Podcast
Questions and Answers
What finding exemplifies healthy or normal wound healing?
What finding exemplifies healthy or normal wound healing?
- Eschar
- Granulation (correct)
- Slough
- Serous fluid
A client's wound is closed with staples; how would this wound be classified?
A client's wound is closed with staples; how would this wound be classified?
- Emergency intention
- Primary intention (correct)
- Secondary intention
- Tertiary intention
After abdominal surgery, the client reports that something has 'popped'. Upon inspection, the nurse notes protrusion of bowel through the incision. Which action is the priority?
After abdominal surgery, the client reports that something has 'popped'. Upon inspection, the nurse notes protrusion of bowel through the incision. Which action is the priority?
- Cover the wound with sterile, saline-soaked gauze. (correct)
- Apply direct pressure and call for assistance.
- Apply an abdominal binder and monitor vital signs.
- Notify the surgeon and document the findings.
A patient has a deep open wound in the sacral region that is covered with a thick, dry, black material. How should the nurse proceed?
A patient has a deep open wound in the sacral region that is covered with a thick, dry, black material. How should the nurse proceed?
A patient with a pressure injury is being treated with wound packing. What should the nurse do when packing the wound?
A patient with a pressure injury is being treated with wound packing. What should the nurse do when packing the wound?
Which finding indicates that a client is at risk for developing a pressure injury?
Which finding indicates that a client is at risk for developing a pressure injury?
A nurse is assessing a wound and notes a red and shiny wound bed that is open with no slough. How should this wound be staged?
A nurse is assessing a wound and notes a red and shiny wound bed that is open with no slough. How should this wound be staged?
A nurse is caring for a patient who is experiencing a full-thickness wound repair. Which type of tissue will the nurse expect to observe?
A nurse is caring for a patient who is experiencing a full-thickness wound repair. Which type of tissue will the nurse expect to observe?
What is the priority nursing intervention to prevent skin breakdown in an immobile client?
What is the priority nursing intervention to prevent skin breakdown in an immobile client?
Which religious dietary restriction excludes mixing dairy with meat?
Which religious dietary restriction excludes mixing dairy with meat?
A client has dysphagia following a stroke. Which diet is most appropriate?
A client has dysphagia following a stroke. Which diet is most appropriate?
What dietary consideration should the nurse include in nutrition education for an Indian client?
What dietary consideration should the nurse include in nutrition education for an Indian client?
A client has difficulty swallowing and no teeth. Which diet should the nurse encourage the health care provider to order?
A client has difficulty swallowing and no teeth. Which diet should the nurse encourage the health care provider to order?
A nurse is caring for a client receiving enteral bolus feedings several times daily. Which nursing intervention will help prevent diarrhea?
A nurse is caring for a client receiving enteral bolus feedings several times daily. Which nursing intervention will help prevent diarrhea?
The nurse is preparing to insert a nasogastric tube on a patient who is semiconscious. How should the nurse measure the tube?
The nurse is preparing to insert a nasogastric tube on a patient who is semiconscious. How should the nurse measure the tube?
Signs of aspiration risk include which factors?
Signs of aspiration risk include which factors?
Which oxygen delivery device is most appropriate for a client with COPD receiving 2 L/min of oxygen?
Which oxygen delivery device is most appropriate for a client with COPD receiving 2 L/min of oxygen?
When assessing a client, what is the earliest sign of hypoxia?
When assessing a client, what is the earliest sign of hypoxia?
A client is being discharged with atelectasis. Which statement indicates that the client understands discharge teaching?
A client is being discharged with atelectasis. Which statement indicates that the client understands discharge teaching?
Which assessment data indicates acute oxygenation disturbance and indicates the need for immediate intervention?
Which assessment data indicates acute oxygenation disturbance and indicates the need for immediate intervention?
A nurse is educating a client with asthma on how to manage their condition at home. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include?
A nurse is educating a client with asthma on how to manage their condition at home. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include?
Which can cause respiratory depression?
Which can cause respiratory depression?
What is an appropriate intervention when a rapid change in patient respiratory status is observed?
What is an appropriate intervention when a rapid change in patient respiratory status is observed?
Which definition best describes the ethical principle of 'Autonomy'?
Which definition best describes the ethical principle of 'Autonomy'?
After noting that a provider has prescribed an excessively high dosage of medication, the nurse is unable to contact the provider in question. What is the next step?
