Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main function of the menisci in the knee joint?
What is the main function of the menisci in the knee joint?
- To facilitate flexion and extension of the knee joint
- To supply nerves to the capsule of the knee joint
- To provide stability to the joint by deepening the socket for the femoral condyles (correct)
- To rotate the tibial plateau on the femoral condyles
What is the normal range of flexion of the knee joint?
What is the normal range of flexion of the knee joint?
- 135-140 degrees (correct)
- 90-100 degrees
- 150-155 degrees
- 120-125 degrees
What is the purpose of the medial rotation of the femur on the tibia during the final stages of extension?
What is the purpose of the medial rotation of the femur on the tibia during the final stages of extension?
- To adjust ligament tension (correct)
- To deepen the socket for the femoral condyles
- To facilitate hyperextension of the knee
- To rotate the tibial plateau on the femoral condyles
What is the consequence of hyperextending the knee in individuals with normal knees?
What is the consequence of hyperextending the knee in individuals with normal knees?
What is the movement of the tibia during the final stages of extension?
What is the movement of the tibia during the final stages of extension?
How many nerves supply the capsule of the knee joint?
How many nerves supply the capsule of the knee joint?
What is the shape of the menisci?
What is the shape of the menisci?
What is the extent of internal rotation of the knee joint?
What is the extent of internal rotation of the knee joint?
What is the function of the posterior cruciate ligament in the knee joint?
What is the function of the posterior cruciate ligament in the knee joint?
Why is the posterior cruciate ligament thicker than the anterior cruciate ligament?
Why is the posterior cruciate ligament thicker than the anterior cruciate ligament?
What happens to the posterior cruciate ligament during flexion of the knee joint?
What happens to the posterior cruciate ligament during flexion of the knee joint?
Why is the anterior cruciate ligament more prone to injury than the posterior cruciate ligament?
Why is the anterior cruciate ligament more prone to injury than the posterior cruciate ligament?
What is the consequence of a ruptured cruciate ligament?
What is the consequence of a ruptured cruciate ligament?
When is the posterior cruciate ligament most active?
When is the posterior cruciate ligament most active?
What is the role of the quadriceps femoris muscle in preventing femur movement?
What is the role of the quadriceps femoris muscle in preventing femur movement?
When are the cruciate ligaments most susceptible to injury?
When are the cruciate ligaments most susceptible to injury?
What is the primary function of the popliteus muscle in the knee joint?
What is the primary function of the popliteus muscle in the knee joint?
What is the result of the medial rotation of the femur on the tibia in the final 15 degrees of extension?
What is the result of the medial rotation of the femur on the tibia in the final 15 degrees of extension?
What is the difference between the medial and lateral femoral condyles?
What is the difference between the medial and lateral femoral condyles?
What happens to the femoral condyles during the movement from flexion to extension?
What happens to the femoral condyles during the movement from flexion to extension?
What is the purpose of the arcuate ligament in the knee joint?
What is the purpose of the arcuate ligament in the knee joint?
What happens to the lateral femoral condyle during extension?
What happens to the lateral femoral condyle during extension?
During which phase of gait is the knee joint in extension?
During which phase of gait is the knee joint in extension?
What is the significance of the 'close-packed' position of the knee joint?
What is the significance of the 'close-packed' position of the knee joint?
What is the primary reason for the patella to dislocate laterally in patients with a wasting of the vastus medialis?
What is the primary reason for the patella to dislocate laterally in patients with a wasting of the vastus medialis?
What is the average Q-angle in women?
What is the average Q-angle in women?
Which of the following conditions can increase the Q-angle?
Which of the following conditions can increase the Q-angle?
What is the consequence of a high Q-angle on the patella?
What is the consequence of a high Q-angle on the patella?
What is the primary cause of an abnormal Q-angle in some individuals?
What is the primary cause of an abnormal Q-angle in some individuals?
What is the purpose of measuring the Q-angle?
What is the purpose of measuring the Q-angle?
