Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following best describes arthrosis?
Which of the following best describes arthrosis?
- Limitation of a joint without accompanying inflammation. (correct)
- An autoimmune disease affecting the synovial lining of joints.
- Inflammation of a joint with significant swelling.
- A systemic disease causing low-grade fever and fatigue.
What is a common effect of joint swelling or pain on the surrounding muscles?
What is a common effect of joint swelling or pain on the surrounding muscles?
- Disuse or reflex inhibition of stabilizing muscles. (correct)
- Voluntary increase in range of motion.
- Enhanced balance and coordination.
- Increased muscle performance and strengthening.
Which T-score from a bone mineral density scan (BMD) indicates osteoporosis?
Which T-score from a bone mineral density scan (BMD) indicates osteoporosis?
- -1.0 or higher
- -2.5 or less (correct)
- 0 or above
- Between -1.0 and -2.4
What type of exercise is recommended at least 5 days a week for someone with osteoporosis?
What type of exercise is recommended at least 5 days a week for someone with osteoporosis?
Which of the following sensory inputs are impacted, leading to impaired balance due to joint disorders?
Which of the following sensory inputs are impacted, leading to impaired balance due to joint disorders?
Which of the following is a precaution when exercising with osteoporosis?
Which of the following is a precaution when exercising with osteoporosis?
What is the primary characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis (RA)?
What is the primary characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis (RA)?
Which intervention would be used to address a trigger point?
Which intervention would be used to address a trigger point?
Where does rheumatoid arthritis (RA) typically begin?
Where does rheumatoid arthritis (RA) typically begin?
What can occur as a result of joint deformation in rheumatoid arthritis?
What can occur as a result of joint deformation in rheumatoid arthritis?
What is the primary mechanical effect of exercise that helps improve bone mass density?
What is the primary mechanical effect of exercise that helps improve bone mass density?
In addition to joint problems, how else does Rheumatoid Arthritis affect the body?
In addition to joint problems, how else does Rheumatoid Arthritis affect the body?
What is a key principle of managing rheumatoid arthritis during an active inflammatory period?
What is a key principle of managing rheumatoid arthritis during an active inflammatory period?
What is a typical timeframe for immobilization in adults?
What is a typical timeframe for immobilization in adults?
Which of the following is a local tissue response to post-traumatic immobilization?
Which of the following is a local tissue response to post-traumatic immobilization?
During post-immobilization management, joint mobilization is used for what purpose?
During post-immobilization management, joint mobilization is used for what purpose?
Why is it important to monitor the intensity of contraction during PNF stretching post-immobilization?
Why is it important to monitor the intensity of contraction during PNF stretching post-immobilization?
What type of exercises are typically initiated to minimize secondary physiological changes that occur while immobilized?
What type of exercises are typically initiated to minimize secondary physiological changes that occur while immobilized?
When can PRE (Progressive Resistive Exercise) and other intense dynamic exercises be initiated post-fracture?
When can PRE (Progressive Resistive Exercise) and other intense dynamic exercises be initiated post-fracture?
What should be the focus when applying resistive force during muscle performance exercises after immobilization?
What should be the focus when applying resistive force during muscle performance exercises after immobilization?
What restricts tissue mobility when soft tissue damage occurred at the time of the fracture?
What restricts tissue mobility when soft tissue damage occurred at the time of the fracture?
Which of the following is a commonly reported location of pain in individuals with fibromyalgia?
Which of the following is a commonly reported location of pain in individuals with fibromyalgia?
Which of the following is NOT considered a typical contributing factor to fibromyalgia flare-ups?
Which of the following is NOT considered a typical contributing factor to fibromyalgia flare-ups?
What type of exercise is particularly emphasized in the management of fibromyalgia?
What type of exercise is particularly emphasized in the management of fibromyalgia?
Which of the following is a hallmark characteristic of myofascial pain syndrome?
Which of the following is a hallmark characteristic of myofascial pain syndrome?
What is a likely cause of trigger points in muscles according to the text?
What is a likely cause of trigger points in muscles according to the text?
Which of the following is NOT a suggested principle to manage myofascial pain syndrome?
Which of the following is NOT a suggested principle to manage myofascial pain syndrome?
Besides medication, which other non-pharmacological intervention is recommended in the management of fibromyalgia?
Besides medication, which other non-pharmacological intervention is recommended in the management of fibromyalgia?
What is a common feature of fibromyalgia symptoms?
What is a common feature of fibromyalgia symptoms?
In the subacute and chronic stages of rheumatoid arthritis, which of the following treatment approaches should be prioritized?
In the subacute and chronic stages of rheumatoid arthritis, which of the following treatment approaches should be prioritized?
What is an important aspect of joint protection and activity modification for those with rheumatoid arthritis?
