Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary mechanism by which Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) work to treat rheumatoid arthritis?
What is the primary mechanism by which Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) work to treat rheumatoid arthritis?
- Suppressing the immune system to decrease joint inflammation and prevent further joint damage. (correct)
- Directly stimulating cartilage regeneration in affected joints to reverse damage..
- Increasing the production of synovial fluid to improve joint lubrication and reduce friction.
- Blocking pain receptors in the brain to provide immediate relief from arthritis-related discomfort.
A patient newly diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis is prescribed both a DMARD and an NSAID. What is the most likely reason for this combination therapy?
A patient newly diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis is prescribed both a DMARD and an NSAID. What is the most likely reason for this combination therapy?
- To enhance the absorption of the DMARD, improving its efficacy through the anti-inflammatory actions of the NSAID.
- To counteract the side effects of prolonged DMARD use with the protective properties of NSAIDs.
- To prevent potential liver damage caused by long-term DMARD therapy using the anti-inflammatory effects of NSAIDs.
- To achieve faster initial pain relief with the NSAID while waiting for the DMARD to take effect. (correct)
Which of the following is the primary goal of medication therapy for osteoporosis?
Which of the following is the primary goal of medication therapy for osteoporosis?
- To decrease the potential for fractures by increasing bone density and strength. (correct)
- To manage autoimmune responses contributing to bone degradation.
- To improve mobility and range of motion in the hips, wrists, and spine.
- To reduce joint pain and inflammation through immunosuppression.
Why are older adults more susceptible to fractures in the hip, wrist, and spinal vertebrae?
Why are older adults more susceptible to fractures in the hip, wrist, and spinal vertebrae?
Which statement best describes the rationale for discontinuing NSAIDs in a rheumatoid arthritis patient who is also taking DMARDs?
Which statement best describes the rationale for discontinuing NSAIDs in a rheumatoid arthritis patient who is also taking DMARDs?
Which of the following is the MOST accurate description of rheumatoid arthritis (RA)?
Which of the following is the MOST accurate description of rheumatoid arthritis (RA)?
A client is diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis. Which of the following is the PRIMARY goal of medication therapy?
A client is diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis. Which of the following is the PRIMARY goal of medication therapy?
Which of the following factors contributes to the development of osteoporosis?
Which of the following factors contributes to the development of osteoporosis?
A post-menopausal client is diagnosed with osteoporosis. Which physiological change is the MOST likely cause of this condition?
A post-menopausal client is diagnosed with osteoporosis. Which physiological change is the MOST likely cause of this condition?
In osteoporosis, an imbalance between osteoblastic and osteoclastic activity leads to decreased bone mineral density (BMD). Which of the following BEST describes this imbalance?
In osteoporosis, an imbalance between osteoblastic and osteoclastic activity leads to decreased bone mineral density (BMD). Which of the following BEST describes this imbalance?
For a male client, what role does testosterone play in maintaining bone health, and how does its reduction affect the risk of developing osteoporosis?
For a male client, what role does testosterone play in maintaining bone health, and how does its reduction affect the risk of developing osteoporosis?
A doctor is prescribing medication for a client with osteoporosis. What is the primary goal of this medication therapy?
A doctor is prescribing medication for a client with osteoporosis. What is the primary goal of this medication therapy?
A 65-year-old client is diagnosed with osteoporosis. Which lifestyle factor, if present, would MOST significantly exacerbate their condition?
A 65-year-old client is diagnosed with osteoporosis. Which lifestyle factor, if present, would MOST significantly exacerbate their condition?
Flashcards
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
An autoimmune disease affecting all ages, more common in young to middle-age women, with the goal of decreasing joint pain and inflammation.
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
A progressive disease, most commonly caused by menopause, with the goal of decreasing the potential for fractures.
DMARDs
DMARDs
Immunosuppressive medications that decrease joint inflammation and damage, delaying the progression of rheumatoid arthritis.
NSAIDs & DMARDs
NSAIDs & DMARDs
Signup and view all the flashcards
DMARD Categories
DMARD Categories
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
RA Medication Therapy Goal
RA Medication Therapy Goal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menopause and Osteoporosis
Menopause and Osteoporosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bone Remodeling
Bone Remodeling
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteoporosis Development
Osteoporosis Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
BMD Peak Age
BMD Peak Age
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteoporosis Medication Goal
Osteoporosis Medication Goal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis are common disorders of the joints and bones, both causing severe deformities and loss of function.
- Medications are important in managing these disorders.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
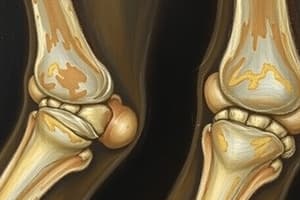
- RA is an inflammatory, systemic, autoimmune disease affecting joints and surrounding structures.
- It primarily affects synovial joints but can occur wherever connective tissue is widespread.
- RA leads to joint stiffness, pain, swelling, and deformity.
- People of all ages can be affected although the risk of onset increases after age 60.
- Both environmental and genetic factors are believed to play a role in the development of RA.
- Medication therapy aims to decrease joint pain and inflammation and prevent disabling deformities.
Osteoporosis
- Osteoporosis is a progressive disease characterized by reduced bone mass, decreased bone density, and increased fracture risk.
- Natural or surgical menopause is a common cause, due to decreased estrogen production.
- Aging, long-term glucocorticoid therapy, lack of weight-bearing activity, and excessive caffeine, alcohol, and tobacco use can also cause osteoporosis.
- Bone is constantly changing through a process called bone remodeling.
- Osteoporosis and osteopenia occur when bone reabsorption (osteoclastic activity) exceeds bone formation (osteoblastic activity).
- This imbalance leads to decreased bone mineral density (BMD).
- BMD peaks around ages 25 to 30 and is a determinant of bone strength.
- Estrogen prevents bone loss, making post-menopausal clients more susceptible to osteoporosis, and thus, fractures.
- Testosterone aids in bone building, so its reduction in aging men increases their risk of osteoporosis.
- Medication therapy focuses on decreasing the possibility of fractures.
- Medications maintain or increase bone strength by reducing bone reabsorption and promoting bone formation.
- Common fracture sites in older adults include the hip, wrist, and spinal vertebrae.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
- DMARDs are immunosuppressive medications that reduce joint inflammation and damage.
- They can delay the progression of RA, in addition to relieving symptoms.
- DMARDs are often administered with NSAIDs, as DMARDs' therapeutic effects can take weeks to manifest.
- NSAIDs may be discontinued once the DMARDs take effect and provide adequate pain control.
- DMARDs are categorized into conventional synthetic, biologic, and targeted synthetic types.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.