What is the relationship between the Q-angle and patellar dislocation?
What is the relationship between the Q-angle and patellar dislocation?
What is the method of measuring the Q-angle?
What is the method of measuring the Q-angle?
What degree of knee bend is required to relax the hamstrings?
What degree of knee bend is required to relax the hamstrings?
Which ligament is not at risk of injury during twisting of the body upon full extension?
Which ligament is not at risk of injury during twisting of the body upon full extension?
What type of tackle is likely to tear both the anterior cruciate and medial collateral ligament?
What type of tackle is likely to tear both the anterior cruciate and medial collateral ligament?
Who first described the 'unhappy triad' of injuries?
Who first described the 'unhappy triad' of injuries?
What is the result of a valgus or varus bending in full extension?
What is the result of a valgus or varus bending in full extension?
What is attached to the medial meniscus?
What is attached to the medial meniscus?
What is the term for the common association of injuries involving the anterior cruciate ligament, medial collateral ligament, and medial meniscus?
What is the term for the common association of injuries involving the anterior cruciate ligament, medial collateral ligament, and medial meniscus?
What is the focus of the final part of the lecture on the knee joint?
What is the focus of the final part of the lecture on the knee joint?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
The Knee Joint
- The knee joint is a modified synovial hinge joint that is capable of flexion by 135-140 degrees, but cannot extend beyond 0 degrees in the normal knee.
- The joint has some rotation at the extremes of flexion and extension, allowing the tibial plateau to rotate on the femoral condyles.
Menisci
- The knee joint has two intra-synovial articular discs called menisci: medial meniscus and lateral meniscus.
- The menisci are wedge-shaped semi-circular discs that help to deepen the socket for the femoral condyles and provide added support to the joint.
Muscles Crossing the Knee Joint
- The stability of the knee joint is added to by the tone of the muscles of the thigh and leg that cross it.
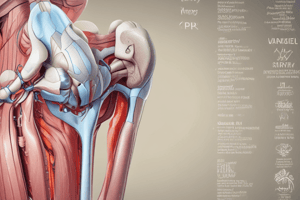
Neurovasculature of the Knee Joint
- The capsule of the knee joint is supplied by four nerves: femoral nerve, obturator nerve, tibial nerve, and common fibular nerve.
- The nerves supply the joint anteriorly and medially (femoral nerve and obturator nerve) and posteriorly and laterally (tibial nerve and common fibular nerve).
Q-Angle
- The Q-angle is the angle created by the quadriceps muscle pulling along the mechanical axis rather than the anatomical one, due to the femur being angled.
- The Q-angle is measured by drawing two lines: one from the anterior superior iliac spine to the center of the patella, and another from the tibial tuberosity to the center of the patella.
- The Q-angle is greater in women (about 17 degrees) than in men (about 14 degrees) due to wider hips.
Popliteus Muscle
- The popliteus muscle laterally rotates the femur to unlock the knee joint when it is locked in full extension.
- The muscle arises from the triangular area in the back of the tibia, just proximal to the soleal line, and inserts onto the lateral femoral epicondyle.
Cruciate Ligaments
- The anterior cruciate ligament prevents excessive forward movement of the femur.
- The posterior cruciate ligament performs the opposite action to the anterior one, preventing excessive backward movement of the femur.
- The posterior cruciate ligament is about three times the thickness of the anterior one and is only part of it is taut in extension.
Cruciate Ligament Injury
- The anterior cruciate ligament is more prone to injury than the posterior one due to its thinner structure.
- Rupture of the cruciate ligaments may cause bleeding inside the joint capsule, leading to swelling, discoloration, and pain.
The Unhappy Triad
- The unhappy triad is a common association of injuries that occurs when there is a twisting of the body upon full extension, resulting in tears to the anterior cruciate ligament, medial collateral ligament, and medial meniscus.
- The injuries are often seen in contact sports, such as rugby or football, where the foot is fixed firmly on the ground and the momentum of the trunk twists and tears the ligaments.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.