Podcast
Questions and Answers
A patient who had a closed abdominal wound reports a sudden "pop" after coughing. Upon examination, the nurse observes open sutures and the presence of small bowel at the bottom of the wound. What are the priority nursing interventions? (Select all that apply)
A patient who had a closed abdominal wound reports a sudden "pop" after coughing. Upon examination, the nurse observes open sutures and the presence of small bowel at the bottom of the wound. What are the priority nursing interventions? (Select all that apply)
- Allow the area to be exposed to air until all drainage has stopped
- Cover the area with sterile gauze and apply an abdominal binder
- Place several cold packs over the area, protecting the skin around the wound
- Cover the area with sterile, saline-soaked gauzes immediately (correct)
- Notify the health care provider (correct)
Which nursing assessment finding indicates that the patient is at greatest risk for pressure ulcer formation?
Which nursing assessment finding indicates that the patient is at greatest risk for pressure ulcer formation?
- The patient is bed bound
- The patient refuses to be turned
- The patient has fecal incontinence (correct)
- The patient's capillary refill is >2 seconds
A nurse admits a patient from a nursing home and observes a shallow open reddish-pink ulcer without slough on the right heel. How should the nurse stage this pressure ulcer?
A nurse admits a patient from a nursing home and observes a shallow open reddish-pink ulcer without slough on the right heel. How should the nurse stage this pressure ulcer?
- Stage 1
- Stage 4
- Stage 2 (correct)
- Stage 3
A nurse is attending to a patient who is experiencing a full-thickness wound repair. Which type of tissue should the nurse expect to observe when the wound is healing?
A nurse is attending to a patient who is experiencing a full-thickness wound repair. Which type of tissue should the nurse expect to observe when the wound is healing?
A nurse is preparing to insert a nasogastric tube in a semiconscious patient. To determine the length of the tube needed for insertion, how should the nurse measure the tube?
A nurse is preparing to insert a nasogastric tube in a semiconscious patient. To determine the length of the tube needed for insertion, how should the nurse measure the tube?
A nurse is providing nutrition education to a patient from India using the five food groups. What should be the focus of the teaching?
A nurse is providing nutrition education to a patient from India using the five food groups. What should be the focus of the teaching?
An older adult is admitted to the hospital for multiple health problems and has no teeth, making eating difficult. Which diet should the nurse encourage the primary health-care provider to order?
An older adult is admitted to the hospital for multiple health problems and has no teeth, making eating difficult. Which diet should the nurse encourage the primary health-care provider to order?
A nurse caring for a patient receiving bolus enteral feedings several times daily. Which nursing intervention is most important to include in the plan of care to help prevent diarrhea?
A nurse caring for a patient receiving bolus enteral feedings several times daily. Which nursing intervention is most important to include in the plan of care to help prevent diarrhea?
A nurse teaches a patient about atelectasis. Which statement by the patient indicates an understanding of atelectasis?
A nurse teaches a patient about atelectasis. Which statement by the patient indicates an understanding of atelectasis?
A nurse is caring for a patient with respiratory problems. Which assessment finding indicates a late sign of hypoxia?
A nurse is caring for a patient with respiratory problems. Which assessment finding indicates a late sign of hypoxia?
A nurse is caring for a patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who is receiving 2 L/min of oxygen. Which oxygen delivery device is most appropriate for the nurse to administer the oxygen?
A nurse is caring for a patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who is receiving 2 L/min of oxygen. Which oxygen delivery device is most appropriate for the nurse to administer the oxygen?
Which assessment findings indicate that the patient is experiencing an acute disturbance in oxygenation and requires immediate intervention? (Select all that apply)
Which assessment findings indicate that the patient is experiencing an acute disturbance in oxygenation and requires immediate intervention? (Select all that apply)
The nurse calls the primary health care provider (PHCP) regarding a new medication prescription, because the dosage prescribed is higher than the recommended dosage. The nurse is unable to locate the PHCP, and the medication is due to be administered. Which action should the nurse take?
The nurse calls the primary health care provider (PHCP) regarding a new medication prescription, because the dosage prescribed is higher than the recommended dosage. The nurse is unable to locate the PHCP, and the medication is due to be administered. Which action should the nurse take?
The nurse has made an error in a narrative documentation of a physical assessment finding on a client and obtains the client's record to correct the error. What is the correct way to correct the error?