What is an important aspect of joint protection and activity modification for those with rheumatoid arthritis?
Which of the following considerations should guide flexibility, strength, and endurance exercises for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis?
Which of the following considerations should guide flexibility, strength, and endurance exercises for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis?
What type of conditioning exercises are most appropriate for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis when considering cardiopulmonary endurance?
What type of conditioning exercises are most appropriate for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis when considering cardiopulmonary endurance?
Which of these statements best describe the characteristics of osteoarthritis?
Which of these statements best describe the characteristics of osteoarthritis?
What is a primary focus of patient instruction when managing osteoarthritis?
What is a primary focus of patient instruction when managing osteoarthritis?
Which factor is NOT used to classify fractures?
Which factor is NOT used to classify fractures?
Which of the following is a key consideration when prescribing resistance exercise for someone with osteoarthritis?
Which of the following is a key consideration when prescribing resistance exercise for someone with osteoarthritis?
What type of bone typically heals most rapidly due to its rich blood supply?
What type of bone typically heals most rapidly due to its rich blood supply?
What is the main goal of stretching and joint mobilization exercises for individuals with osteoarthritis?
What is the main goal of stretching and joint mobilization exercises for individuals with osteoarthritis?
Which of the following is a key difference between fibromyalgia and myofascial pain syndrome?
Which of the following is a key difference between fibromyalgia and myofascial pain syndrome?
Which of these is NOT a risk factor for fractures?
Which of these is NOT a risk factor for fractures?
What is the primary way that cancellous bone heals?
What is the primary way that cancellous bone heals?
How long must chronic widespread pain persist to be classified as fibromyalgia?
How long must chronic widespread pain persist to be classified as fibromyalgia?
In cortical bone healing, what immediately follows the inflammatory phase?
In cortical bone healing, what immediately follows the inflammatory phase?
Which of the following factors does NOT directly influence the healing time of a fracture?
Which of the following factors does NOT directly influence the healing time of a fracture?
What is a key concern regarding epiphyseal plate fractures in children?
What is a key concern regarding epiphyseal plate fractures in children?
What does a 'closed' fracture indicate?
What does a 'closed' fracture indicate?
Flashcards
Arthritis
Arthritis
Inflammation of a joint.
Arthrosis
Arthrosis
Limitation of a joint's movement without inflammation.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
An autoimmune disease that primarily affects the synovial lining of joints, causing inflammation and potentially leading to joint damage.
Active Inflammatory Period in RA
Active Inflammatory Period in RA
Signup and view all the flashcards
Joint Protection
Joint Protection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Energy Conservation
Energy Conservation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patient Education in RA
Patient Education in RA
Signup and view all the flashcards
Overall Treatment Plan for RA
Overall Treatment Plan for RA
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Joint Mobility
Joint Mobility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Joint Protection and Activity Modification (RA)
Joint Protection and Activity Modification (RA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functional Training
Functional Training
Signup and view all the flashcards
Resistance Exercise (OA)
Resistance Exercise (OA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stretching and Joint Mobilization (OA)
Stretching and Joint Mobilization (OA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiopulmonary Endurance
Cardiopulmonary Endurance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Balance Activities (OA)
Balance Activities (OA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
T-score
T-score
Signup and view all the flashcards
Weight-bearing Exercises for Osteoporosis
Weight-bearing Exercises for Osteoporosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exercise and Osteoporosis
Exercise and Osteoporosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fracture
Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myofascial Pain Syndrome (MPS)
Myofascial Pain Syndrome (MPS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibromyalgia Flares
Fibromyalgia Flares
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibromyalgia Flare Triggers
Fibromyalgia Flare Triggers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myofascial Trigger Points
Myofascial Trigger Points
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aerobic Exercise for Fibromyalgia
Aerobic Exercise for Fibromyalgia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Activity Pacing for Fibromyalgia
Activity Pacing for Fibromyalgia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for Fibromyalgia
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for Fibromyalgia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Complete Fracture
Complete Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Incomplete Fracture
Incomplete Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Displaced Fracture
Displaced Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Undisplaced Fracture
Undisplaced Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Open Fracture
Open Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Closed Fracture
Closed Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inflammatory Phase of Bone Healing
Inflammatory Phase of Bone Healing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reparative Phase of Bone Healing
Reparative Phase of Bone Healing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Local Tissue Response in Posttraumatic Immobilization
