Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the ventricles in the heart?
What is the primary function of the ventricles in the heart?
- Oxygenating the blood
- Partitioning the heart chambers
- Receiving blood from the body
- Pumping blood to the lungs and body (correct)
The left atrium receives oxygen-poor blood from the body.
The left atrium receives oxygen-poor blood from the body.
False (B)
What separates the chambers of the heart?
What separates the chambers of the heart?
Septum
The _______ is the largest vein that sends oxygen-poor blood back to the heart.
The _______ is the largest vein that sends oxygen-poor blood back to the heart.
Match each blood vessel to its function:
Match each blood vessel to its function:
Which valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle?
Which valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle?
Veins transport oxygen-rich blood away from the heart.
Veins transport oxygen-rich blood away from the heart.
What is the primary function of the valves in the heart?
What is the primary function of the valves in the heart?
The ______ are the blood vessels that connect arterioles and venules.
The ______ are the blood vessels that connect arterioles and venules.
Match the following types of blood vessels with their characteristics:
Match the following types of blood vessels with their characteristics:
What happens to the AV valves when the ventricles contract?
What happens to the AV valves when the ventricles contract?
The pulmonary artery carries oxygenated blood to the lungs.
The pulmonary artery carries oxygenated blood to the lungs.
What is the role of the semilunar valves during ventricular contraction?
What is the role of the semilunar valves during ventricular contraction?
Where does oxygen-poor blood return to the heart?
Where does oxygen-poor blood return to the heart?
The left ventricle pumps oxygen-poor blood to the lungs.
The left ventricle pumps oxygen-poor blood to the lungs.
What is the primary role of cardiologists?
What is the primary role of cardiologists?
The smallest blood vessels, which are just one-cell thick, are called ______.
The smallest blood vessels, which are just one-cell thick, are called ______.
Match the following terms with their descriptions:
Match the following terms with their descriptions:
What is the final step to become a licensed cardiologist in the Philippines?
What is the final step to become a licensed cardiologist in the Philippines?
An open circulatory system is common among mammals.
An open circulatory system is common among mammals.
What condition is often associated with the malfunction of the mitral valve?
What condition is often associated with the malfunction of the mitral valve?
What is the primary function of red blood cells (RBCs)?
What is the primary function of red blood cells (RBCs)?
White blood cells (WBCs) are anucleated.
White blood cells (WBCs) are anucleated.
Who discovered blood groups and in what year?
Who discovered blood groups and in what year?
The liquid portion of blood is called ______.
The liquid portion of blood is called ______.
Which type of blood cell is responsible for producing antibodies?
Which type of blood cell is responsible for producing antibodies?
Match the blood types with their characteristics:
Match the blood types with their characteristics:
Platelets are whole cells responsible for blood clotting.
Platelets are whole cells responsible for blood clotting.
What structural feature distinguishes granulocytes from agranulocytes?
What structural feature distinguishes granulocytes from agranulocytes?
What is the main risk associated with mixing incompatible blood groups?
What is the main risk associated with mixing incompatible blood groups?
The blood clotting process can take up to five minutes after an injury occurs.
The blood clotting process can take up to five minutes after an injury occurs.
What is the consequence of blood clumping in the bloodstream?
What is the consequence of blood clumping in the bloodstream?
The _______ is the body's mechanism to stop bleeding caused by injury.
The _______ is the body's mechanism to stop bleeding caused by injury.
Match the following actions with their appropriate precautions:
Match the following actions with their appropriate precautions:
What are blood platelets primarily involved in?
What are blood platelets primarily involved in?
Blood platelets are types of cells that can be viewed in fresh blood samples.
Blood platelets are types of cells that can be viewed in fresh blood samples.
Who discovered the four different blood groups in 1900?
Who discovered the four different blood groups in 1900?
Blood type O has ______ antigens and ______ antibodies in the plasma.
Blood type O has ______ antigens and ______ antibodies in the plasma.
Which blood type has both A and B antigens and no antibodies?
Which blood type has both A and B antigens and no antibodies?
A person with blood type AB can receive blood from any other blood type.
A person with blood type AB can receive blood from any other blood type.
Match the following blood types with their respective antigens:
Match the following blood types with their respective antigens:
What is the main safety tip to remember when handling a microscope?
What is the main safety tip to remember when handling a microscope?
Which blood type is known as the universal donor?
Which blood type is known as the universal donor?
People with blood type AB can only receive blood from people with blood type O.
People with blood type AB can only receive blood from people with blood type O.
What is the most common antigen in the Rh factor?
What is the most common antigen in the Rh factor?
People with Rh- blood can receive blood from someone with _____ blood without any issue.
People with Rh- blood can receive blood from someone with _____ blood without any issue.
Match the following blood types with their characteristics:
Match the following blood types with their characteristics:
What is the primary function of thromboplastin in the blood clotting process?
