Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the approximate size of the human heart?
What is the approximate size of the human heart?
- The size of a grapefruit
- The size of a baseball
- The size of a closed fist (correct)
- The size of a football
Where is the heart located in the body?
Where is the heart located in the body?
- In the pelvis, posterior to the pubic symphysis
- In the abdomen, superior to the diaphragm
- In the neck, anterior to the vertebral column
- In the thorax cavity, between the two lungs (correct)
What is the shape of the human heart?
What is the shape of the human heart?
- Pyramidal (correct)
- Cylindrical
- Rectangular
- Spherical
Which ventricle forms the apex of the heart?
Which ventricle forms the apex of the heart?
Where is the apex of the heart located?
Where is the apex of the heart located?
Which of the following is NOT a surface of the heart?
Which of the following is NOT a surface of the heart?
What is the name of the double-walled sac surrounding the heart?
What is the name of the double-walled sac surrounding the heart?
Which of the following is NOT a border of the heart?
Which of the following is NOT a border of the heart?
The serous pericardium consists of how many layers?
The serous pericardium consists of how many layers?
What is the name of the surface of the heart that rests on the central tendon of the diaphragm?
What is the name of the surface of the heart that rests on the central tendon of the diaphragm?
What is the pathway of blood flow from the right ventricle to the lungs and back to the left atrium called?
What is the pathway of blood flow from the right ventricle to the lungs and back to the left atrium called?
Which of the following statements about cardiac muscle is true?
Which of the following statements about cardiac muscle is true?
What is the function of the sinoatrial (SA) node?
What is the function of the sinoatrial (SA) node?
What is the role of the atrioventricular (AV) node?
What is the role of the atrioventricular (AV) node?
What is the function of the bundle branches in the heart conduction system?
What is the function of the bundle branches in the heart conduction system?
What are the structures that carry the electrical impulse to the ventricular walls and apex of the heart?
What are the structures that carry the electrical impulse to the ventricular walls and apex of the heart?
What is the sequence of events during the cardiac cycle?
What is the sequence of events during the cardiac cycle?
What is the significance of the first heart sound (lub) during the cardiac cycle?
What is the significance of the first heart sound (lub) during the cardiac cycle?
Which area is used for auscultation (listening) to the mitral valve?
Which area is used for auscultation (listening) to the mitral valve?
What is the effect of the parasympathetic nervous system on the heart?
What is the effect of the parasympathetic nervous system on the heart?
Which component of the autonomic nervous system increases heart rate and blood pumping force?
Which component of the autonomic nervous system increases heart rate and blood pumping force?
Which of the following vessels carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart?
Which of the following vessels carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart?
What is the pathway of blood flow through the heart and lungs?
What is the pathway of blood flow through the heart and lungs?
What is an atrial septal defect?
What is an atrial septal defect?
What is the effect of a ventricular septal defect?
What is the effect of a ventricular septal defect?
What is the systemic circulation?
What is the systemic circulation?
Which of the following vessels carries oxygenated blood away from the heart?
Which of the following vessels carries oxygenated blood away from the heart?
Study Notes
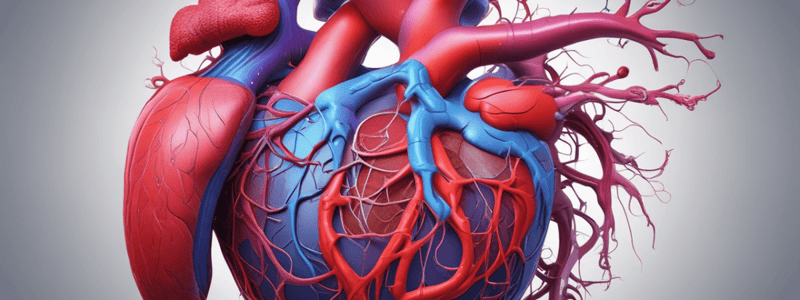
Heart Structure and Location
- The human heart is approximately the size of a fist.
- The heart is located in the thoracic cavity, between the lungs, and slightly offset to the left side of the chest.
- The heart is cone-shaped, with the apex (bottom) forming the pointed end.
- The left ventricle forms the apex of the heart.
- The apex of the heart is located near the diaphragm, a dome-shaped muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity.
Heart Surfaces and Borders
- The heart has three surfaces: the sternocostal surface, the diaphragmatic surface, and the base.
- The pulmonary surface is NOT a surface of the heart.
- The heart has four borders: the superior border, the inferior border, the left border, and the right border.
- The right coronary border is NOT a border of the heart.
Pericardium
- The heart is surrounded by a double-walled sac called the pericardium.
- The serous pericardium consists of two layers: the parietal layer and the visceral layer.
Heart Conduction System
- The pathway of blood flow from the right ventricle to the lungs and back to the left atrium is called the pulmonary circulation.
- Cardiac muscle is self-excitable, meaning it can generate its own electrical impulses.
- The sinoatrial (SA) node is the natural pacemaker of the heart, generating electrical impulses at a rate of 60-100 beats per minute.
- The atrioventricular (AV) node relays electrical impulses from the SA node to the ventricles, delaying them to allow the atria to fully contract.
- The bundle branches carry electrical impulses from the AV node to the ventricular walls and apex of the heart.
- The Purkinje fibers are structures that carry electrical impulses to the ventricular walls and apex of the heart.
Cardiac Cycle
- The sequence of events during the cardiac cycle is: diastole (relaxation), atrial contraction, ventricular contraction, and isovolumic contraction.
- The first heart sound (lub) occurs during ventricular contraction, when the atrioventricular valves close.
Heart Sounds and Auscultation
- The mitral valve is auscultated (listened to) in the fifth intercostal space, medial to the nipple.
Autonomic Nervous System and Heart Rate
- The parasympathetic nervous system decreases heart rate and blood pumping force.
- The sympathetic nervous system increases heart rate and blood pumping force.
Blood Flow and Circulation
- The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart to the lungs.
- The pathway of blood flow through the heart and lungs is: right atrium → right ventricle → pulmonary artery → lungs → pulmonary veins → left atrium → left ventricle → aorta → body.
- An atrial septal defect is a hole in the wall between the left and right atria, allowing oxygenated blood to flow back into the right atrium.
- A ventricular septal defect is a hole in the wall between the left and right ventricles, allowing oxygenated blood to flow back into the right ventricle.
- The systemic circulation is the pathway of oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the rest of the body.
- The aorta carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to the rest of the body.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Test your knowledge on the anatomy of the heart with this quiz by Paria SHOJAOLSADATI, assistant professor in human anatomy at Istanbul Okan University School of Medicine. Learn about the location, size, and shape of the heart.