Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main function of the reproductive systems?
What is the main function of the reproductive systems?
- To enable digestion of food
- To regulate body temperature
- To facilitate breathing in humans
- To continue the human species by producing offspring (correct)
Which process produces gametes with the haploid number of chromosomes?
Which process produces gametes with the haploid number of chromosomes?
- Fertilization
- Binary fission
- Meiosis (correct)
- Mitosis
Where does spermatogenesis occur?
Where does spermatogenesis occur?
- In the uterus
- In the ovaries
- In the prostate gland
- In the seminiferous tubules of the testes (correct)
What role does FSH play in sperm production?
What role does FSH play in sperm production?
What is produced as a result of meiosis in oogenesis?
What is produced as a result of meiosis in oogenesis?
What triggers the secretion of estrogen during oogenesis?
What triggers the secretion of estrogen during oogenesis?
What temperature is optimal for sperm production in the testes?
What temperature is optimal for sperm production in the testes?
How many chromosomes are found in a sperm cell's head?
How many chromosomes are found in a sperm cell's head?
What is the primary function of the seminal vesicles in semen production?
What is the primary function of the seminal vesicles in semen production?
What is the function of the external genitals?
What is the function of the external genitals?
Which hormone is responsible for causing ovulation?
Which hormone is responsible for causing ovulation?
What happens to the primary ovarian follicles that do not mature?
What happens to the primary ovarian follicles that do not mature?
What hormonal changes occur in preparation for milk production during pregnancy?
What hormonal changes occur in preparation for milk production during pregnancy?
How long can an unfertilized ovum survive after its release during ovulation?
How long can an unfertilized ovum survive after its release during ovulation?
What condition is characterized by the enlargement of the prostate in men over age 60?
What condition is characterized by the enlargement of the prostate in men over age 60?
What phase of the menstrual cycle directly follows menstruation?
What phase of the menstrual cycle directly follows menstruation?
The fallopian tubes are instrumental in which process?
The fallopian tubes are instrumental in which process?
What is the main role of the corpus luteum after ovulation?
What is the main role of the corpus luteum after ovulation?
Which treatment is commonly used for prostate cancer?
Which treatment is commonly used for prostate cancer?
Which structure provides support and holds the ovaries in place?
Which structure provides support and holds the ovaries in place?
What is the approximate length of the vagina?
What is the approximate length of the vagina?
What is the primary function of the flagella in sperm?
What is the primary function of the flagella in sperm?
Where do sperm mature and gain functional flagella?
Where do sperm mature and gain functional flagella?
What is the primary role of the seminal vesicles?
What is the primary role of the seminal vesicles?
Which structure surrounds the first inch of the urethra?
Which structure surrounds the first inch of the urethra?
What occurs during ejaculation in terms of smooth muscle contraction?
What occurs during ejaculation in terms of smooth muscle contraction?
What is the purpose of the alkaline secretion from the bulbourethral glands?
What is the purpose of the alkaline secretion from the bulbourethral glands?
How does the penis achieve an erection?
How does the penis achieve an erection?
Which structure is involved in the formation of the ejaculatory duct?
Which structure is involved in the formation of the ejaculatory duct?
What is the main function of the clitoris?
What is the main function of the clitoris?
Which phase of the menstrual cycle involves the shedding of the uterine lining?
Which phase of the menstrual cycle involves the shedding of the uterine lining?
What is the role of Prolactin during lactation?
What is the role of Prolactin during lactation?
Which gland produces milk after pregnancy?
Which gland produces milk after pregnancy?
What is a common consequence of benign prostatic hypertrophy?
What is a common consequence of benign prostatic hypertrophy?
How do lactiferous ducts function in the milk production process?
How do lactiferous ducts function in the milk production process?
What are the two primary hormones that prepare mammary glands for milk production during pregnancy?
What are the two primary hormones that prepare mammary glands for milk production during pregnancy?
What usually triggers benign prostatic hypertrophy?
What usually triggers benign prostatic hypertrophy?
What is the significance of the areola in the breastfeeding process?
What is the significance of the areola in the breastfeeding process?
What treatment is commonly used for prostate cancer in men?
What treatment is commonly used for prostate cancer in men?
What is the primary function of the ductus deferens?
What is the primary function of the ductus deferens?
What is the role of the seminal vesicles in sperm function?
What is the role of the seminal vesicles in sperm function?
Which structure contributes to semen expulsion during ejaculation?
Which structure contributes to semen expulsion during ejaculation?