After noting that a provider has prescribed an excessively high dosage of medication, the nurse is unable to contact the provider in question. What is the next step?
Which option describes the correct way for a nurse to correct an error in documentation?
Which option describes the correct way for a nurse to correct an error in documentation?
Which duty is exclusively performed by a registered nurse (RN)?
Which duty is exclusively performed by a registered nurse (RN)?
What action does 'Safe Harbor' prevent?
What action does 'Safe Harbor' prevent?
The sympathetic nervous system affects blood pressure via which biological mechanism?
The sympathetic nervous system affects blood pressure via which biological mechanism?
Which category of blood pressure readings aligns with the AHA's 'Hypertension Stage 1'?
Which category of blood pressure readings aligns with the AHA's 'Hypertension Stage 1'?
Patients who smoke cigarettes have which physiological responses, affecting blood pressure readings?
Patients who smoke cigarettes have which physiological responses, affecting blood pressure readings?
What is the most important lifestyle modification for patients with hypertension to manage their blood pressure, reduce their risk of cardiovascular disease, and improve their overall health?
What is the most important lifestyle modification for patients with hypertension to manage their blood pressure, reduce their risk of cardiovascular disease, and improve their overall health?
Which action may lead to an inaccurate, low blood pressure reading?
Which action may lead to an inaccurate, low blood pressure reading?
During a follow-up appointment for hypertension management, the client inquires about modifiable risk factors. Which responses are appropriate? (Select all that apply.)
During a follow-up appointment for hypertension management, the client inquires about modifiable risk factors. Which responses are appropriate? (Select all that apply.)
Where is most of the body's water?
Where is most of the body's water?
Which of the following common electrolytes is the body's most abundant?
Which of the following common electrolytes is the body's most abundant?
A nurse reviews a client's most recent blood work and has concerns regarding a specific result. Which result is the greatest concern?
A nurse reviews a client's most recent blood work and has concerns regarding a specific result. Which result is the greatest concern?
Which of the following assessment findings would a nurse expect to see in a client who has dehydration and hypernatremia?
Which of the following assessment findings would a nurse expect to see in a client who has dehydration and hypernatremia?
A client who has diarrhea and is taking a potassium-wasting diuretic is at risk for developing which electrolyte imbalance?
A client who has diarrhea and is taking a potassium-wasting diuretic is at risk for developing which electrolyte imbalance?
While reviewing lab results, a nurse notices that a client's calcium level is low. What other electrolyte should the nurse analyze?
While reviewing lab results, a nurse notices that a client's calcium level is low. What other electrolyte should the nurse analyze?
A client presents with hyperactive reflexes. Which intervention is most appropriate?
A client presents with hyperactive reflexes. Which intervention is most appropriate?
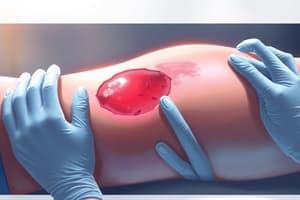
A patient with a closed abdominal wound reports a sudden 'pop' after coughing. Upon examination, the nurse notes that the sutures are open and pieces of small bowel are visible. Which nursing interventions are the priority?
A patient with a closed abdominal wound reports a sudden 'pop' after coughing. Upon examination, the nurse notes that the sutures are open and pieces of small bowel are visible. Which nursing interventions are the priority?
Which nursing observation indicates that a patient is at greatest risk for pressure ulcer formation?
Which nursing observation indicates that a patient is at greatest risk for pressure ulcer formation?
A nurse is admitting an older patient from a nursing home. During the assessment, the nurse notes a shallow open reddish-pink ulcer without slough on the right heel. How should the nurse stage this pressure ulcer?
A nurse is admitting an older patient from a nursing home. During the assessment, the nurse notes a shallow open reddish-pink ulcer without slough on the right heel. How should the nurse stage this pressure ulcer?
An older adult is admitted to the hospital with difficulty eating and no teeth. The nurse, collaborating with the health-care provider, recognizes the need to recommend a diet that accommodates these challenges. Which diet should the nurse advocate for?
An older adult is admitted to the hospital with difficulty eating and no teeth. The nurse, collaborating with the health-care provider, recognizes the need to recommend a diet that accommodates these challenges. Which diet should the nurse advocate for?