The nurse has made an error in a narrative documentation of a physical assessment finding on a client and obtains the client's record to correct the error. What is the correct way to correct the error?
A nurse is caring for a patient who smokes and drinks caffeine. Which point is important for the nurse to understand before assessing the patient's blood pressure (BP)?
A nurse is caring for a patient who smokes and drinks caffeine. Which point is important for the nurse to understand before assessing the patient's blood pressure (BP)?
Which of the following would most likely lead to an inaccurate, low blood pressure reading?
Which of the following would most likely lead to an inaccurate, low blood pressure reading?
During a routine follow up, a patient asks about what risk factors he can address to manage his hypertension. Which of the following are modifiable risk factors? (Select all that apply)
During a routine follow up, a patient asks about what risk factors he can address to manage his hypertension. Which of the following are modifiable risk factors? (Select all that apply)
A patient has dehydration. While planning care, the nurse considers that the majority of the patient's total water volume exists in which compartment?
A patient has dehydration. While planning care, the nurse considers that the majority of the patient's total water volume exists in which compartment?
After reviewing the laboratory results, which cation would the nurse identify as the most abundant in the blood?
After reviewing the laboratory results, which cation would the nurse identify as the most abundant in the blood?
The nurse receives the patient's most recent blood work results. Which laboratory value is of greatest concern?
The nurse receives the patient's most recent blood work results. Which laboratory value is of greatest concern?
Which type of exudate indicates healthy/normal healing tissues in a wound assessment?
Which type of exudate indicates healthy/normal healing tissues in a wound assessment?
What color is associated with purulent exudate, suggesting infection?
What color is associated with purulent exudate, suggesting infection?
When should eschar be removed from a wound?
When should eschar be removed from a wound?
What is the defining characteristic of a wound healing by primary intention?
What is the defining characteristic of a wound healing by primary intention?
Which stage of wound healing involves filling the wound with granulation tissue?
Which stage of wound healing involves filling the wound with granulation tissue?
What is the first stage of wound healing?
What is the first stage of wound healing?
What does 'dehiscence' refer to in the context of wound complications?
What does 'dehiscence' refer to in the context of wound complications?
The nurse assesses a patient's sacrum and observes non-blanchable redness. The skin is intact. Which pressure ulcer stage correlates to these findings?
The nurse assesses a patient's sacrum and observes non-blanchable redness. The skin is intact. Which pressure ulcer stage correlates to these findings?
When a pressure ulcer is obscured by slough or eschar, which of the following is true?
When a pressure ulcer is obscured by slough or eschar, which of the following is true?
What is a key component in the patient care plan with lateral wounds?
What is a key component in the patient care plan with lateral wounds?
During wound cleaning, which of the following is important to remember?
During wound cleaning, which of the following is important to remember?
When is it appropriate to schedule wound care/dressing changes?
When is it appropriate to schedule wound care/dressing changes?
What is important to consider when packing a wound?
What is important to consider when packing a wound?
Religious Restrictions of Islam include which of the following?
Religious Restrictions of Islam include which of the following?
Which of the following is characteristic of dysphasia?
Which of the following is characteristic of dysphasia?
If a patient has signs of distress during NG placement, what should you do?
If a patient has signs of distress during NG placement, what should you do?
According to the information provided when should Gastric Residual Volume be checked when a patient has an NG tube?
According to the information provided when should Gastric Residual Volume be checked when a patient has an NG tube?
Which of the following negatively impacts oxygenation?
Which of the following negatively impacts oxygenation?
According to the information, what is an early sign of Hypoxia?
According to the information, what is an early sign of Hypoxia?
How much flow needs a humidifier?
How much flow needs a humidifier?
What are the two components to Emphysema?
What are the two components to Emphysema?
According to the information, nurses should be aware of what, regarding electronic BP measurements?
According to the information, nurses should be aware of what, regarding electronic BP measurements?
Which phase is most important to control, for patients with HTN according to the information?
Which phase is most important to control, for patients with HTN according to the information?
When assessing a patient's skin, which finding is most indicative of a potential decrease in skin integrity?
When assessing a patient's skin, which finding is most indicative of a potential decrease in skin integrity?
During a wound assessment, a nurse observes a wound with white-yellow stringy tissue. How should the nurse document this finding?
During a wound assessment, a nurse observes a wound with white-yellow stringy tissue. How should the nurse document this finding?
