Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the function of the medial collateral ligament in the knee joint?
What is the function of the medial collateral ligament in the knee joint?
- Resists varus angulation and provides restraint to axial rotation
- Resists valgus angulation and provides restraint to axial rotation (correct)
- Stabilizes the patella and prevents lateral dislocation
- Provides support to the menisci and assists in weight-bearing
Which of the following bursae is located posteriorly in the knee joint?
Which of the following bursae is located posteriorly in the knee joint?
- Prepatellar bursa
- Suprapatellar bursa
- Semimembranosus bursa (correct)
- Deep infrapatellar bursa
What is the type of joint that the knee joint is classified as?
What is the type of joint that the knee joint is classified as?
- Diarthrodial joint with features of gliding and hinge joints (correct)
- Synovial pivot joint
- Synovial ball-and-socket joint
- Synovial hinge joint
Which of the following ligaments is intracapsular in the knee joint?
Which of the following ligaments is intracapsular in the knee joint?
What is the attachment of the ligamentum patellae in the knee joint?
What is the attachment of the ligamentum patellae in the knee joint?
What is the primary function of the Anterolateral bundle of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament?
What is the primary function of the Anterolateral bundle of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament?
Which of the following muscles is responsible for internal rotation of the knee joint?
Which of the following muscles is responsible for internal rotation of the knee joint?
What is the main function of the Menisci in the knee joint?
What is the main function of the Menisci in the knee joint?
During the last 30 degrees of knee extension, what happens to the tibia and femur?
During the last 30 degrees of knee extension, what happens to the tibia and femur?
Which of the following muscles is important for patella stability?
Which of the following muscles is important for patella stability?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Knee Joint
- Largest synovial joint and a diarthrodial joint
- Articulation occurs between the round condyles of the femur and tibial plateaus and menisci, and the gliding joint between the patella and the patellar surface of the femur
- Classified as a synovial hinge joint
Capsule and Synovium
- Attached to the margins of the articular surfaces and surrounds the sides and posterior aspect of the joint
- Synovial membrane lines the capsule and attaches to the margins of the articular surfaces
Bursae Related to Knee Joint
- Anterior bursae:
- Suprapatellar bursa
- Prepatellar bursa
- Superficial infrapatellar bursa
- Deep infrapatellar bursa
- Posterior bursae:
- Popliteal bursa
- Semimembranosus bursa
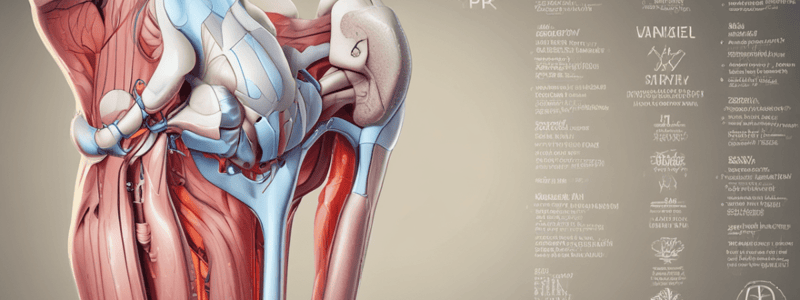
Ligaments of the Knee
- Extracapsular ligaments:
- Lateral collateral ligament:
- Attachment: lateral epicondyle of the femur to the head of the fibula
- Function: resists varus angulation and provides restraint to axial rotation
- Medial collateral ligament:
- Attachment: medial epicondyle of the femur to the medial condyle of the tibia
- Function: resists valgus angulation and provides restraint to axial rotation
- Lateral collateral ligament:
- Other extracapsular ligaments:
- Ligamentum patellae: attaches the patella to the tibia
- Oblique popliteal ligament: a tendinous expansion derived from the semimembranosus muscle
- Intracapsular ligaments:
- Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL):
- Bundles: anteromedial and posterolateral bands
- Attachment: anteromedial area of the tibia to the medial surface of the lateral femoral condyle
- Function: restrains anterior tibial translation and provides rotational stability
- Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL):
- Attachment: posterior intercondylar area of the tibia to the anterior part of the lateral surface of the medial femoral condyle
- Bundles: anterolateral and posteromedial bands
- Function: prevents posterior tibial translation in relation to the femur
- Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL):
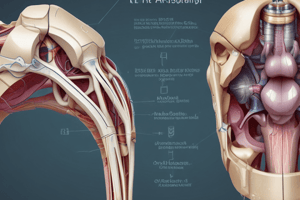
Menisci
- C-shaped sheets of fibrocartilage
- Medial and lateral menisci connected by the transverse ligament of the knee
- Medial meniscus is attached to the capsule, while the lateral meniscus is more mobile
- Function: deepens the articular surfaces of the tibial condyles, serves as a cushion between the two bones, and distributes forces transmitted through the joint
Knee Movement
- Main movement:
- Flexion: 145-160 degrees by the hamstring muscles
- Extension: 0-5 degrees by the quadriceps muscle
- Minor movement:
- Internal rotation: 10 degrees by the popliteus and semitendinosus muscles
- External rotation: 10 degrees by the biceps femoris muscle
Stability of the Knee Joint
- Bony factors
- Ligamentous factors
- Muscular factors
- Special situations
Muscular Factors
- Vitally important for knee stability
- Muscles involved:
- Vasti
- Medialis (VMO) - important for patella stability
- Ilio-tibial band - stabilizes the slightly flexed knee (varus)
Knee Locking
- Occurs during the last 30 degrees of knee extension
- Tibia externally rotates, and the femur internally rotates
- Knee joint is slightly hyperextended and stabilized with the tightening of the cruciate and collateral ligaments
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.