Local Tissue Response in Posttraumatic Immobilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Maintaining Normal Function During Immobilization
Maintaining Normal Function During Immobilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
General Exercises for Uninvolved Body Parts
General Exercises for Uninvolved Body Parts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functional Adaptations During Immobilization
Functional Adaptations During Immobilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impairments After Immobilization
Impairments After Immobilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Joint Mobilization After Immobilization
Joint Mobilization After Immobilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
PNF Stretching After Immobilization
PNF Stretching After Immobilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Resuming Functional Activities Post-Immobilization
Resuming Functional Activities Post-Immobilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Chapter 11: Joint, Connective Tissue, and Bone Disorders and Management
- Arthritis is inflammation of a joint
- Arthrosis is limitation of a joint without inflammation
- Impaired Mobility often involves a firm end-feel, decreased and possibly painful joint play, and joint swelling
- Impaired Muscle Performance can occur due to disuse or reflex inhibition of stabilizing muscles when there is joint swelling or pain
- Impaired Balance is often caused by altered or decreased sensory input from joint mechanoreceptors and muscle spindles
- Activity Limitations and Participation Restrictions can range from minimally to significantly restricted.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- An autoimmune, chronic, inflammatory, systemic disease of unknown etiology primarily affecting synovial lining of joints and other connective tissues
- Characteristics:
- Erosive synovitis with periods of exacerbation and remission
- Inflammatory changes in tendon sheaths
- Extra-articular pathological changes sometimes occur
- Progressive deterioration in function often due to muscular changes and progressive muscle weakness
- Degree of involvement varies
- Mild symptoms result in mild lifestyle changes and medication. Significant symptoms result in major lifestyle adaptations.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) - Signs and Symptoms
- Active Disease Periods: Often include effusion (fluid accumulation) and swelling of the joints. Onset typically in smaller joints of hands and feet, potentially leading to deformity and ankylosis (fusion) or subluxation (partial dislocation). Pain frequently spreads to muscles, potentially causing muscle atrophy and weakness. Low-grade fever, loss of appetite and weight, fatigue, and malaise can also occur.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) - Management
- Patient Education: Includes overall treatment plan, safe activity, and joint protection techniques. Patients should be taught to recognize and respect fatigue, resting to avoid undue stress on body systems.
- Joint Mobility & Exercise: Focus on active exercises utilizing as much range of motion (ROM) as possible, contingent on symptoms. Functional training is also emphasized, adapting Activities of Daily Living (ADLs) to protect joints.
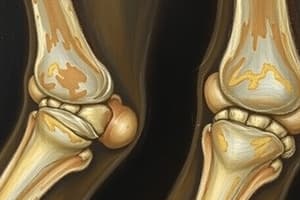
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) - Location of Erosion
- X-rays of affected hands demonstrate areas of erosion (damage in the bone).
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) - Principles of Management (Subacute and Chronic Stages)
- Treatment Approach: Precautions are vital due to potential tissue susceptibility to further damage from pathological changes associated with the disease.
- Joint Protection and Activity Modification: Prioritize protecting joints by adapting the environment and modifying activities to prevent further injury.
- Flexibility and Strength: Exercises for flexibility, strength, and endurance should be within patient tolerance.
- Cardiopulmonary Endurance: Non-impact or low-impact conditioning exercises performed within patient tolerance are critical.
Osteoarthritis (OA)
- A chronic degenerative disorder primarily affecting the articular cartilage of synovial joints, with eventual bony remodeling and overgrowth at the margins of the joints.
- Characteristics:
- Capsular laxity resulting from bone remodeling and capsule distension can lead to hypermobility or instability.
- Cartilage can degenerate, split, and thin, losing its ability to withstand stress.
- Affected joints may become enlarged.
- Common sites include weight-bearing joints (hips and knees), cervical and lumbar spine, DIP joints of fingers and CM joints of the thumbs.
Osteoarthritis (OA) - Imaging
- X-rays demonstrate reduced joint space and the presence of osteophytes (bone spurs)
Osteoarthritis (OA) - Management
- Patient Instruction: Emphasize how to protect joints while remaining active and managing symptoms.
- Pain Management: Early stages (stiffness) necessitate balance between activity, rest, and correct biomechanical stresses. Late stages emphasize activity modification, assistive devices, and orthoses.
- Assistive Devices and Activity: Supportive devices can minimize joint stress.
- Resistance Exercise: Within tolerance of the joint, strong muscles protect the joint.
- Stretching and Joint Mobilization: Movement through the full available ROM prevents restrictions.
- Balance Activities: Enhance balance to prevent falls.
- Aerobic Conditioning: Avoid activities causing repetitive intense loading of joints.
Fibromyalgia (FM)
- A chronic condition characterized by widespread pain affecting multiple body regions, including the axial skeleton, lasting more than three months.
- Prevalence: Affects approximately 2% of the adult population (18+). Women are more frequently affected than men.
- Characteristics: Can occur at any age, often appearing during early or middle adulthood. Symptoms may develop after physical trauma or viral infections. Pain is often described as originating in muscles, commonly in the scapula, head, neck, chest, and lower back. Symptoms fluctuate. The condition is associated with other health concerns such as tendonitis, headaches, irritable bowel syndrome, temporomandibular joint dysfunction, restless legs syndrome, mitral valve prolapse, anxiety, depression, and memory problems.