What is the anatomical location of the ejaculatory ducts?
What is the anatomical location of the ejaculatory ducts?
What is the primary composition of the secretion from the bulbourethral glands?
What is the primary composition of the secretion from the bulbourethral glands?
How does smooth muscle contribute to the function of the ductus deferens?
How does smooth muscle contribute to the function of the ductus deferens?
What is the role of mitochondria in the sperm's middle piece?
What is the role of mitochondria in the sperm's middle piece?
What anatomical feature is described as a natural weak spot in the male reproductive system?
What anatomical feature is described as a natural weak spot in the male reproductive system?
What happens to the penis during sexual stimulation?
What happens to the penis during sexual stimulation?
Which gland secretes an alkaline fluid to promote sperm motility?
Which gland secretes an alkaline fluid to promote sperm motility?
What substances comprise semen?
What substances comprise semen?
Which hormone is responsible for triggering ovulation?
Which hormone is responsible for triggering ovulation?
How long can an ovum survive if it is not fertilized?
How long can an ovum survive if it is not fertilized?
What occurs to the ruptured follicle after ovulation?
What occurs to the ruptured follicle after ovulation?
What is the main function of the fimbrae in the fallopian tubes?
What is the main function of the fimbrae in the fallopian tubes?
What is the typical pH of semen?
What is the typical pH of semen?
How many primary follicles are present at birth?
How many primary follicles are present at birth?
What is the relationship between the ovum and the zygote?
What is the relationship between the ovum and the zygote?
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the uterine structure?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the uterine structure?
What is the primary result of spermatogenesis?
What is the primary result of spermatogenesis?
What role does inhibin play in male reproductive physiology?
What role does inhibin play in male reproductive physiology?
At which stage does oogenesis complete its second meiotic division?
At which stage does oogenesis complete its second meiotic division?
Where does the production of testosterone occur in the male reproductive system?
Where does the production of testosterone occur in the male reproductive system?
What is the main purpose of the diploid to haploid transition during meiosis?
What is the main purpose of the diploid to haploid transition during meiosis?
Which hormone stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles during oogenesis?
Which hormone stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles during oogenesis?
What is the optimal temperature range for sperm production in the testes?
What is the optimal temperature range for sperm production in the testes?
In the process of oogenesis, what happens to the three polar bodies that result from meiosis?
In the process of oogenesis, what happens to the three polar bodies that result from meiosis?
How often is a mature ovum produced in the female reproductive system?
How often is a mature ovum produced in the female reproductive system?
What structures within the testes are responsible for sperm generation?
What structures within the testes are responsible for sperm generation?
Flashcards
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis
The process of sperm cell formation in the testes.
Meiosis
Meiosis
A type of cell division that produces gametes (sperm and egg) with half the number of chromosomes.
Oogenesis
Oogenesis
The process of egg cell formation in the ovaries.
Gametes
Gametes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testes location
Testes location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seminiferous tubules
Seminiferous tubules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Function of Reproductive Systems
Function of Reproductive Systems
Signup and view all the flashcards
FSH and Sperm Production
FSH and Sperm Production
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mitochondria in Sperm
Mitochondria in Sperm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sperm Maturation Location
Sperm Maturation Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ductus Deferens Function
Ductus Deferens Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ejaculatory Duct
Ejaculatory Duct
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seminal Vesicle Role
Seminal Vesicle Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prostate Gland Duty
Prostate Gland Duty
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bulbourethral Gland Act
Bulbourethral Gland Act
Signup and view all the flashcards
Penis Erection Explanation
Penis Erection Explanation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vulva
Vulva
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bartholin's Glands
Bartholin's Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Areola
Areola
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prolactin's Role
Prolactin's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy (BPH)
Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy (BPH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
What's the role of semen?
What's the role of semen?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What's a primary follicle?
What's a primary follicle?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What's ovulation?
What's ovulation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What's a Graafian follicle?
What's a Graafian follicle?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What's the corpus luteum?
What's the corpus luteum?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are fimbriae?
What are fimbriae?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where does fertilization occur?
Where does fertilization occur?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sperm Delivery
Sperm Delivery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Semen Composition
Semen Composition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovaries Location
Ovaries Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary Follicle
Primary Follicle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovulation
Ovulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corpus Luteum
Corpus Luteum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fallopian Tube Function
Fallopian Tube Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fertilization Location
Fertilization Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic Pregnancy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uterus Structure
Uterus Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sperm Maturation
Sperm Maturation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ductus Deferens
Ductus Deferens
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seminal Vesicles
Seminal Vesicles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prostate Gland
Prostate Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bulbourethral Glands
Bulbourethral Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Penis Structure
Penis Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Erection Mechanism
Erection Mechanism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Circumcision
Circumcision
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glans Penis
Glans Penis
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the reproductive systems?
