Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the function of the endothelial cells in the afferent arteriole?
What is the function of the endothelial cells in the afferent arteriole?
- To line the blood vessel and allow smooth blood flow (correct)
- To regulate blood pressure in the kidney
- To transport oxygen and nutrients to the kidney cells
- To filter waste and excess substances from the blood
What is the direction of blood flow in the afferent arteriole?
What is the direction of blood flow in the afferent arteriole?
- Away from the glomerulus
- Towards the glomerulus (correct)
- From the efferent arteriole to the afferent arteriole
- Between the proximal and distal convoluted tubules
What is the location of the distal convoluted tubule in relation to the afferent and efferent arterioles?
What is the location of the distal convoluted tubule in relation to the afferent and efferent arterioles?
- Between the proximal convoluted tubule and the loop of Henle
- Between the afferent and efferent arterioles (correct)
- Inside the glomerulus
- Outside the Bowman's capsule
What is the purpose of the efferent arteriole?
What is the purpose of the efferent arteriole?
What is the function of the cells surrounding the distal convoluted tubule?
What is the function of the cells surrounding the distal convoluted tubule?
What is the relationship between the afferent and efferent arterioles?
What is the relationship between the afferent and efferent arterioles?
What is the location of the Bowman's capsule in relation to the glomerulus?
What is the location of the Bowman's capsule in relation to the glomerulus?
What is the function of the special cells in the distal convoluted tubule?
What is the function of the special cells in the distal convoluted tubule?
What is the main function of mesangial cells in the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
What is the main function of mesangial cells in the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
What is the term for the specialized smooth muscle cells that produce granules containing renin?
What is the term for the specialized smooth muscle cells that produce granules containing renin?
Where are the macula densa cells primarily located?
Where are the macula densa cells primarily located?
What is the purpose of the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
What is the purpose of the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
Which of the following is NOT a component of the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
Which of the following is NOT a component of the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
What is the location of the juxtaglomerular cells?
What is the location of the juxtaglomerular cells?
What is the trigger for the release of renin from the juxtaglomerular cells?
What is the trigger for the release of renin from the juxtaglomerular cells?
What is the term for the cells that make up the inner layer of the arteriole?
What is the term for the cells that make up the inner layer of the arteriole?
What is the function of the granules in the juxtaglomerular cells?
What is the function of the granules in the juxtaglomerular cells?
Which of the following cell types is responsible for regulating the diameter of the afferent arteriole?
Which of the following cell types is responsible for regulating the diameter of the afferent arteriole?
What is the role of the local hormone released by the macula densa cells?
What is the role of the local hormone released by the macula densa cells?
What is the trigger that the macula densa cells sense to release the local hormone?
What is the trigger that the macula densa cells sense to release the local hormone?
What is the function of renin?
What is the function of renin?
What type of hormone is renin?
What type of hormone is renin?
What is the location of the cells that release renin?
What is the location of the cells that release renin?
What is the effect of low sodium levels in the filtrate on the macula densa cells?
What is the effect of low sodium levels in the filtrate on the macula densa cells?
What is the direct trigger for the release of renin by juxtaglomerular cells in response to low blood pressure?
What is the direct trigger for the release of renin by juxtaglomerular cells in response to low blood pressure?
What type of cells are the juxtaglomerular cells specialized as?
What type of cells are the juxtaglomerular cells specialized as?
What is the location of the sympathetic nerve endings that trigger the release of renin?
What is the location of the sympathetic nerve endings that trigger the release of renin?
What is the function of the macula densa cells?
What is the function of the macula densa cells?
What is the local messenger molecule that the macula densa cells send to the juxtaglomerular cells?
What is the local messenger molecule that the macula densa cells send to the juxtaglomerular cells?
What is the response of the juxtaglomerular cells to low blood pressure?
What is the response of the juxtaglomerular cells to low blood pressure?
How do the macula densa cells sense low sodium levels in the distal convoluted tubule?
How do the macula densa cells sense low sodium levels in the distal convoluted tubule?
What is the ultimate goal of the macula densa cells in response to low sodium levels?
What is the ultimate goal of the macula densa cells in response to low sodium levels?
What is the significance of low sodium levels in the distal convoluted tubule?
What is the significance of low sodium levels in the distal convoluted tubule?
What is the relationship between the macula densa cells and the juxtaglomerular cells?
What is the relationship between the macula densa cells and the juxtaglomerular cells?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
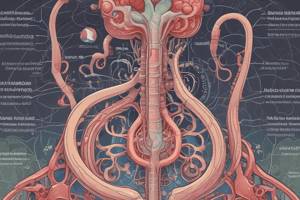
The Juxtaglomerular Apparatus
- The juxtaglomerular apparatus consists of the afferent and efferent arterioles, the glomerulus, and the distal convoluted tubule.
- The distal convoluted tubule has cells called the macula densa cells, which play a special role in the apparatus.
Structure of the Afferent and Efferent Arterioles
- The afferent arteriole has endothelial cells lining its inner layer (tunica intima).
- The endothelial cells are surrounded by smooth muscle cells in the tunica media layer.
- There are also specialized smooth muscle cells called juxtaglomerular cells, which are located near the glomerulus.
- The juxtaglomerular cells have granules that contain renin.
Function of the Juxtaglomerular Apparatus
- The juxtaglomerular apparatus releases renin in response to certain triggers.
- Renin is a protein hormone that plays a key role in blood pressure regulation.
Triggers for Renin Release
- Low Blood Pressure: Low blood pressure is a direct trigger for renin release, sensed by the juxtaglomerular cells.
- Sympathetic Nerve Endings: Sympathetic nerve endings in the tunica externa layer of the arterioles can stimulate renin release when they fire.
- Low Sodium Levels in the Distal Convoluted Tubule: Low sodium levels in the distal convoluted tubule, sensed by the macula densa cells, trigger the release of prostaglandin, a local hormone that stimulates renin release.
The Role of the Macula Densa Cells
- Macula densa cells in the distal convoluted tubule monitor sodium levels and sense low blood pressure in the glomerulus.
- When sodium levels are low, the macula densa cells release prostaglandin, which stimulates renin release by the juxtaglomerular cells.
The Release of Renin
- Renin is released from the juxtaglomerular cells into the bloodstream in response to the triggers mentioned above.
- Renin then flows into the afferent arteriole, through the glomerulus, and out the efferent arteriole.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.