A nurse is teaching a patient about atelectasis. Which statement by the patient indicates an understanding of atelectasis?
A nurse is teaching a patient about atelectasis. Which statement by the patient indicates an understanding of atelectasis?
Flashcards
Skin assessment frequency
Skin assessment frequency
Minimum is once a day; every 4 hours for at-risk patients.
Granulation appearance
Granulation appearance
Healthy, normal healing tissue.
Slough appearance
Slough appearance
White-yellow, stringy or pudding-like; needs removal.
Eschar appearance
Eschar appearance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Serous exudate
Serous exudate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Purulent exudate
Purulent exudate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Serosanguinous exudate
Serosanguinous exudate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sanguineous exudate
Sanguineous exudate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary intention
Primary intention
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secondary intention
Secondary intention
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tertiary intention
Tertiary intention
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hemostasis
Hemostasis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inflammatory stage
Inflammatory stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proliferative stage
Proliferative stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Maturation stage
Maturation stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dehiscence
Dehiscence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Evisceration
Evisceration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Non-blanchable redness
Non-blanchable redness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stage 2 pressure ulcer
Stage 2 pressure ulcer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stage 3 pressure ulcer
Stage 3 pressure ulcer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stage 4 pressure ulcer
Stage 4 pressure ulcer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Unstageable pressure ulcer
Unstageable pressure ulcer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Suspected deep tissue injury
Suspected deep tissue injury
Signup and view all the flashcards
Turn patient frequency
Turn patient frequency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Schedule wound care/dressing change
Schedule wound care/dressing change
Signup and view all the flashcards
Assess wound
Assess wound
Signup and view all the flashcards
Measuring NG tube insertion
Measuring NG tube insertion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Islam Restrictions
Islam Restrictions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Christianity Restrictions
Christianity Restrictions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hinduism Restrictions
Hinduism Restrictions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Judaism Restrictions
Judaism Restrictions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Church of Christ of Latter-Day Saints
Church of Christ of Latter-Day Saints
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clear liquid diet
Clear liquid diet
Signup and view all the flashcards
Full liquid diet
Full liquid diet
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pureed/Thickened liquids
Pureed/Thickened liquids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mechanical diet
Mechanical diet
Signup and view all the flashcards
Soft/Low Residue diet
Soft/Low Residue diet
Signup and view all the flashcards
High fiber diet
High fiber diet
Signup and view all the flashcards
Low Sodium diet
Low Sodium diet
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetic diet
Diabetic diet
Signup and view all the flashcards
Physiologic oxygenation factors
Physiologic oxygenation factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lifestyle oxygenation
Lifestyle oxygenation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Environmental factors
Environmental factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypoxia
Hypoxia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Skin and Wound Assessment Notes
- Minimum skin assessment is once per day; high-risk patients require assessment every four hours.
- Assess bony prominences like heels and elbows and skin around devices.
- Note whether the skin is blanchable or non-blanchable
- Moisture is a primary cause of decreased skin integrity.
- Darker skin may not visibly blanch; inflammation may appear purplish or blue.
- Assess wound location, depth, tissue involvement, dimensions (L, W, depth, undermining), exudate, periwound, and drains in a well-lit area.
Color or Appearance
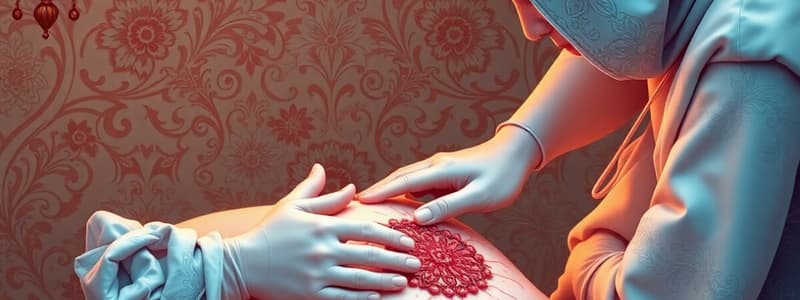
- Granulation tissue indicates healthy, normal healing.
- Slough is white-yellow and stringy and must be removed.
- Eschar is a scab that must be removed, except on the foot, where it protects thin skin.
Exudates
- Serous exudate consists of clear, watery plasma.
- Purulent exudate indicates infection and is thick, yellow, green, or tan.
