Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of these muscles is an inspiration muscle?
Which of these muscles is an inspiration muscle?
- M. serratus posterior inferior
- M. latissimus dorsi
- M. serratus posterior superior (correct)
- M. transversus thoracis
Which part of the pectoralis major muscle does not originate on the ribs?
Which part of the pectoralis major muscle does not originate on the ribs?
- Pars abdominalis
- Pars sternocostalis
- Pars clavicularis (correct)
What is the primary function of the subclavius muscle?
What is the primary function of the subclavius muscle?
Elevates the first rib or pulls the clavicle downward
What is the primary function of the trapezius muscle?
What is the primary function of the trapezius muscle?
Which muscle is an expiration muscle?
Which muscle is an expiration muscle?
Which of these muscles does not originate on the vertebral column?
Which of these muscles does not originate on the vertebral column?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the superficial fascia of the thorax?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the superficial fascia of the thorax?
The intercostal muscles are located between the ribs.
The intercostal muscles are located between the ribs.
What is the primary function of the diaphragm in respiration?
What is the primary function of the diaphragm in respiration?
Which of these muscles is primarily responsible for pulling the ribs downward?
Which of these muscles is primarily responsible for pulling the ribs downward?
The serratus anterior muscle is an inspiration muscle.
The serratus anterior muscle is an inspiration muscle.
The transversus thoracis muscle is an inspiration muscle.
The transversus thoracis muscle is an inspiration muscle.
The external intercostal muscles are primarily responsible for:
The external intercostal muscles are primarily responsible for:
What type of connective tissue is fascia?
What type of connective tissue is fascia?
Which of these muscles is an additional inspiration muscle?
Which of these muscles is an additional inspiration muscle?
The Mm. intercostales interni are inspiration muscles.
The Mm. intercostales interni are inspiration muscles.
The Mm. levatores costarum contribute to inspiration.
The Mm. levatores costarum contribute to inspiration.
The Mm. subcostales are inspiration muscles.
The Mm. subcostales are inspiration muscles.
Which muscle acts as an additional expiration muscle?
Which muscle acts as an additional expiration muscle?
The fascia thoracis superficialis is located beneath the skin.
The fascia thoracis superficialis is located beneath the skin.
What is the name of the membrane that covers the walls of the thoracic cavity?
What is the name of the membrane that covers the walls of the thoracic cavity?
Which one of these muscles is an additional inspiration muscle?
Which one of these muscles is an additional inspiration muscle?
The pectoralis major muscle is an inspiration muscle.
The pectoralis major muscle is an inspiration muscle.
What is the name of the muscle that elevates the scapula?
What is the name of the muscle that elevates the scapula?
The pectoralis minor muscle is an expiration muscle.
The pectoralis minor muscle is an expiration muscle.
Which of these muscles is NOT a part of the Mm. superficialis dorsi?
Which of these muscles is NOT a part of the Mm. superficialis dorsi?
Which muscle group is responsible for pulling the ribs downward?
Which muscle group is responsible for pulling the ribs downward?
Which of these muscles is located in the subcutaneous tissue?
Which of these muscles is located in the subcutaneous tissue?
The fascia pectoralis covers the pectoralis major and serratus anterior muscles.
The fascia pectoralis covers the pectoralis major and serratus anterior muscles.
Which of these muscles helps to rotate the scapula?
Which of these muscles helps to rotate the scapula?
The Mm. intercostales externi are expiration muscles.
The Mm. intercostales externi are expiration muscles.
What is the name of the superficial fascia located in the subcutaneous tissue of the thorax?
What is the name of the superficial fascia located in the subcutaneous tissue of the thorax?
What is the main inspiration muscle?
What is the main inspiration muscle?
The fascia clavipectoralis covers the pectoralis major and subclavius muscles.
The fascia clavipectoralis covers the pectoralis major and subclavius muscles.
Which muscle is part of the 2nd layer of the superficial back muscles (Mm. superficialis dorsi)?
Which muscle is part of the 2nd layer of the superficial back muscles (Mm. superficialis dorsi)?
The fascia endothoracica is a superficial fascia.
The fascia endothoracica is a superficial fascia.
Which of these are NOT expiration muscles?
Which of these are NOT expiration muscles?
The Mm. levatores costarum help to pull the ribs downward.
The Mm. levatores costarum help to pull the ribs downward.
Which muscle is responsible for pulling both scapulae together?
Which muscle is responsible for pulling both scapulae together?
The transversus abdominis is an inspiration muscle.
The transversus abdominis is an inspiration muscle.
What is the primary function of the rhomboideus major muscle?
What is the primary function of the rhomboideus major muscle?
What are the main inspiration muscles?
What are the main inspiration muscles?
Which of these muscles is NOT a part of the Mm. profundi thoracis?
Which of these muscles is NOT a part of the Mm. profundi thoracis?
The Mm. intercostales externi are superficial muscles.
The Mm. intercostales externi are superficial muscles.
Flashcards
Pectoralis Major
Pectoralis Major
A large chest muscle that adducts, internally rotates, and flexes the arm.
Pectoralis Minor
Pectoralis Minor
A smaller chest muscle that pulls the shoulder forward and downward.
Subclavius Muscle
Subclavius Muscle
A muscle that elevates the first rib or pulls the clavicle downward.
