Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the term used to describe a vertical section through the soil that shows the different layers?
What is the term used to describe a vertical section through the soil that shows the different layers?
- Soil Horizon
- Soil Layer
- Soil Profile (correct)
- Soil Structure
Which horizon is considered the most fertile part of the soil, rich in minerals and humus?
Which horizon is considered the most fertile part of the soil, rich in minerals and humus?
- A – Horizon (correct)
- C – Horizon
- B – Horizon
- D – Horizon
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of the B – Horizon?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of the B – Horizon?
- Contains slightly bigger rock particles
- Rich in humus (correct)
- Harder and more compact
- Lighter in colour
What primarily composes the C – Horizon?
What primarily composes the C – Horizon?
How do plants obtain nutrients from the soil?
How do plants obtain nutrients from the soil?
Which layer of soil contains a high number of living organisms, like insects and worms?
Which layer of soil contains a high number of living organisms, like insects and worms?
What is the primary factor in the formation of soil that also affects the soil profile?
What is the primary factor in the formation of soil that also affects the soil profile?
Which statement correctly describes the characteristics of the sub-soil?
Which statement correctly describes the characteristics of the sub-soil?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
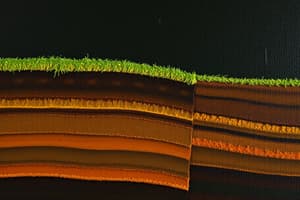
Soil Profile Overview
- A vertical section through the soil displaying various layers is known as a soil profile.
- The soil profile comprises three distinct layers, each referred to as a horizon: A, B, and C.
A - Horizon (Top Soil)
- The A horizon, also called top soil, is the uppermost layer of soil.
- This layer is dark in color, rich in minerals and humus, making it highly fertile.
- Roots of plants primarily grow in the A horizon.
- It supports a diverse ecosystem, including insects (ants, beetles), worms (earthworms), small mammals (rodents, moles), bacteria, and fungi.
- Rich in decayed organic matter from dead plants and animals, enhancing soil fertility.
- The top soil is characterized as soft, porous, and capable of retaining significant amounts of water.
- Provides essential nutrients and minerals for plant growth.
B - Horizon (Sub-Soil)
- Positioned beneath the A horizon, the B horizon is known as sub-soil.
- Composed of slightly larger rock particles compared to the A horizon.
- Typically lighter in color, harder, and more compact than top soil.
- Contains fewer living organisms than the A horizon.
- Some tree roots can extend into the sub-soil, although it has limited humus content.
- Less fertile compared to the A horizon, resulting in lower agricultural productivity.
C - Horizon (Sub-Stratum)
- Located below the B horizon, the C horizon is also called sub-stratum.
- Composed of small fragments of broken rocks, which are a result of the partial weathering of bedrock (parent rock).
- This layer continues to undergo the weathering process, progressively breaking down into smaller particles.
- Below the C horizon lies unweathered soil rock known as bedrock, which is the source of soil formation over extended periods.
- Various climatic factors such as wind, temperature, rainfall, light, and humidity significantly influence the soil profile and contribute to changes in soil structure.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.