Fibromyalgia (FM) - Factors Contributing to Flare-ups
- Environmental stresses: (e.g., weather changes)
- Physical stresses: (e.g., repetitive activities, prolonged sitting/standing, shift work)
- Emotional stresses: (e.g., common life stressors)
Fibromyalgia (FM) - Management
- Exercise: Aerobic exercise (particularly) to reduce symptoms.
- Prescription/OTC Medications: For pain management.
- Pacing Techniques: Instructing in and encouraging pacing activities.
- Other Interventions: Cognitive behavior therapy, avoiding stress fractures, minimizing alcohol and caffeine consumption, diet modification, and manual therapy.
Myofascial Pain Syndrome (MPS)
- A chronic regional pain syndrome. The hallmark is myofascial trigger points (specific points in muscle) associated with referred pain patterns, and additional sensory, motor, and autonomic symptoms.
- Possible Causes of Trigger Points:
- Chronic overload of muscles due to repetitive activities.
- Acute overload of muscles (e.g., slipping, catching oneself).
- Poor muscle conditioning.
- Postural stresses (e.g., prolonged sitting).
- Poor body mechanics.
Myofascial Pain Syndrome (MPS) - Management
- Correct Chronic Overload: Education emphasizing the importance of intermittent mini-breaks to prevent overload.
- Eliminate Trigger Points:
- Contract-relax-passive stretch
- Trigger point release
- Spray and stretch
- Dry needling or injection
- Strengthen Muscle and improve Muscle Endurance
Osteoporosis
- A bone disease characterized by decreased mineral content and bone weakness.
- Diagnosis: Determined by T-score from BMD (bone mineral density) scan.
- Normal T-score = -1.0 or higher
- Osteopenia T-score = -1.0 to -2.4
- Osteoporosis T-score = -2.5 or less
- Prevention:
- Balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D.
- Regular weight-bearing exercise.
- Healthy lifestyle, including moderate alcohol consumption (2-3 drinks/day) and no smoking.
- Physical Activity: Maintains or increases bone density to prevent fractures.
- Effects of Exercise: Muscle contraction and mechanical loading stimulate osteoblastic activity to improve body mass density.
Fractures
- A structural break in the continuity of a bone, epiphyseal plate, or cartilaginous joint surface.
- Identification:
- Site (location of fracture).
- Extent (complete or incomplete fracture).
- Configuration (direction of fracture line).
- Relationship to fragments (displaced or undisplaced).
- Relationship to the environment (closed or open - penetratated skin).
- Fracture Types: Transverse, Linear, Oblique, Spiral, Greenstick, Comminuted
Fractures - Risk Factors
- Sudden impact (e.g., trauma, accidents, abuse, assault)
- Osteoporosis (women more than men)
- History of Falls
- Repetitive stress/microtrauma
- Poor health conditions/disease
Fractures - Bone Healing
- Cancellous Bone healing occurs primarily through internal callus formation (endosteal callus). There is a rich blood supply leading to faster healing than dense cortical bone.
- Epiphyseal Plate healing can cause growth disturbances and bony deformity during maturation.
Fractures - Post-Fracture Healing Stages
- Stages include: inflammation, soft callus, hard callus, and bone remodeling phase. The times vary depending on location, type of fracture, soft tissue involvement, and surgical intervention.
Post-Traumatic Immobilization Management
- Local Tissue Response during immobilization can cause weakening of connective tissues, articular cartilage degeneration, muscle atrophy, and contracture development, and sluggish circulation. It is crucial to maintain near-normal conditions.
- Immobilization in Bed: General exercises are key for uninvolved body parts to minimize secondary physiological changes.
- Functional Adaptations: Device choice, gait patterns, and patient functional aptitudes are all important in adapting to immobilization.
Post-Immobilization Management (Impairments)
- Impairments: Postimmobilization can lead to decreased ROM, joint play, muscle flexibility. Muscle atrophy and weakness are potential issues. If soft tissue damage occurred with the fracture, scar tissue can impair mobility. Pain and decrease ROM can occur with movement but the pain should decrease as movement occurs.
- Management:
- Joint Mobilization: Effective for regaining lost joint play without harming articular cartilage and stressing the fracture site.
- PNF Stretching (Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation): Control contraction intensity to prevent resistance or stretch force beyond the fracture site
Post-Immobilization Management (Functional Activities)
- Functional Activities: Resume normal activities with caution. Avoid traumatizing weakened tissues.
- Muscle Performance: Important to apply resistive force proximal to the fracture site until radiological healing occurs. Once healed, more intense dynamic exercises can be initiated.
- Scar Tissue Mobilization: Manual mobilization techniques are used. Technique selection depends on the tissue involved.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.