Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the O-horizon?
What is the O-horizon?
Soil layers with a high percentage of organic matter.
What is the A-horizon?
What is the A-horizon?
Topmost mineral horizon; often referred to as topsoil.
What does the B-horizon contain?
What does the B-horizon contain?
Deposits of leached material.
What is the C-horizon composed of?
What is the C-horizon composed of?
What is the D-horizon?
What is the D-horizon?
What is humus?
What is humus?
What is topsoil?
What is topsoil?
What is subsoil?
What is subsoil?
What are weathered rock fragments?
What are weathered rock fragments?
What is bedrock?
What is bedrock?
Flashcards
O-horizon
O-horizon
Soil layer rich in organic matter.
A-horizon
A-horizon
Topsoil, the uppermost mineral soil layer.
B-horizon
B-horizon
Soil layer with leached material.
C-horizon
C-horizon
Signup and view all the flashcards
D-horizon
D-horizon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Humus
Humus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Topsoil
Topsoil
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subsoil
Subsoil
Signup and view all the flashcards
Weathered rock fragments
Weathered rock fragments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bedrock
Bedrock
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
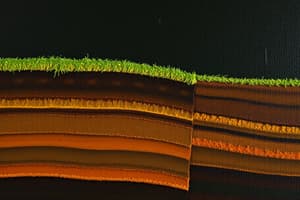
Soil Profile Components
- O-horizon: Rich in organic matter, typically includes layers of leaves, pine needles, twigs, and decomposed humus.
- A-horizon (Topsoil): The uppermost mineral layer, known for its darker color due to high levels of humified organic matter.
- B-horizon: Characterized by leached material accumulation, including soluble materials and minerals like clay, iron, or aluminum.
- C-horizon: Composed of weathered rock that has minimal influence from soil-forming processes.
- D-horizon (Bedrock): The deepest layer, consisting of unweathered mineral matter or different mineral complexes that form the foundation of soil layers.
Soil Features
- Humus: Organic component created from the decomposition of plant material, essential for soil health and fertility.
- Topsoil: The uppermost layer, typically 2-8 inches deep, crucial for plant growth due to its highest organic matter content.
- Subsoil: Located beneath the topsoil, a mix of fine particles lacking organic matter and humus, important for water and nutrient retention.
- Weathered rock fragments: The lowest zone in soil profiles, primarily made up of loose rock materials that may serve as a substrate for soil development.
- Bedrock: Solid, intact rock located below regolith; serves as the foundational layer from which soil layers develop.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.