What is the function of the reproductive systems?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does meiosis do?
What does meiosis do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where does spermatogenesis occur?
Where does spermatogenesis occur?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What role does testosterone play in spermatogenesis?
What role does testosterone play in spermatogenesis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the process of oogenesis?
What is the process of oogenesis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is the temperature of the testes slightly lower?
Why is the temperature of the testes slightly lower?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the functions of the sustentacular cells and interstitial cells?
What are the functions of the sustentacular cells and interstitial cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the main parts of a sperm cell?
What are the main parts of a sperm cell?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How many functional sperm cells are produced from one primary spermatocyte?
How many functional sperm cells are produced from one primary spermatocyte?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens when fertilization occurs?
What happens when fertilization occurs?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clitoris
Clitoris
Signup and view all the flashcards
Labia Majora
Labia Majora
Signup and view all the flashcards
Labia Minora
Labia Minora
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mammary Glands
Mammary Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prolactin
Prolactin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxytocin
Oxytocin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prostatic Hypertrophy
Prostatic Hypertrophy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Reproductive Systems Overview
- The reproductive systems enable the continuation of the human species by producing offspring.
- The male and female systems create gametes (sperm and egg cells) and facilitate fertilization.
Meiosis
- Meiosis produces gametes.
- A single cell with 46 chromosomes (diploid number) divides twice to form four cells, each with 23 chromosomes (haploid number).
Spermatogenesis
- This process occurs in the testes.
- Seminiferous tubules contain spermatogonia (sperm-generating cells).
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) initiates sperm production.
- Luteinizing hormone (LH) stimulates testosterone secretion, promoting sperm maturation.
- Inhibin regulates FSH secretion.
- Each primary spermatocyte produces four functional sperm cells through meiosis.
- Sperm production begins at puberty and continues throughout a man's life.
Oogenesis
- Oogenesis is the process for egg cell formation, occurring in the ovaries.
- Oogenesis is regulated by hormones.
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates ovarian follicle growth, which contains an oogonium (egg-generating cell).
- Only one functional egg is produced from a primary oocyte; the other three cells are polar bodies that deteriorate.
- FSH triggers follicle cells to secrete estrogen, promoting ovum maturation.
- A mature ovarian follicle also contains a secondary oocyte; the second meiotic division occurs only if fertilization takes place.
- Egg production begins at puberty and continues until menopause.
- Egg release is cyclical, with a mature ovum produced roughly every 28 days.
Testes
- The testes are located in the scrotum.
- The temperature in the scrotum is slightly lower than body temperature, which is necessary for sperm production.
- In the male fetus, the testes develop near the kidneys and descend into the scrotum before birth.
- Testes are divided into lobes, each containing seminiferous tubules where spermatogenesis occurs.
- Sustentacular cells produce inhibin, stimulated by testosterone.
- Interstitial cells produce testosterone when stimulated by luteinizing hormone (LH).
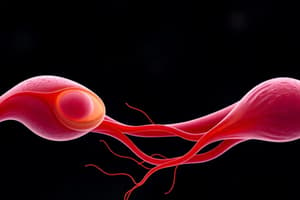
Sperm
- Sperm have 23 chromosomes.
- The acrosome (head) contains enzymes to digest the egg's membrane.
- The middle piece contains mitochondria for ATP production.
- The flagella provide motility.
- Sperm from seminiferous tubules enter a network called rete testis and then the epididymis.
Epididymis
- A 20-foot long coiled tube on the posterior of each testis, sperm complete maturation here and flagella become functional.
- Smooth muscle propels sperm into the ductus deferens.
Ductus Deferens
- Also called the vas deferens.
- Extends from the epididymis in the scrotum into the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal.
- The inguinal canal is a natural weak spot (susceptible to hernia formation).
- Once inside the abdominal cavity, the ductus deferens travels over the urinary bladder, then to the posterior side, to join the ejaculatory duct.
- Smooth muscle in the ductus deferens contracts in waves (peristalsis) during ejaculation.
Ejaculatory Ducts
- Sperm from the ductus deferens and secretions from the seminal vesicles enter and empty into the urethra.