A patient has a wound described as a surgical incision that is closed with staples. This wound is healing by which intention?
A patient has a wound described as a surgical incision that is closed with staples. This wound is healing by which intention?
A nurse is caring for a patient with a wound that requires packing. What is the primary purpose of wound packing?
A nurse is caring for a patient with a wound that requires packing. What is the primary purpose of wound packing?
A nurse is scheduling dressing changes for a patient with a chronic wound. When is the most appropriate time?
A nurse is scheduling dressing changes for a patient with a chronic wound. When is the most appropriate time?
The nurse is reviewing the Braden Scale assessment for a patient at risk for pressure injuries. Which factor is evaluated by the Braden Scale?
The nurse is reviewing the Braden Scale assessment for a patient at risk for pressure injuries. Which factor is evaluated by the Braden Scale?
When providing wound care, a nurse cleans a wound with a drain. Which technique is most appropriate?
When providing wound care, a nurse cleans a wound with a drain. Which technique is most appropriate?
A patient with a deep open wound is being treated with vacuum-assisted closure. What is the primary benefit of this therapy?
A patient with a deep open wound is being treated with vacuum-assisted closure. What is the primary benefit of this therapy?
A nurse is caring for a patient with a pressure ulcer. Which intervention is most important for the nurse to implement regarding patient positioning?
A nurse is caring for a patient with a pressure ulcer. Which intervention is most important for the nurse to implement regarding patient positioning?
A nurse is providing dietary instructions to a client who follows Islamic dietary restrictions. Which food selection is inappropriate?
A nurse is providing dietary instructions to a client who follows Islamic dietary restrictions. Which food selection is inappropriate?
During the insertion of a nasogastric (NG) tube, the patient begins to cough and shows signs of respiratory distress. Which action should the nurse take first?
During the insertion of a nasogastric (NG) tube, the patient begins to cough and shows signs of respiratory distress. Which action should the nurse take first?
A nurse is caring for a patient receiving enteral feedings via NG tube. What is the recommended range of air to inject into the NG tube to check for gastric residual volume?
A nurse is caring for a patient receiving enteral feedings via NG tube. What is the recommended range of air to inject into the NG tube to check for gastric residual volume?
During NG tube insertion, the nurse instructs the patient to flex their head toward the chest. What is the purpose of this action?
During NG tube insertion, the nurse instructs the patient to flex their head toward the chest. What is the purpose of this action?
A patient with dysphagia is at high risk for aspiration. Which nursing intervention is most important to implement during mealtime?
A patient with dysphagia is at high risk for aspiration. Which nursing intervention is most important to implement during mealtime?
A patient is prescribed a pureed diet due to dysphagia. Which food choice would be appropriate?
A patient is prescribed a pureed diet due to dysphagia. Which food choice would be appropriate?
During a nutritional assessment, which component focuses on factors like social history and socioeconomic status?
During a nutritional assessment, which component focuses on factors like social history and socioeconomic status?
What is the maximum oxygen flow rate, via nasal cannula, at which to administer oxygen to a COPD patient?
What is the maximum oxygen flow rate, via nasal cannula, at which to administer oxygen to a COPD patient?
A patient with a respiratory disorder exhibits an early sign of hypoxia. Which assessment finding should the nurse recognize?
A patient with a respiratory disorder exhibits an early sign of hypoxia. Which assessment finding should the nurse recognize?
A patient is receiving oxygen therapy at 5 L/min. Which intervention is essential for the nurse to implement?
A patient is receiving oxygen therapy at 5 L/min. Which intervention is essential for the nurse to implement?
What is atelectasis primarily caused by?
What is atelectasis primarily caused by?
During assessment of a patient with emphysema, what finding would the nurse expect to encounter?
During assessment of a patient with emphysema, what finding would the nurse expect to encounter?
A patient has a new prescription for oxygen via a simple face mask. What is the minimum flow rate required for this device?
A patient has a new prescription for oxygen via a simple face mask. What is the minimum flow rate required for this device?
The nurse is assessing an older adult. Which finding signals a need for immediate oxygenation?
The nurse is assessing an older adult. Which finding signals a need for immediate oxygenation?
A nurse accidentally administers the wrong dose of medication to a patient. According to ethical principles, which action should the nurse take first?
A nurse accidentally administers the wrong dose of medication to a patient. According to ethical principles, which action should the nurse take first?
