Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the common tendon of gastrocnemius and soleus known as?
What is the common tendon of gastrocnemius and soleus known as?
- Tibialis tendon
- Hamstring tendon
- Patellar tendon
- Achilles tendon (correct)
Which muscles are considered antagonists to the iliopsoas and pectineus muscles?
Which muscles are considered antagonists to the iliopsoas and pectineus muscles?
- Tibialis anterior and peroneals
- Quadriceps and adductors
- Gluteus maximus and hamstrings (correct)
- Gastrocnemius and soleus
Which muscle in the lower limb is most commonly used for intramuscular injections?
Which muscle in the lower limb is most commonly used for intramuscular injections?
- Adductor longus
- Rectus femoris
- Vastus lateralis
- Gluteus medius (correct)
Which type of muscle tissue is primarily involved in voluntary movement?
Which type of muscle tissue is primarily involved in voluntary movement?
What distinguishes cardiac muscle from the other muscle types?
What distinguishes cardiac muscle from the other muscle types?
Which of the following muscles primarily acts to flex the hip joint?
Which of the following muscles primarily acts to flex the hip joint?
Which muscle is NOT part of the hamstring group?
Which muscle is NOT part of the hamstring group?
What is the primary action of the quadriceps muscle group?
What is the primary action of the quadriceps muscle group?
Which of these muscles is located on the anterior aspect of the thigh?
Which of these muscles is located on the anterior aspect of the thigh?
Which muscles are primarily involved in the adduction of the thigh?
Which muscles are primarily involved in the adduction of the thigh?
Which muscle is involved in plantar flexion at the ankle joint?
Which muscle is involved in plantar flexion at the ankle joint?
The vastus medialis muscle is classified under which category?
The vastus medialis muscle is classified under which category?
Which muscle acts to laterally rotate the hip joint?
Which muscle acts to laterally rotate the hip joint?
Which muscle is classified as a sphincter muscle?
Which muscle is classified as a sphincter muscle?
What is the primary action of the sternocleidomastoid muscle?
What is the primary action of the sternocleidomastoid muscle?
Which of the following muscles are classified as muscles of facial expression?
Which of the following muscles are classified as muscles of facial expression?
Among the following, which muscles are primarily responsible for mastication?
Among the following, which muscles are primarily responsible for mastication?
Which of the following muscles acts on the shoulder joint?
Which of the following muscles acts on the shoulder joint?
What is the meaning of 'rectus' in the term rectus abdominis?
What is the meaning of 'rectus' in the term rectus abdominis?
How are the muscles of the upper limb categorized based on their location and function?
How are the muscles of the upper limb categorized based on their location and function?
Which statement is true regarding the erector spinae muscle?
Which statement is true regarding the erector spinae muscle?
Which structure acts as the boundary for a muscle fiber and plays a critical role in maintaining cellular integrity?
Which structure acts as the boundary for a muscle fiber and plays a critical role in maintaining cellular integrity?
What is the primary function of the endomysium in muscle tissues?
What is the primary function of the endomysium in muscle tissues?
Which of the following components is directly involved in the contraction mechanism of muscles?
Which of the following components is directly involved in the contraction mechanism of muscles?
In muscle anatomy, which band is characterized by the presence of actin filaments?
In muscle anatomy, which band is characterized by the presence of actin filaments?
Which structure serves to align the myofibrils in muscle cells and is critical in the organization of sarcomeres?
Which structure serves to align the myofibrils in muscle cells and is critical in the organization of sarcomeres?
Which muscle primarily enables the flexion of the elbow joint?
Which muscle primarily enables the flexion of the elbow joint?
Which muscle acts as an antagonist to the biceps brachii during elbow extension?
Which muscle acts as an antagonist to the biceps brachii during elbow extension?
Which muscle is responsible for pronation of the forearm?
Which muscle is responsible for pronation of the forearm?
Which muscle assists in wrist flexion and is located near the palm?
Which muscle assists in wrist flexion and is located near the palm?
Which of the following muscles would counteract the action of the flexor carpi radialis?
Which of the following muscles would counteract the action of the flexor carpi radialis?
Which muscles in the list are antagonists to each other in terms of actions at the elbow joint?