Seminal Vesicles
- Located posterior to the bladder.
- The secretion contains fructose for sperm energy and is alkaline to enhance sperm motility.
- Each duct joins the ductus deferens on its side to form the ejaculatory duct.
Prostate
- A muscular gland below the urinary bladder.
- It surrounds the first inch of the urethra.
- Glands secrete alkaline fluid to maintain sperm motility.
- The smooth prostate muscle contracts to aid semen expulsion from the urethra.
Bulbourethral Glands
- Also called Cowper's glands.
- Located below the prostate and empty into the urethra.
- The alkaline secretion coats the urethra before ejaculation, neutralizing any acidic urine.
Urethra - Penis
- The urethra is the final duct for semen travel with the longest section enclosed within the penis.
- The penis is the external male genital organ.
- The distal end of the penis is the glans penis, covered in foreskin (circumcision).
- The penis contains three masses of cavernous tissue (blood sinuses, smooth muscle, connective tissue).
- Blood flow to these tissues diminishes making the penis flaccid, and is stimulated by parasympathetic activity.
- Increased blood flow during stimulation causes the penis to become erect and firm (in parasympathetic activity).
- This allows the penis to penetrate the vagina and deposit sperm.
- Ejaculation is the culmination of this process.
Semen
- Semen comprises sperm and secretions from seminal vesicles, prostate, and bulbourethral glands.
- Semen has a pH of 7.4.
- Typical ejaculation expels 2-4 mL of semen.
- Each mL typically contains 100 million sperm.
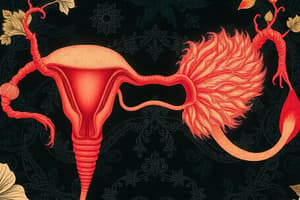
Female Reproductive System
- Ovaries are a pair of oval structures located on either side of the uterus in the pelvic cavity.
- The broad ligament supports the ovaries.
- Several hundred thousand primary follicles are present at birth.
- Typically 300-400 mature.
- Each primary ovarian follicle contains an oocyte, a potential egg.
- Follicle cells surround oocytes secreting estrogen.
- Mature follicle may also be called a Graafian follicle.
- LH triggers ovulation (rupture of mature follicle and release of ovum).
- Other developing follicles degenerate.
- Rupture follicle transforms to corpus luteum, secreting progesterone and estrogen.
Fallopian Tubes
- 4 inches long, lateral end encloses ovary, fimbriae creating current pulling ovum into fallopian tube.
- The medial end opens into the uterus.
- Smooth muscle causes peristalsis, the mucosa is ciliated to sweep the ovum to the uterus.
- Fertilization takes place in the fallopian tube.
- If the ovum isn't fertilized, it dies within 24-48 hours and disintegrates.
- If fertilized, the ovum becomes a zygote and is swept into the uterus over 4–5 days.
Uterus
- 3 inches long by 2 inches wide.
- Superior to the urinary bladder and between the two ovaries in the pelvic cavity.
- The broad ligament covers the uterus.
Vagina
- Muscular tube 4 inches long.
- It extends from the cervix to the vaginal orifice in the perineum (pelvic floor).
- It is posterior to the urethra and anterior to the rectum.
- The hymen (partially covering it initially) is ruptured with sexual intercourse.
- Functions include receiving sperm, menstrual blood flow exit, and birth canal.
External Genitals
- Also known as vulva.
- Features include the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, and Bartholin's glands.
Mammary Glands
- Produce milk for offspring.
- Glandular tissue is surrounded by adipose (fat) tissue, alveolar glands produce milk after pregnancy, entering lactiferous ducts and converging at the nipple.
- Areola is the skin around the nipple.
Prolactin and Oxytocin
- Hormones essential for milk production and release.
Menstrual Cycle
- A cycle of about 28 days.
- Key phases include menstrual, follicular, and luteal.
- Hormonal regulation is crucial during the phases.
- Reduction of body fat can lead to amenorrhea.
Prostatic Hypertrophy
- Enlargement of the prostate.
- Benign prostatic hypertrophy is common in men over age 60.
- An enlarged prostate compresses the urethra, potentially causing urination difficulties or urinary retention.
Cancer of Prostate
- 2nd most common cancer in men, usually occurring after age 50.
- Treatment options include prostate removal, radiation, or hormone therapy to reduce testosterone production.
Other Important Concepts
- Normal vaginal flora creates an acidic pH to inhibit pathogen growth.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.