A nurse is preparing to delegate tasks to unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP). Which task is within the scope of practice for a UAP?
A nurse is preparing to delegate tasks to unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP). Which task is within the scope of practice for a UAP?
A nursing student is working under the supervision of a registered nurse. Which action violates the scope of practice for a nursing student?
A nursing student is working under the supervision of a registered nurse. Which action violates the scope of practice for a nursing student?
A nurse is asked to perform a procedure that she is unfamiliar with and believes could potentially harm the patient. What protection does the nurse have in this situation?
A nurse is asked to perform a procedure that she is unfamiliar with and believes could potentially harm the patient. What protection does the nurse have in this situation?
During BP measurement, how would wrapping the cuff too loose impact blood pressure result?
During BP measurement, how would wrapping the cuff too loose impact blood pressure result?
The clinic nurse prepares to assess the blood pressure of a client diagnosed with hypertension. The nurse should ensure that the client has avoided which of the following before the assessment?
The clinic nurse prepares to assess the blood pressure of a client diagnosed with hypertension. The nurse should ensure that the client has avoided which of the following before the assessment?
A nurse is teaching a patient about hypertension. The nurse recognizes that further teaching is needed when the patient says which of the following?
A nurse is teaching a patient about hypertension. The nurse recognizes that further teaching is needed when the patient says which of the following?
A patient is diagnosed with hypertension. The physician instructs the patient that it is important to control which phase?
A patient is diagnosed with hypertension. The physician instructs the patient that it is important to control which phase?
A nurse is reviewing arterial blood gas results for a patient with a respiratory disorder. Which pH value indicates acidosis.
A nurse is reviewing arterial blood gas results for a patient with a respiratory disorder. Which pH value indicates acidosis.
The nurse cares for clients on a medical unit. Which client does the nurse assess first?
The nurse cares for clients on a medical unit. Which client does the nurse assess first?
A patient is being treated for hypernatremia. Which intervention is most appropriate for the nurse to initiate?
A patient is being treated for hypernatremia. Which intervention is most appropriate for the nurse to initiate?
The doctor prescribes an increase of dietary potassium for a client. Which food should the nurse teach the client to include in the diet?
The doctor prescribes an increase of dietary potassium for a client. Which food should the nurse teach the client to include in the diet?
A patient receiving treatment for hypokalemia reports muscle weakness and constipation. Which action should the nurse take first?
A patient receiving treatment for hypokalemia reports muscle weakness and constipation. Which action should the nurse take first?
The nurse is reviewing a patient's lab results and notes that the patient's calcium level is 11.5 mg/dL. Which signs and symptoms should the nurse expect the patient to exhibit?
The nurse is reviewing a patient's lab results and notes that the patient's calcium level is 11.5 mg/dL. Which signs and symptoms should the nurse expect the patient to exhibit?
What electrolyte imbalance to monitor for a patient that has renal failure?
What electrolyte imbalance to monitor for a patient that has renal failure?
The nurse is caring for a hospitalized client. Select the assessment finding that requires the most rapid intervention.
The nurse is caring for a hospitalized client. Select the assessment finding that requires the most rapid intervention.
After abdominal surgery, a patient reports a sensation of something 'popping' when coughing. Upon examination, the nurse observes an open wound with visible bowel. Which immediate actions should the nurse take?
After abdominal surgery, a patient reports a sensation of something 'popping' when coughing. Upon examination, the nurse observes an open wound with visible bowel. Which immediate actions should the nurse take?
A nurse is assessing patients for pressure ulcer risk. Which patient is at greatest risk for pressure ulcer formation?
A nurse is assessing patients for pressure ulcer risk. Which patient is at greatest risk for pressure ulcer formation?
The nurse is caring for a patient with a wound healing by secondary intention. What characteristic should the nurse expect to observe?
The nurse is caring for a patient with a wound healing by secondary intention. What characteristic should the nurse expect to observe?
A registered nurse (RN) is delegating tasks to an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP). Which task is appropriate?
A registered nurse (RN) is delegating tasks to an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP). Which task is appropriate?
A nurse is preparing to measure a patient's blood pressure. Which factor could cause a falsely high reading?
A nurse is preparing to measure a patient's blood pressure. Which factor could cause a falsely high reading?
Flashcards
Skin Assessment Frequency?
Skin Assessment Frequency?
Minimum frequency is 1/day; q4h for high risk patients.
Granulation Tissue?
