Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main function of the rib cage in the human body?
What is the main function of the rib cage in the human body?
Protection for vital organs such as the heart and lungs.
How many pairs of ribs make up the human rib cage?
How many pairs of ribs make up the human rib cage?
12 pairs
What is the scientific term for the breast bone?
What is the scientific term for the breast bone?
Sternum
How do true ribs differ from false ribs in terms of connection to the sternum?
How do true ribs differ from false ribs in terms of connection to the sternum?
What are the components of a rib, as described in the text?
What are the components of a rib, as described in the text?
What are the three parts of the sternum and their respective functions?
What are the three parts of the sternum and their respective functions?
Explain the role of the rib cage in respiration.
Explain the role of the rib cage in respiration.
How does the sternum protect the heart?
How does the sternum protect the heart?
Discuss the treatment options for rib fractures.
Discuss the treatment options for rib fractures.
What can cause breast bone deformity, and what are the treatment options?
What can cause breast bone deformity, and what are the treatment options?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Ribs and Breast Bone Facts
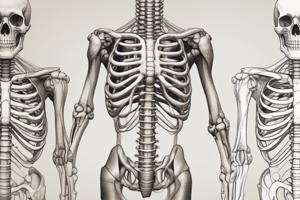
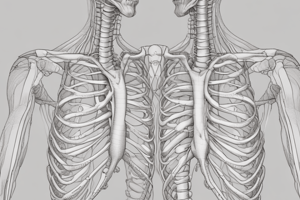
The rib cage is a critical part of the human skeletal system, providing protection for vital organs such as the heart and lungs. It consists of 24 ribs, 12 pairs on either side of the body, which surround the chest cavity. The rib cage is also responsible for helping us breathe by expanding and contracting with each breath.
The breast bone, scientifically referred to as the sternum, is another essential component of the ribcage. It lies flat against the thoracic vertebrae and forms the front wall of the thorax, protecting the heart and major blood vessels from external blows.
The rib cage and breast bone work together to protect our internal organs, allow us to breathe effectively, and facilitate movement. Here are some key facts about these structures.
Structure of the Rib Cage
The rib cage is made up of 12 pairs of ribs, with the first seven pairs being called 'true' ribs, while the remaining five pairs are known as false ribs. True ribs have cartilage connecting them directly to the sternum, allowing for flexibility, while false ribs do not. In addition, there are two pairs of floating ribs, which have no connection to the sternum and are not considered part of the rib cage.
Each rib has a head, neck, body, and tubercle. The head articulates with the vertebral column, the neck connects to the 7th cervical vertebra, the body attaches above and below to other ribs or to the sternum, and the tubercle points towards the back. The ribcage is composed mainly of bone, except for the anterior portion of the upper six ribs, which are primarily composed of cartilage.
Structure of the Sternum
The sternum is a flat bone that runs horizontally along the midline of the chest. It has three parts: the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process. The manubrium is the uppermost part of the sternum, which connects it to the clavicle and the first pair of true ribs. The body of the sternum extends downwards and is connected to the next nine pairs of ribs. Lastly, the xiphoid process is a small, thin, and elongated end of the sternum, located at the bottom of the sternum and extending into the abdominal muscles.
The sternum is held together by costal cartilages, which are attached to the seventh, eighth, and ninth ribs. The sternum is also connected to the thoracic vertebrae by the sternoclavicular joints and the sternocostal joints.
Functions of the Ribs and Breast Bone
The rib cage and breast bone serve various important functions. They protect the thoracic organs, such as the heart and lungs, and provide support for the abdominal muscles. The rib cage also plays a significant role in respiration, expanding and contracting as we breathe, allowing oxygen to enter the lungs and carbon dioxide to exit the body.
The sternum is essential in protecting the heart from external blows. It also helps to anchor the muscles used in respiration and provides a point of attachment for the diaphragm, a key muscle involved in breathing.
Common Rib and Breast Bone Conditions
Rib and breast bone conditions can affect the quality of life and may require medical attention. Here are some common conditions related to these structures:
- Rib fractures: These occur when the rib bones are broken, often due to trauma such as car accidents or falls. Treatment may include pain relief, rest, and occasionally surgery.
- Breast bone fractures: These are rare and usually occur as a result of severe trauma, such as high-impact accidents or falls from great heights. Treatment may involve pain relief, rest, or surgery.
- Breast bone deformity: This can occur due to various factors, including genetics, chest wall abnormalities, or surgical procedures. Treatment may involve wearing a breast supporter, undergoing surgery, or using botulinum toxin injections.
- Rib cage tumors: These are rare but can be benign or malignant, affecting the quality of life and requiring appropriate medical treatment.
In conclusion, the rib cage and breast bone are integral components of the human skeleton responsible for protecting vital organs, enabling respiration, and facilitating movement. Understanding their structure and functions can help us appreciate the complexity and importance of our skeletal system.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.