- Serosanguineous exudate is blood mixed with plasma; pale and watery.
- Sanguineous exudate indicates acute bleeding; bright red.
Wound Classification
- Primary intention wounds are closed with sutures or staples and heal quickly with minimal scarring.
- Secondary intention wounds have edges that cannot be approximated due to tissue loss or contamination and heal with granulation.
- Tertiary intention wounds are left open for several days and then approximated; closure is delayed due to infection risk.
Stages of Wound Healing
- Hemostasis is the initial stage involving blood loss control.
- The Inflammatory stage occurs within 24 hours, activating inflammatory responses with mast cells and WBCs.
- The Proliferative stage lasts 3-24 days, involving angiogenesis, filling with tissue, resurfacing, and epithelialization.
- Maturation can take over a year.
Wound Complications
- Hemorrhage is a potential complication; check for internal blood pooling.
- External hemorrhage is more easily detected.
- Infection is a risk in any wound.
- Dehiscence is when a wound pulls apart.
- Evisceration is the protrusion of organs, most commonly the intestine, requiring covering with sterile wet gauze and immediate surgical notification.
Pressure Ulcers
Stage 1
- Non-blanchable redness
- Intact skin
- Warmth and hardness
Stage 2
- Skin loss limited to dermis
- Shallow open ulcer with shiny bed
- No slough or bruising and blistering
Stage 3
- Full-thickness skin loss involving to subcutaneous fat
- No visualized bone, tendon and muscle are not present.
- Slough may be present.
Stage 4
- Deeper tissue loss
- Exposed, palpable bone, tendon, or muscle
- Undermining and tunneling due to pressure
- Risk of osteomyelitis
Unstageable Pressure Ulcer
- Obscured, requiring debridement
Suspected Deep Tissue Injury
- Localized purple or maroon area with intact skin
- Caused by soft tissue damage from pressure or shear force
- Depth unknown
Factors Affecting Wound Healing
- Adequate protein and caloric intake
- Tissue perfusion
- Absence of infection
- Age/comorbidities
- Psychosocial well-being
Patient Care
- Cultures before dressings
- Bed and chair support surfaces
- Wound irrigation, if needed
- Abdominal splinting
- Elevate the bed to max 30 degrees
- Turn the patient every 1.5 to 2 hours for lateral position, every 15 mins for upright position
Wound Management
- Schedule around current pain regime
- Moist dressings for dry wounds + gauze/saline
- Dry dressing for moisture wicks
- Self Adhesive dressing for moisture control
- packing is for those tunnelling
- Use analgesic at least 30 minutes prior
- Clean gloves for old dressings, clean gloves for the wound
- Use non-cytotoxic cleaning solution
- Never use the same gauze twice
- Sterilize and least contaminate areas prior
GI Intubation and Nutrition Notes
Diet & Health History During nutritional assessment
- Review nutrition knowledge to tailor education.
- Social history is taken as well to determine things that are in the pt's control vs not
- Sociocultural and socioeconomic factors are assessed
- Monitor nutrition with a 3-7 day food diary
Religious Restrictions influence Diet
- No pork, alcohol, caffeine is restricted in Islam. You must practice Ramadan fasting
- Some Christians practice minimal alcohol, or fast during Lent/ meatless Fridays
- Hinduism prevents eating meat
- Judaism does not allow park or dairy products
- Latter day saints exclude caffeine, alcohol consumption
Types of Therapeutic Diets
- Clear Liquid: clear/fat-free broth, tea, and jello
- Full Liquid: anything smooth eg ice cream and pudding
- Pureed/thick: foods scrambled, mashed meats/pots
- mechanical soft: ground meat, cheese, rice
- Soft/Low Residue: low fibre foods, pasta
- high fibre: raw fruits, steamed veg
- low-sodium: 4g/2, 1g limits
- Low cholesterol: 300mg
- Diabetic: balances of carbs, fats and protein
Dysphagia Notes
-
Dysphagia means difficulty in swallowing
-
Caused by disorders obstructing the upper and lower portions of the throat Warning signs of dysphagia:
-
Coughing during eating
-
Change in voice tone
-
Abnormal tongue/mouth
-
Slow, weak speech Be aware of aspiration
-
Aspiration risk include those with a poor gag reflex, and suction at bedside
Dysphagia management
- Upright seated position
- Tuck chin in
- Position in stronger side of mouth- unilateral weakness
- Feed in 0.5/1 teaspoon
GI Intubation
Types:
- Naso(gastric, jejunostomy, duodenal, permanent tubes) Indications: (enteral feeding, decompress, lavage(irrigating)
GI Feeding Safety
Placement: pH or chest XR Discomfort: oral care Procedure: high fowler Meaure: nose to earlobe to xiphoid process to sternum Coughing? stop feeding
Gastric Notes
- if over 500ml or 250ml, stop feeding!