Granulation Tissue?
Healthy/normal healing tissues.
Slough?
Slough?
White-yellow, stringy or pudding like; must be removed.
Eschar?
Eschar?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary Intention?
Primary Intention?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secondary Intention?
Secondary Intention?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tertiary Intention?
Tertiary Intention?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hemostasis?
Hemostasis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inflammatory (wound healing)
Inflammatory (wound healing)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proliferative (wound healing)
Proliferative (wound healing)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Maturation (wound healing)
Maturation (wound healing)
Signup and view all the flashcards
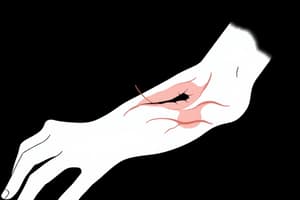
Dehiscence?
Dehiscence?
Signup and view all the flashcards
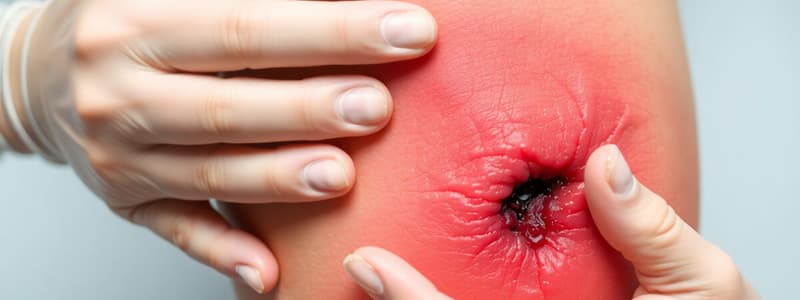
Evisceration
Evisceration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Suspected Deep Tissue Injury?
Suspected Deep Tissue Injury?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Position for wound healing?
Position for wound healing?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wound Packing Assessment?
Wound Packing Assessment?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Unstageable Pressure Injury
Unstageable Pressure Injury
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nutritional Assessment Includes?
Nutritional Assessment Includes?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clear Liquid Diet
Clear Liquid Diet
Signup and view all the flashcards
Full Liquid Diet
Full Liquid Diet
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pureed/Thickened Liquids Diet
Pureed/Thickened Liquids Diet
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mechanical Soft Diet
Mechanical Soft Diet
Signup and view all the flashcards
High risk factors for aspiration?
High risk factors for aspiration?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How To Prevent/Decrease Risk of Aspiration?
How To Prevent/Decrease Risk of Aspiration?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dysphagia
Dysphagia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Warning Signs of Dysphagia?
Warning Signs of Dysphagia?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How to measure the length of the NG tube
How to measure the length of the NG tube
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gastric Residual Volume indicates?
Gastric Residual Volume indicates?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lifestyle Factors Affecting Oxygenation?
Lifestyle Factors Affecting Oxygenation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiac Chest Pain described
Cardiac Chest Pain described
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pleuritic Chest Pain?
Pleuritic Chest Pain?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypoxia level of consciousness
Hypoxia level of consciousness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary Secretions
Pulmonary Secretions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flow rate
Flow rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
COPD - Emphysema
COPD - Emphysema
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic Bronchitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Autonomy
Autonomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Beneficence
Beneficence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Advocacy
Advocacy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Fluid Volume Control
Renal Fluid Volume Control
Signup and view all the flashcards
BP Measurements
BP Measurements
Signup and view all the flashcards
Causes
Causes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clinical Manifestation
Clinical Manifestation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Treatment
Treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Potassium
Potassium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Broccoli
Broccoli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dosage
Dosage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Skin and Wound Assessment
- Skin requires assessment at least once per day, but every 4 hours for high-risk patients.
- Assess bony prominences, skin under devices, and for blanching.
- Moisture is the number one cause of decreased skin integrity.
- Darker skin may not show blanching, but inflammation may appear purplish or blue. Use good lighting for assessment.
- Assess location, depth, tissue involvement (staging), dimensions, exudate, periwound, and drains.
Appearance
- Granulation indicates healthy, normal healing tissues.
- Slough appears white-yellow and stringy.
- Eschar is a scab of necrotic tissue.
- Slough and Eschar must be removed, except on the foot if it is covering thin skin.