What is the primary function of thromboplastin in the blood clotting process?
HDL is referred to as 'bad cholesterol' because it contributes to plaque formation in blood vessels.
HDL is referred to as 'bad cholesterol' because it contributes to plaque formation in blood vessels.
What forms the network that seals an injured part during the blood clotting process?
What forms the network that seals an injured part during the blood clotting process?
The __________ is the liquid part of blood that carries nutrients, hormones, and waste products.
The __________ is the liquid part of blood that carries nutrients, hormones, and waste products.
Match the following types of cholesterol with their characteristics:
Match the following types of cholesterol with their characteristics:
Which of the following is NOT a component of the blood clot?
Which of the following is NOT a component of the blood clot?
Calcium ions play a role in the transformation of prothrombin to thrombin.
Calcium ions play a role in the transformation of prothrombin to thrombin.
What role does prothrombin play in the blood clotting process?
What role does prothrombin play in the blood clotting process?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
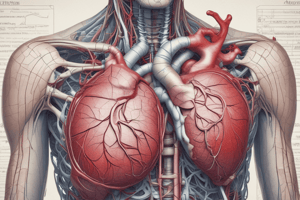
The Heart and Its Chambers
- The human heart is a four-chambered organ located at the center of the chest, roughly the size of a clenched fist.
- Heart chambers include two atria (upper chambers) and two ventricles (lower chambers), separated by a muscular wall known as the septum.
The Atria
- Right atrium receives oxygen-poor blood from the body.
- Left atrium receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs.
The Ventricles
- Right ventricle pumps oxygen-poor blood to the lungs for oxygenation.
- Left ventricle pumps oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body.
Blood Vessels and Valves in the Heart
- The vena cava is the largest vein, with two branches:
- Superior vena cava drains the head and neck into the right atrium.
- Inferior vena cava drains the lower body into the right atrium.
- Pulmonary artery carries blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
- Pulmonary veins return oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium.
- The aorta is the largest artery and distributes oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle to the body.
Heart Valves
- Valves ensure one-way blood flow and prevent backflow:
- Atrioventricular (AV) valves:
- Tricuspid valve (right atrium to right ventricle).
- Bicuspid (mitral) valve (left atrium to left ventricle).
- Semilunar (SL) valves:
- Pulmonic valve (opening of the pulmonary artery).
- Aortic valve (opening of the aorta).
- Atrioventricular (AV) valves:
- AV valves are open when atria contract and closed during ventricular contraction.
Blood Vessel Types
- Circulatory system is a closed network comprising arteries, veins, and capillaries.
- Arteries:
- Thick-walled to withstand high pressure.
- Carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart.
- Veins:
- Thinner walls, return blood to the heart, equipped with valves to prevent backflow.
- Capillaries:
- One-cell thick for efficient exchange of gases and nutrients between blood and cells.
Blood Circulation Process
- Oxygen-poor blood returns to the right atrium via the vena cava, moves to the right ventricle, and is pumped to the lungs through the pulmonary artery for oxygenation.
- Oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium via pulmonary veins and is then sent to the left ventricle, which pumps it out to the body through the aorta.
Cardiologist Career Path
- Requires completion of a life sciences degree, a four-year medical degree, a residency of six to eight years, and passing the Medical Board Licensure Exam.
- Cardiologists specialize in diagnosing and treating heart and blood vessel conditions.
Blood Composition
- Blood consists of plasma (liquid) and formed elements (cells).
- Red Blood Cells (RBCs): Carry oxygen; biconcave shape; contain hemoglobin.
- White Blood Cells (WBCs): Fight infections; classified into granulocytes and agranulocytes.
- Platelets: Cell fragments involved in blood clotting.
Blood Types and Compatibility
- Blood groups A, B, AB, and O are defined by the specific combination of antigens and antibodies discovered by Karl Landsteiner in 1900.
- Type A: Antigen A, antibody B.
- Type B: Antigen B, antibody A.
- Type AB: Both antigens A & B, no antibodies.
- Type O: No antigens, both antibodies A & B; considered universal donor.
- Type AB: Universal recipient.
Rh Factor
- Second most significant blood group system, primarily involving antigen D.
- Rh+ means the Rh factor is present, while Rh- means it is absent.
- Rh- individuals can safely receive Rh+ blood once but can develop antibodies against Rh+ if exposed repeatedly.
Blood Clotting Process
- Initiates when thrombocytes disintegrate upon injury, converting thromboplastinogen into thrombin.
- Thrombin catalyzes the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin, forming a clot to seal the wound.
- Clots prevent excessive bleeding and allow healing to begin.
Cardiovascular Disease and Cholesterol
- Two forms of cholesterol: High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL - "good cholesterol") and Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL - "bad cholesterol").
- LDL contributes to plaque formation in arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease, while HDL helps transport LDL to the liver for removal.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.