Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the zona pellucida?
What is the primary function of the zona pellucida?
- To act as a barrier against multiple sperm (correct)
- To assist in the cleavage divisions
- To aid in sperm motility
- To provide nutrients to the oocyte
What role do cortical granules play after sperm interaction with the oocyte?
What role do cortical granules play after sperm interaction with the oocyte?
- They enhance oocyte nutrition during development
- They contribute to the formation of the tail of the sperm
- They initiate cortical reaction to prevent multiple fertilizations (correct)
- They are involved in the cleavage stages of the zygote
Which of the following statements about the sperm structure is NOT correct?
Which of the following statements about the sperm structure is NOT correct?
- The head contains mitochondria (correct)
- The midpiece is packed with organelles for energy
- The tail aids in motility
- The head contains genetic material
What happens to the zona pellucida after fertilization?
What happens to the zona pellucida after fertilization?
What is the first stage of development that occurs after fertilization?
What is the first stage of development that occurs after fertilization?
What marks the beginning of human fertilization?
What marks the beginning of human fertilization?
Which stage of oogenesis results in the release of a secondary oocyte?
Which stage of oogenesis results in the release of a secondary oocyte?
What occurs during sperm capacitation?
What occurs during sperm capacitation?
What is the purpose of the cortical reaction during fertilization?
What is the purpose of the cortical reaction during fertilization?
Which process occurs first after sperm binds to the zona pellucida?
Which process occurs first after sperm binds to the zona pellucida?
What is the significance of sperm traversing through the female reproductive tract?
What is the significance of sperm traversing through the female reproductive tract?
Which structure helps sperm penetrate the zona pellucida?
Which structure helps sperm penetrate the zona pellucida?
What is the result of the union of sperm and egg nuclei?
What is the result of the union of sperm and egg nuclei?
Flashcards
Zona Pellucida and Granulosa Cells
Zona Pellucida and Granulosa Cells
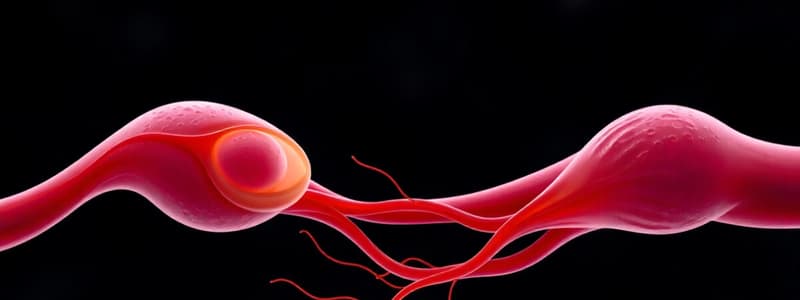
The oocyte is covered by a protective layer called the zona pellucida, surrounded by granulosa cells. These layers are important for oocyte development and prevent multiple sperm from entering.
Sperm Structure
Sperm Structure
The sperm consists of three main parts: the head, which carries the genetic material (DNA), the midpiece, packed with mitochondria to provide energy for movement, and the tail, which acts like a flagellum enabling it to swim.
Cortical Granules and Cortical Reaction
Cortical Granules and Cortical Reaction
Cortical granules are tiny sacs located within the oocyte's cytoplasm. Upon sperm interaction, these granules release their contents, causing a change in the zona pellucida, preventing other sperm from entering. This is called the cortical reaction.
Transformation of the Zona Pellucida
Transformation of the Zona Pellucida
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blastomere Formation and Zona Pellucida
Blastomere Formation and Zona Pellucida
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oogenesis
Oogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovulation
Ovulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Capacitation
Capacitation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Penetration of the Zona Pellucida
Penetration of the Zona Pellucida
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acrosome Reaction
Acrosome Reaction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fusion of Sperm and Egg Membranes
Fusion of Sperm and Egg Membranes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cortical Reaction
Cortical Reaction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Human Fertilization: Stages and Changes
- Fertilization Definition: The union of an ovum (egg) and sperm, creating a zygote. This initiates pregnancy.
Stages of Fertilization
- Preparation:
- Oogenesis: Ovary develops immature eggs (oocytes) through stages (primordial, secondary, Graafian follicle) leading to ovulation.
- Spermatogenesis: Testes produce sperm (spermatozoa) from spermatogonia during puberty.
- Ovulation:
- Ovulation Phase: Mature ovarian follicle (Graafian) bursts, releasing a secondary oocyte (ovum) into the peritoneal cavity, typically midway through the menstrual cycle.
- Histological Changes: LH surge triggers follicle wall degeneration; granulosa cells reorganize to form the corpus luteum.
- Sperm Journey:
- Ejaculation and Capacitation: Sperm ejaculated into female tract, undergo capacitation (chemical changes) enhancing motility and zona pellucida penetration.
- Travel: Sperm travel through cervix, uterus, and into fallopian tubes for fertilization.
- Fertilization:
- Zona Pellucida Penetration: Sperm binds to zona pellucida (glycoprotein layer), assisted by receptors and enzymes (e.g., acrosin).
- Acrosome Reaction: Acrosome (sperm head cap) releases enzymes to digest zona pellucida, allowing sperm entry.
- Fusion: Sperm and egg membranes fuse; sperm nucleus enters egg.
- Block to Polyspermy:
- Cortical Reaction: Cortical granules (in egg cytoplasm) release contents, changing zona pellucida structure preventing multiple sperm entry.
- Zygote Formation:
- Nuclei Union: Sperm and egg nuclei unite, forming a zygote with a diploid set of chromosomes.
Histological Changes
- Oocyte: Protected by zona pellucida and granulosa cells (support and barrier).
- Sperm: Head (DNA), midpiece (mitochondria), tail (flagellum for motility).
- Cortical Granules: In oocyte cytoplasm, crucial for cortical reaction, preventing polyspermy.
- Zona Pellucida Transformation: Zona pellucida changes structure post-fertilization (due to enzymes).
- Blastomere Formation: Zygote divides, initially producing two-cell and four-cell stages preserving zona pellucida until implantation.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.