- check every 4hrs
Respiration & Oxygenation Notes
Factors Affecting Oxygenation
Physiological
- Decreased oxygen carrying (anemia)
- Decreased inspired oxygen (hypoventilation)
- Neuromuscular disorders
Development
- Infants and toddlers with immature immune system
- Adolescents with smoking habits
- RI in older adults
Assessment History Inspection
Level of Consciousness Earliest sign: restlessness Wall movement with use of muscle usage Tripod position with hands on thighs Nail clubbing means it's late
- kussmaul- metabolic acidosis
- Cheyne-strokes, apneas and brain injury
Pleuritic Chest Pain
- Sharp knife in the chest while breathing
Airway Management
- Coughing and suction
- Hydration
- Humidification to prevent mucosa from drying out Necessary for patient getting 4L of oxygen
Airways
Open airways for those getting surgical procedures
Lung Expansion Promotion
Semi-Fowlers Encourage deep breathing
Oxygen Delivery
- Nasal Cannula: 6,24 (flow and range), humidifiers required
- Simple Face: 4,40 CO2, retention contraindicated, no more than 2L
- non breather: minimum 10, valve between the bag prevents released air.
- venturii: 24, depends on setting
Respiratory disorders
- Atelectasis: deep breathing
- Asthma: triggers, wheezing, chest
Legal & Ethics Notes
Ethical Principles
- Autonomy: independence, patient choice
- Beneficence: promote health, patients rights
- non-maleficence. Do no har
- Justice: fairness of treament
- Fidelity: Keep promises
Nursing Actions for Ethical Duties
- Respect all obligations and follow patients, respect, advocate, answer etc
- Protect client info
delegation
- Only give people things you are 100 percent certain they can carry out
Scope of Practice UAP: (VS, ROM and Urine Spec) LVN: Everything that UAPs can do while adding dressing changes and medication RN: Nursing process and development of care Student: No phone or written orders
Hypertension and Vital Signs Notes
• Cardiogenic risk factors linked to high BP include heart rate, contractility, and conductivity
• Sympathetic Nervous System in relation to high BP is due to Adrenergic receptors
Factors that contribute and don't are
- age, gender, ethnic are unmodifiable
- diet, alch, smoking are modifiable
Electronic BP measurements:
- if any irregularity or low value, avoid.
- Cuff should fit and line the forearm
- take 3 heart rate readings, positive if: heart rate increases or mmHg decreases
- if arm is above the heart it underestimates.
- repeat the high
- smoking results in vasoconstriction
Fluid & Electrolytes Notes
Electrolytes and Normal Ranges
- Sodium: 135-145, prevalent in ECF
- Chloride: 98-107
- Pottasium: 3.5-5 mEq/L
- calcium and ionized 4.5 for calcium
- phosphate and magnesium 2.5
Osmolality: water and tonicity
- imbalance result in:
- volume isotonic
- hyper and hypo natremai /volemic
Hyponatermia Causes
- diuretics, burns and vomiting and dehydration, signs: (seizures, lethargy, muscle
Hypernatremia Causes
- diarrhea and diuretics signs: (seizures, arrhythmia)
Potassium Imbalance
- Kalemia: 3.5-5 mEq/I
Signs and symptoms of hyperkalemia: abdominal cramps, anxiety, diarrhea, muscle
- force K+ from the cell. Prevent
Signs and symptoms of hypokalemia: muscle, constipation, weak
- NEVER BOLUS
Calcium level: 8.6-10.2
Signs of hypercalcemia: constapation, N/V
- give diuretic for calcium execess
Signs of Hypo:
- spasms, trousseau's sign
Magnesium Level: 1.5
Signs of hyper low respiration rate
signs of level
- dyspepsia and high blood pressure
- avoid for people on Admin: glocunate
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.