Which muscles in the list are antagonists to each other in terms of actions at the elbow joint?
What is the primary shape classification of the biceps brachii?
What is the primary shape classification of the biceps brachii?
Which of the following actions does the teres major muscle perform?
Which of the following actions does the teres major muscle perform?
Flashcards
Achilles Tendon
Achilles Tendon
The common tendon of the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles.
Antagonists of Iliopsoas and Pectineus
Antagonists of Iliopsoas and Pectineus
Muscles that oppose the actions of the iliopsoas and pectineus muscles.
Intramuscular Injection Site
Intramuscular Injection Site
A specific muscle in the lower limb commonly used for injections.
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Smooth Muscle
Smooth Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biceps brachii
Biceps brachii
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brachialis
Brachialis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Triceps
Triceps
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deltoid
Deltoid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Teres major
Teres major
Signup and view all the flashcards
Teres minor
Teres minor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brachioradialis
Brachioradialis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pronator teres
Pronator teres
Signup and view all the flashcards
Palmaris longus
Palmaris longus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flexor carpi ulnaris
Flexor carpi ulnaris
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extensor carpi ulnaris
Extensor carpi ulnaris
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extensor digitorum
Extensor digitorum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extensor carpi radialis longus
Extensor carpi radialis longus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flexor carpi radialis
Flexor carpi radialis
Signup and view all the flashcards
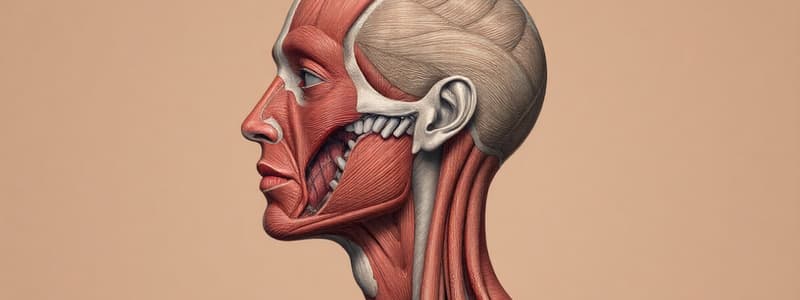
Superficial Muscles of Head and Neck
Superficial Muscles of Head and Neck
Signup and view all the flashcards
Frontalis
Frontalis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Temporalis
Temporalis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Masseter
Masseter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Orbicularis oculi
Orbicularis oculi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Orbicularis oris
Orbicularis oris
Signup and view all the flashcards
Occipitalis
Occipitalis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Buccinator
Buccinator
Signup and view all the flashcards
Platysma
Platysma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sternocleidomastoid
Sternocleidomastoid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal intercostal
Internal intercostal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diaphragm
Diaphragm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Serratus anterior
Serratus anterior
Signup and view all the flashcards
Latissimus dorsi
Latissimus dorsi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trapezius
Trapezius
Signup and view all the flashcards
Erector spinae
Erector spinae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rhomboid major
Rhomboid major
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rectus abdominis
Rectus abdominis
Signup and view all the flashcards
External oblique
External oblique
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal oblique
Internal oblique
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pectoralis major
Pectoralis major
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pectoralis minor
Pectoralis minor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscles of Facial Expression
Muscles of Facial Expression
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscles of Mastication
Muscles of Mastication
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscles of Upper Limb
Muscles of Upper Limb
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscle Actions
Muscle Actions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rectus
Rectus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epimysium
Epimysium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endomysium
Endomysium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Perimysium
Perimysium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sarcolemma
Sarcolemma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myofibrils
Myofibrils
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mitochondria
Mitochondria
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sarcomere
Sarcomere
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dark band
Dark band
Signup and view all the flashcards
Light band
Light band
Signup and view all the flashcards
H-zone
H-zone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Z disc
Z disc
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nucleus
Nucleus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pectineus muscle
