Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the primary organs responsible for sperm production in the male reproductive system?
What are the primary organs responsible for sperm production in the male reproductive system?
- Vas deferens
- Seminal vesicles
- Epididymis
- Testes (correct)
In which phase of the menstrual cycle does ovulation typically occur?
In which phase of the menstrual cycle does ovulation typically occur?
- Menstrual Phase
- Follicular Phase
- Luteal Phase
- Ovulation Phase (correct)
Which of the following methods is classified as a barrier contraceptive method?
Which of the following methods is classified as a barrier contraceptive method?
- Condoms (correct)
- Withdrawal
- Birth control pills
- IUDs
What is the main purpose of the prostate gland in the male reproductive system?
What is the main purpose of the prostate gland in the male reproductive system?
What hormone is primarily responsible for regulating the female menstrual cycle?
What hormone is primarily responsible for regulating the female menstrual cycle?
During which trimester of pregnancy does organ formation primarily occur?
During which trimester of pregnancy does organ formation primarily occur?
What is the process by which a sperm cell penetrates an egg called?
What is the process by which a sperm cell penetrates an egg called?
Which sexually transmitted infection is NOT commonly associated with potential long-term complications?
Which sexually transmitted infection is NOT commonly associated with potential long-term complications?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Reproductive System Overview
- Definition: The reproductive system is responsible for producing offspring and includes organs and structures that facilitate reproduction.
Male Reproductive System
-
Primary Organs:
- Testes: Produce sperm and testosterone.
- Epididymis: Stores and matures sperm.
- Vas deferens: Transports sperm from epididymis to urethra.
- Seminal vesicles: Produce seminal fluid.
- Prostate gland: Adds fluid to semen.
- Penis: Delivers sperm to female reproductive tract.
-
Spermatogenesis:
- Process of sperm production in the testes.
- Occurs in seminiferous tubules.
- Takes approximately 64-72 days.
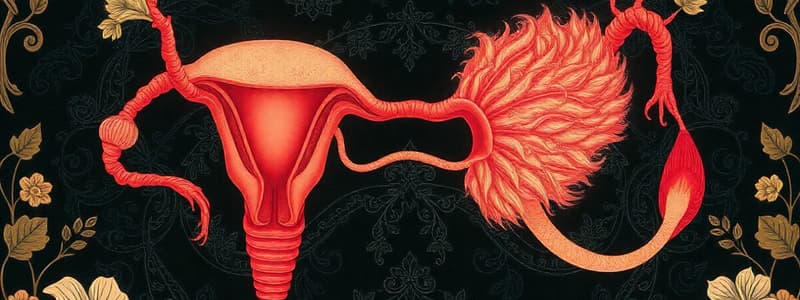
Female Reproductive System
-
Primary Organs:
- Ovaries: Produce eggs (ova) and hormones (estrogen, progesterone).
- Fallopian tubes: Transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus.
- Uterus: Houses and nourishes the developing fetus.
- Vagina: Serves as the birth canal and receives sperm.
-
Oogenesis:
- Process of egg production in the ovaries.
- Begins before birth, resumes at puberty.
- Each menstrual cycle typically releases one mature egg.
Menstrual Cycle
- Phases:
- Menstrual Phase: Shedding of the uterine lining.
- Follicular Phase: Follicle develops in the ovary, estrogen levels rise.
- Ovulation: Release of a mature egg; occurs around day 14.
- Luteal Phase: The body prepares for potential pregnancy; if no fertilization occurs, the cycle restarts.
Fertilization
- Process: Occurs when a sperm cell penetrates an egg, forming a zygote.
- Location: Typically takes place in the fallopian tube.
Pregnancy
- Stages:
- First Trimester: Organ formation, embryo development.
- Second Trimester: Continued growth and development; organs mature.
- Third Trimester: Final growth; preparing for childbirth.
Contraceptive Methods
- Barrier Methods: Condoms, diaphragms.
- Hormonal Methods: Birth control pills, patches, injections.
- Intrauterine Devices (IUDs): Prevent implantation.
- Natural Methods: Tracking menstrual cycle, withdrawal.
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
- Common STIs: Chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, HIV.
- Prevention: Safe sex practices, regular screening, vaccination.
Reproductive Health
- Importance: Regular check-ups, screenings (Pap smears, prostate exams), education on reproductive health rights.
Key Hormones
- Estrogen: Regulates female reproductive system, menstrual cycle.
- Progesterone: Prepares uterus for pregnancy.
- Testosterone: Regulates male reproductive system and development of male characteristics.
Summary
The reproductive system encompasses complex processes essential for sexual reproduction, including gametogenesis, fertilization, and pregnancy, alongside various health considerations and contraceptive methods essential for responsible reproductive health management.
Reproductive System Overview
- The reproductive system is responsible for producing offspring.
- It consists of organs and structures that facilitate reproduction.
Male Reproductive System
- Testes: produce sperm and testosterone.
- Epididymis: stores and matures sperm.
- Vas deferens: transports sperm from the epididymis to the urethra.
- Seminal vesicles: produce seminal fluid.
- Prostate gland: adds fluid to semen.
- Penis: delivers sperm to the female reproductive tract.
- Spermatogenesis: the process of sperm production in the testes.
- Takes place in seminiferous tubules.
- Takes approximately 64-72 days.
Female Reproductive System
- Ovaries: produce eggs (ova) and hormones (estrogen, progesterone).
- Fallopian tubes: transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus.
- Uterus: houses and nourishes the developing fetus.
- Vagina: serves as the birth canal and receives sperm.
- Oogenesis: the process of egg production in the ovaries.
- Begins before birth.
- Resumes at puberty.
- Each menstrual cycle typically releases one mature egg.
Menstrual Cycle
- Menstrual Phase: shedding of the uterine lining.
- Follicular Phase: follicle develops in the ovary, estrogen levels rise.
- Ovulation: release of a mature egg; occurs around day 14.
- Luteal Phase: the body prepares for potential pregnancy; if no fertilization occurs, the cycle restarts.
Fertilization
- Occurs when a sperm cell penetrates an egg, forming a zygote.
- Typically takes place in the fallopian tube.
Pregnancy
- First Trimester: organ formation, embryo development.
- Second Trimester: continued growth and development; organs mature.
- Third Trimester: final growth; preparing for childbirth.
Contraceptive Methods
- Barrier Methods: condoms, diaphragms.
- Hormonal Methods: birth control pills, patches, injections.
- Intrauterine Devices (IUDs): prevent implantation.
- Natural Methods: tracking menstrual cycle, withdrawal.
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
- Common STIs: Chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, HIV.
- Prevention: safe sex practices, regular screening, vaccination.
Reproductive Health
- Importance: regular check-ups, screenings (Pap smears, prostate exams), education on reproductive health rights.
Key Hormones
- Estrogen: regulates the female reproductive system, menstrual cycle.
- Progesterone: prepares the uterus for pregnancy.
- Testosterone: regulates the male reproductive system and development of male characteristics.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.