Wound Classification - Primary Intention
- Wound edges which are closed with sutures or staples
- Surgical incision
- Heals quickly with minimal scarring
Wound Classification - Secondary Intention
- Wound edges not approximated
- Tissue loss or contamination is present
- Granulation is present
Wound Classification - Tertiary Intention
- Wound is left open for days, then approximated
- Wound is infected
- Closure is delayed until infection risk has resolved
Stages of Wound Healing
- Hemostasis involves control of blood loss via clotting.
- Inflammation occurs within 24 hours, activating inflammatory response (mast cells, WBCs).
- Proliferation lasts 3-24 days, involving angiogenesis, granulation filling, resurfacing, and epithelization.
- Maturation can take over a year.
Complications
- Hemorrhage: Internal, check where blood pools. External, easier to detect.
- Dehiscence: when a wound pulls apart.
- Evisceration: the protrusion of organs. Cover with sterile, wet gauze and notify surgery immediately.
Pressure Ulcers
- These are staged to indicate the amount of damage
Stage 1 Pressure Ulcer
- Non-blanchable redness.
- Skin is intact
- There will be warmth, edema, pain.
Stage 2 Pressure Ulcer
- Partial-Thickness skin loss
- Loss of Dermal Layer
- Shallow, open ulcer that is pink and reddish.
Stage 3 Pressure Ulcer
- Full-Thickness Skin Loss is visible
- Lose SQ Fat
- Bone, tendon, and muscle is NOT visible, if it is visible then it is a stage 4.
- Slough may be present.
Stage 4 Pressure Ulcer
- Full-Thickness Tissue Loss
- Exposure of Bone, Tendon, Muscle, and SQ Fat.
- Possible undermining and tunneling.
- Depth varies.
- Risk for Osteomyelitis/Osteitis.
Factors Affecting Wound Healing
- Factors include nutrition, tissue perfusion, presence of infection, age, and psychosocial aspects.
- Adequate protein and caloric intake promotes healing.
- Infection impairs wound healing.
- Delayed inflammatory response and comorbidities can affect healing.
- Psychosocial aspects like body image and scarring play a role.
Patient Care - Wound Healing
- Obtain wound cultures and change dressings.
- Elevate bed to 30 degrees. Turn patient every 1.5-2 hours in the lateral position.
- Limit upright or sitting position, promote weight shifting every 15 minutes.
- Assess skin after positioning.
- Therapeutic beds and wound management through irrigation and debridement aid healing.
- Protect abdominal wounds during coughing using binders, keeping a splint within reach.
Wound Management
- Schedule wound care/dressing change around pain medication administration.
- Give analgesic at least 30 minutes prior to procedure.
- Dressing types include moist (gauze + saline for dry wounds) and dry (for wet wounds), self-adhesive, and packing.
- Cleaning should use clean gloves are used to remove the old dressing, along with a sterile gloves/technique.
- To clean, use noncytotoxic, sterile solution only and never reuse gauze.
- Irrigate from LEAST → MOST contaminated area and clean around drains in circular rotations.
- Sterile technique Irrigation uses a 35 ml syringe with a 19 gauge soft angiocath tip
Wound Packing
- Assess the wound (length, width, depth, and shape).
- Overpacking can cause pressure.
- The procedure can also be vacuum-assisted.
Nutritional Assessment
- Gathering detailed diet and health history.
- Knowledge of nutrition and social history.
- Must consider sociocultural and socioeconomic factors, and include a food diary (3-7 Day Hx)
- Includes Screening to asses for Malnutrition Risk Factors
- Monitor Signs of Nutritional Status including Dysphagia
Religious Restrictions
- Islam – No pork, alcohol, caffeine, Ramadan fasting.
- Christianity – Baptists (minimal/no alcohol), Catholics (Lent and meatless days).
- Hinduism – No meats, alcohol.
- Judaism – No pork, no mixing dairy/milk products with meat.
- Church of Christ of Latter-Day Saints – No alcohol, tobacco, caffeine.
Therapeutic Diets
- Clear Liquid: Clear broth, coffee/tea (no cream), Jell-O
- Full Liquid (Beneficial for Dysphagia): Smooth dairy, blended soups, custards, pudding
- Pureed/Thickened Liquids: Clear + Full liquid + scrambled eggs, pureed meats & vegetables, mashed potatoes
- Mechanical Soft: Ground or diced meats, fish, cottage cheese, rice, potatoes
- Soft/Low Residue: Low-fiber foods, pasta, casseroles, canned fruits and vegetables
- High Fiber: Raw/steamed fruits/vegetables, oatmeal, dried fruit.