Serratus Anterior
Serratus Anterior
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trapezius Muscle
Trapezius Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Latissimus Dorsi
Latissimus Dorsi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rhomboid Muscles (Minor & Major)
Rhomboid Muscles (Minor & Major)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Levator Scapulae
Levator Scapulae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intercostal Muscles (External)
Intercostal Muscles (External)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intercostal Muscles (Internal)
Intercostal Muscles (Internal)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subcostal Muscles
Subcostal Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Levatores Costarum
Levatores Costarum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transversus Thoracis
Transversus Thoracis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory Muscles
Respiratory Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Superficial Muscles of the Trunk
- The trunk muscles are categorized as superficial and deep.
- Thoracic muscles include superficial and deep layers, as well as the diaphragm.
- Abdominal muscles are also categorized into anterior, lateral, and posterior groups.
Muscles of the Trunk
- Mm. thoracis (thoracic muscles): These muscles include superficial and deep muscles, and the diaphragm.
- Mm. dorsi (back muscles): These muscles have superficial and deep layers.
- Mm. abdominis (abdominal muscles): These include anterior, lateral, and posterior groups.
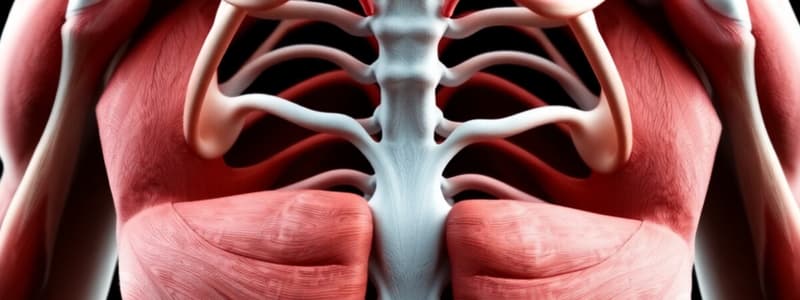
Superficial Thorax Muscles
- M. pectoralis major: This muscle has three parts (clavicular, sternocostal, and abdominal). Its origin is on the external surfaces of the ribs, insertion is on the shoulder girdle and arm bones, and its function is to pull the shoulder girdle forward and downward. It also affects the shoulder joint and is involved in inspiration.
- M. pectoralis minor: Originates from the external surfaces of ribs II-V, inserts into the coracoid process of the scapula, pulls the shoulders forward and downward, and elevates the ribs when the scapula is fixed.
- M. subclavius: Originates from the superior surface of the first rib, inserts into the inferior surface of the clavicle, and elevates the first rib or pulls the clavicle downward.
- M. serratus anterior: Originates from the external surfaces of ribs I-IX, inserts into the medial margin and inferior angle of the scapula, rotates the scapula and elevates the arm.
M. Trapezius
- Origin: External occipital protuberance, superior nuchal line, ligamentum nuchae, and spinous processes of thoracic vertebrae
- Insertion: Spina scapulae, acromion, and lateral clavicle
- Function: Extends the neck, elevates and retracts the scapula, and upper fibers elevate the shoulders. Lower fibers pull shoulders downward.
M. Latissimus Dorsi
- Origin: Crista iliaca, thoracolumbar fascia, spinous processes of T7-T12, external surfaces of ribs IX-XII
- Insertion: Crista tuberculi minoris humeri
- Function: Adducts, extends, and internally rotates the arm, and involved in expiration.
Mm. Rhomboidei
- M. rhomboideus minor: Origin: C6-C7 spinous processes; Insertion: Medial border of scapula
- M. rhomboideus major: Origin: Th1-Th4 spinous processes; Insertion: Medial border of scapula
- Function: Elevates and retracts the scapula and pulls the scapula toward the vertebral column.
M. Levator Scapulae
- Origin: Transverse processes C1-C4
- Insertion: Superior angle of scapula
- Function: Elevates the scapula.
M. Serratus Posterior Superior
- Origin: Spinous processes of C7-T3
- Insertion: External surfaces of ribs II-V
- Function: Elevates the ribs, inspiration muscle
M. Serratus Posterior Inferior
- Origin: Spinous processes of T11-L2
- Insertion: External surfaces of ribs IX-XII
- Function: Pulls the ribs downward, expiration muscle
Deep Muscles of the Thorax
- Mm. intercostales externi: Origin: Upper rib, Tuberculum costae, Insertion: Lower rib; and elevates ribs, inspiration muscle
- Mm. intercostales interni: Origin: Lower rib, Angulus costae, Insertion: Upper rib; and pulls ribs downward, expiration muscle
- Mm. subcostales: Origin: Lower rib, Angulus costae, Insertion: Upper rib; and pulls ribs downward, expiration muscle
- M. transversus thoracis: Origin: Sternum and xiphoid process; Insertion: Internal surface of ribs; and pulls ribs downward, expiration muscle
- Mm. levatores costarum: Origin: Transverse processes C7-T11, Insertion: Lower adjacent rib; and elevates ribs, inspiration muscle
Respiratory Muscles
- Inspiration: Diaphragm, external intercostals, levatores costarum, serratus anterior superior
- Expiration: Internal intercostals, transversus thoracis, subcostales, serratus posterior inferior
Fascia Thoracis
- Superficial: Thin, located in subcutaneous, surrounds mammae in women
- Pectoralis: Covers pectoralis major and serratus anterior, forms fibrous sheaths
- Clavipectoralis: Covers pectoralis minor, subclavius, forms fibrous sheaths
- Endothoracica: Covers internal surfaces of ribs, sternum, vertebrae, and diaphragm.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.