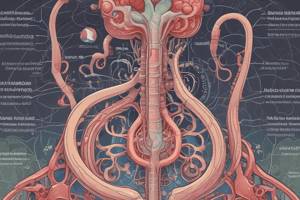
- The kidney is composed of over 1 million nephrons, each consisting of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule.
- The renal corpuscle is the site of plasma filtration, and it is composed of:
- Glomerulus: capillaries where filtration occurs.
- Glomerular (Bowman's) capsule: a double-walled epithelial cup that collects the filtrate.
- The renal tubule is composed of:
- Proximal convoluted tubule.
- Loop of Henle: dips down into the medulla.
- Distal convoluted tubule.
Juxtamedullary Nephron
- 15-20% of nephrons are juxtamedullary nephrons, which are located near the medulla and have long loops of Henle that extend into the deepest medulla.
- These nephrons enable the excretion of dilute or concentrated urine.
Cortical Nephron
- 80-85% of nephrons are cortical nephrons, which are located in the outer cortex and have loops of Henle that lie mainly in the cortex.
Histology of the Nephron and Collecting Duct
- The nephron and collecting duct are composed of a single layer of epithelial cells.
- Each region has distinctive features due to its function:
- Microvilli in the proximal convoluted tubule.
- Cuboidal versus simple epithelial cells in the distal convoluted tubule.
Glomerular Capsule
- The glomerular capsule is composed of visceral and parietal layers.
- The visceral layer is composed of modified simple squamous epithelial cells called podocytes.
- The parietal layer is composed of simple squamous epithelium and forms the outer wall of the capsule.
Structure of Renal Corpuscle
- The renal corpuscle is surrounded by Bowman's capsule.
- The visceral layer is composed of podocytes that cover the capillaries.
- The parietal layer is composed of simple squamous cells.
- Glomerular capillaries arise from the afferent arteriole and form a ball before emptying into the efferent arteriole.
Blood and Nerve Supply of the Kidney
- The kidney is abundantly supplied with blood vessels, receiving approximately 20% of the resting cardiac output via the renal arteries.
- Functions of different capillary beds:
- Glomerular capillaries: where filtration of blood occurs.
- Peritubular capillaries: carry away reabsorbed substances from the filtrate.
- Vasa recta: supplies nutrients to the medulla without disrupting its osmolarity.
- The nerve supply to the kidney is derived from the renal plexus (sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system).
- Sympathetic vasomotor nerves regulate blood flow and renal resistance by altering arterioles.
Nephron Function
- Nephrons perform three basic functions:
- Glomerular filtration.
- Tubular reabsorption.
- Tubular secretion.
- A renal tubule consists of:
- Proximal convoluted tubule.
- Loop of Henle.
- Distal convoluted tubule.
Blood Vessels Around the Nephron
- Glomerular capillaries are formed between the afferent and efferent arterioles.
- Efferent arterioles give rise to the peritubular capillaries and vasa recta.
Nephron Types
- There are two types of nephrons:
- Cortical nephrons: have a short loop of Henle that penetrates only into the outer region of the medulla.
- Juxtamedullary nephrons: have a long loop of Henle that stretches through the medulla and almost reaches the renal papilla.
Renal System
- The urinary system consists of:
- Two kidneys.
- Two ureters.
- One urinary bladder.
- One urethra.
- Urine is excreted from each kidney through its ureter and is stored in the urinary bladder until it is expelled from the body through the urethra.
Kidney Functions
- Regulation of blood ionic composition (Na+, K+, Ca++, Cl-, and phosphate ions).
- Regulation of blood pH, osmolarity, and glucose.
- Regulation of blood volume by conserving or eliminating water.
- Regulation of blood pressure by secreting the enzyme renin and adjusting renal resistance.
- Release of erythropoietin and calcitriol.
- Excretion of wastes and foreign substances.
Anatomy and Histology of the Kidneys
- The paired kidneys are retroperitoneal organs.
- The kidneys are surrounded by three layers of tissue:
- Renal capsule.
- Adipose capsule.
- Renal fascia.
Internal Anatomy of the Kidney
- The kidneys consist of:
- Cortex.
- Medulla.
- Pyramids.
- Papillae.
- Columns.
- Calyces.
- Pelves.
- The renal cortex and renal pyramids constitute the functional portion or parenchyma of the kidney.
Glomerular Filtration Rate
- The amount of filtrate formed in all renal corpuscles of both kidneys per minute.
- Average adult male rate is 125 mL/min.
- Homeostasis requires a constant GFR.
- Changes in net filtration pressure affect GFR.
Juxtaglomerular Apparatus
- A structure where the afferent arteriole makes contact with the ascending limb of the loop of Henle.
- Macula densa is a thickened part of the ascending limb.
- Juxtaglomerular cells are modified muscle cells in the arteriole.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.