- Low Sodium: 4g, 2g, 1g, or 500mg sodium levels.
- Low Cholesterol 300 mg/day
- Diabetic: Balanced intake of carbs, fats, proteins.
Nursing Care - Nutrition
- Create Odor-free and comfy Environment.
- Serve Smaller and more frequent meals
- Pay attention to medications that affect appetite.
- Promote independence and dignity by letting patients select their own foods when possible, and directing patient to decide items order
Aspiration Risk
- Includes Decreased alertness, Poor gag reflex, Difficulty managing saliva
- Can include Oral suction at bedside to consult a SLP if needed
How to Prevent/Decrease Aspiration Risk
- Provide 30 minute rest periods before meals.
- Maintain Upright seated position or 90 degrees upright.
- Flex Head slightly, chin down to prevent aspiration, feed on the stronger side of mouth (unilateral weakness).
- Check if its more then 1/2 to 1 teaspoon
- Maintain a Remain upright position for at least 30-60 minutes after food intake.
- Encourage them to Have patient swallow twice and clear pharynx
- Always Inspect mouth for pocket of food
Dysphagia - Key points
- Defined as difficulty swallowing, where there can be neurological and muscular issues.
- Be aware of silent aspiration.
Warning Signs of Dysphagia
- Including Cough during eating, Change in voice tone or quality, Abnormal movements of mouth, tongue, lips
- Can lead to Slow, weak, imprecise or uncoordinated speech.
- Abnormal gag reflex, Delayed swallowing
Managing Dysphagia
- Requires Liquid diets and spoon-thick (viscosity of pudding)
- One should Feed slowly and at smaller size bites
- Matching speeding of feeding to patient’s readiness by Allowing thorough chewing and swallowing before taking another.
- Remove food immediately if coughing or choking begins & implement suction.
- To help Visual Deficits have the plate setup on the same clock format
GI Intubation
Types
- NG (Nasogastric) and NJ (Nasojejunostomy)
- There are also permanent tubes through Gastrostomy and Jejunostomy.
Intubation
- Requires patient is high Fowlers
- Length needs to be measured from the tip of the nose to earlobe to xiphoid process.
- Patient needs to sip with insertion
- Flex head to chest with placement and try to breath through your mouth
- Should patient cough or show signs of distress than stop and remove tube
- To Manage placement check with the gold stand of Chest X-rays or test pH of fluids collected,
- Check the Discomfort - oral care
Gastric Residual Volume - Details
- Indicates delayed gastric emptying and can be medicines or disease.
- Check 4hrs prior to feeding for how well things emptying
Managing Gastric Residual Volume
- Draw back 10-30 ml for air into syringe and flush tubing
- Pull back to aspirate total gastric content and measure.
- After you can return contents unless its is more than 250ml
- Should volumes come back with 500ml or two consecutive measurements exceeding 250mL within the hour then STOP FEEDING
Factors Affecting Oxygenation
- Including Decreased Oxygen - carrying capacity (anemia), Hypovolemia and FiO2 (high altitude, hypoventilation), Metabolic and Neuromuscular disease, or Central Nervous System Issues
- Consider these Developmental implications:
- Infants and toddlers (URIs, immature immune system) School Age/Adolescents (URIs, smoking) Young Adults (unhealthy diet, lack of exercise, stress smoking, illegal substances) Older Adults (RI, decreased elastic recoil decreased functional cilia) Factors impacting oxygen can be related to Lifestyle(Nutrition (obesity, malnutrition), substance abuse, smoking, exercise and stress) Environmental(Air Quality, Smoke, Urban Pollution)
History and Inspection - Nursing care
Key points
- Chest Pain (Cardiac) and Pleuritic Chest Pain (Lungs)
- Also fatigue, musculoskeletal
- Have fatigue, pay attentition to orthopnea(number of pillows)
- Is there Use of accessory muscles,
- What is the Cough, What are the wheezings, Air Quality, smoking?
- What respiratory infection present and allergies?
- Consider medications being taken
Nursing process
- Check Levels of Consciousness for sensitivity
- What is the Chest Wall Movement (Retractions and Accessory Muscle Use), nail clubbing
- Check for cyanosis, apnea and what are the characteristics for paradoxal and kaussmual respirstations
Airway Management for good lungs
- Mobilization of pulmonary secretions → coughing, suctioning
- thins Hydration → -1500-2500 secretions
- Provide Humidification due to this preventing from drying out.