Pectineus muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Iliopsoas muscle
Iliopsoas muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sartorius muscle
Sartorius muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rectus femoris muscle
Rectus femoris muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vastus medialis muscle
Vastus medialis muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vastus lateralis muscle
Vastus lateralis muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gracilis muscle
Gracilis muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Semitendinosus muscle
Semitendinosus muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Semimembranosus muscle
Semimembranosus muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biceps femoris muscle
Biceps femoris muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gluteus maximus muscle
Gluteus maximus muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gluteus medius muscle
Gluteus medius muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adductor longus muscle
Adductor longus muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tensor fascia lata muscle
Tensor fascia lata muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gastrocnemius muscle
Gastrocnemius muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Soleus muscle
Soleus muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibularis longus muscle
Fibularis longus muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibularis brevis muscle
Fibularis brevis muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tibialis anterior muscle
Tibialis anterior muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tibialis posterior muscle
Tibialis posterior muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hamstring muscles
Hamstring muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Quadriceps femoris muscle
Quadriceps femoris muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Objectives
- Name and identify superficial muscles of the head and neck region
- Differentiate between muscles of facial expression and mastication
- Name and identify muscles of the trunk and understand their actions
- Name, identify and classify muscles of the upper and lower limbs
- Explain the actions of muscles of upper and lower limbs
- Distinguish between different types of muscles based on their histological features
Station 1: Superficial Muscles of Face, Neck and Trunk
- Muscles of the head and neck: Frontalis, Temporalis, Masseter, Orbicularis oculi, Orbicularis oris, Occipitalis, Buccinator, Platysma, Sternocleidomastoid
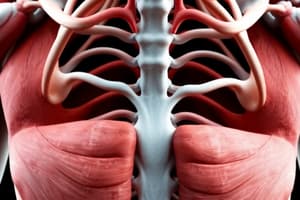
- Muscles of the trunk: Internal intercostal, Diaphragm, Serratus anterior, Latissimus dorsi, Trapezius, Erector spinae, Rhomboid major, Rectus abdominis, Transversus abdominis, External oblique, Internal oblique, Pectoralis major, Pectoralis minor.
Questions
- Which muscles are sphincters?
- What are the attachments of the sternocleidomastoid muscle?
- Which muscles are for facial expression and why?
- Which muscles are for mastication?
- Which muscles act on the shoulder joint and are known as muscles of the upper limb?
Station 2: Muscles of the Upper Limb
-
Muscles: Biceps brachii, Brachialis, Triceps, Deltoid, Teres major, Teres minor, Brachioradialis, Pronator teres, Palmaris longus, Flexor carpi ulnaris, Extensor carpi ulnaris, Extensor digitorum, Extensor carpi radialis longus, Flexor carpi radialis.
-
Classify muscles by shape, location, and action.
-
What are the attachments of brachioradialis?
-
What is the action of biceps brachii? What is the antagonist to biceps brachii?
-
Which other muscles are antagonists to each other?
Station 3: Muscles of the Lower Limb
-
Muscles: Pectineus, Iliopsoas, Sartorius, Rectus femoris, Vastus medialis, Vastus lateralis, Gracilis, Semitendinosus, Fibularis longus, Fibularis brevis, Semimembranosus, Biceps femoris, Gluteus maximus, Gluteus medius, Adductor longus, Tensor fascia lata, Gastrocnemius, Soleus, Tibialis anterior, Tibialis posterior.
-
Classify muscles by shape, size, location, and action.
-
Which muscles are known as hamstring muscles? What are their actions on the knee joint?
-
Which muscle is known as the quadriceps muscle? What is its action on the knee joint? What is its relationship to the patella?
-
Which muscles are on the anterior aspect of the thigh? What is their action on the knee joint?
-
Which muscles are on the medial aspect of the thigh? What is their action?
-
What is the common tendon of gastrocnemius and soleus?
-
Which muscles are antagonists to iliopsoas and pectineus muscles?
-
Which muscle is commonly used for intramuscular injections in the lower limb?
Station 4: Histology of Muscle Fiber
- Muscles are multicellular contractile units (skeletal, smooth, cardiac).
- Muscle fibers have similarities and differences in structure and function.
- Identify the following histological features: Epimysium, Endomysium, Perimysium, Myofibrils, Sarcolemma, Nucleus, Dark band, Light band, H-zone, Z disc, Mitochondria, Sarcomere.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.