- Necessary for patient receiving oxygen (>4L/min)
- Use Nebulization which adds moisture and medication to inspired air; enhances mucociliary clearance
- Coughing and Deep Breathing , Post-Operative (Q2hr while awake various cough methods)
- Acute phase of mucus production (deep breathing Q2hrs while awake cough Q1hr while awake cough Q2-3hr at night) Chest Physiotherapy (CPT which helps in Postural drainage chest percussion and vibration For high recommendation, consider recommendations for patients w/ mucus production of >30 ml/day Suctioning - Use Sterile technique oropharynx and trachea suction orla secretions last Maintenance and Promotion of Lung Expansion with Ambulation (early is best) Positioning (Semi-Fowlers) → ventilation Incentive spirometer (post-operative) Noninvasive ventilation( CPAP)
Oxygen Therapy Types
- Nasal Cannula - Use when Flow rate is Up to 6L/min with 24-40% FIO2 Range with humidifiction above 4L checking skin near nose
- Simple Face Mask use for 6L/min
- There are contraindicated with CO2 Retention with FIO2 Range or 40-60%
- Non-Rebreather need 10L/min minimal of FIO2 Range with 60-80%
- The Valve between the bag prevents from bag to mask.
- There must be little resistance Venturi Mask, uses 4-12L/min of FIO2 Range : with 24-60% rate varies
Respiratory Disorders
- Atelectasis: Collapsed alveoli, reduced lung function.
- Encourage deep breathing and incentive spirometer use.
- Asthma: Chronic inflammation, reversible wheezing.
- Triggers may need to be assessed before
- COPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Progressive Obstruction.
- Emphysema: irreversible airflow limitations during forced exhalation.
- Chronic Bronchitis: Excess Mucus
Legal and Ethical aspects
- Autonomy: freedom from external control (provider & patients)
- Beneficence: best interest of patient
- Nonmale: avoiding harm
- Justice; fairness
- Fidelity: agreement to keep promises
Nursing Code of Ethics:
- Advocacy
- Responsibilty
- Accountability
- Confidentiality
Proof of Negligence:
Required Duty of Care That lead to patient being injured
Delegations
- Transfer Responsiblities whille maintaining account
Important Notes:
- UAP cant order and RN can order, RN use all other
- Use RN ,LPN, UAP
- What can and connot do, and
- Student Nurses are similar to UAPs must not take any orders
Hypertension
- Primar Idiopathic - majority
- Control BP treatment
- Secondary and use Tx what need.
Key Points
- If it's not idenitife and should the cause.
- Must treat cause
Risk factors
Include age and ethnicity along with genetics Modifiable factor including alocohol, sodium intake, lipids and lifestyle
Measurements
Use caution it C/I for Electronic BP Measurements: in case of Irregular HR or Seizures You can used arm or leg if needed.
Nursing Tip
Use what we can do and how they affct BP
Fluids and Electrolytes
Intravascular, interstitial, and transcellular
Fluids move by osmosis and Filtration, and Movement by electrotype.
Osmolality - number of particles/kg of water
- Isotonic-normal-Same as the regular Tonicitiy
- Hypertonic - Solution is more than regular
- Hypotonic- Solution is less than that then the regular and tonicity
Electrolytes
- Range of numbers* Normal Ranges Sodium - is in extra, so can be 135-145 mEq/L Chloride 98 mEq/L 107 Potassium Extra 3.5-5 outside-less Magnesium - inside more
- Volume numbers* Both can lead to clinical dehydration and all
Sodium
- Notes* Hypernaturemia is above 145 Gain less water Gain more sodium
- Manifestaion: 135 is less* Can be caused with with DI etc for above and high water level Ture for sodium gain or water gain,
Key points
Clinical can lead to sodium imbalance
Potassium
- Hyperkalemia* - Too much above Lowers cell and
- Hypokalemia- Under* Weakness
Know to give these potassium - DO NOT EVER give bolus.
Calcium
- Hypercalcemia*: More calcium
- Hypocalcemia* Less water
- Key Signs- Troussiure and chuvontek: check more*
Key Notes
- Treat Magnesium Then potassium* Phosphorus Can Lead to cardiac dysrhythmias and musculoskelectal Check for neuro symptoms and seizures
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.