Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary effect of parathyroid hormone (PTH) on the kidneys?
What is the primary effect of parathyroid hormone (PTH) on the kidneys?
- Inhibits reabsorption of calcium and increases excretion.
- Enhances calcium reabsorption and stimulates calcitriol production. (correct)
- Stimulates the secretion of calcitonin to lower blood calcium levels.
- Reduces glucose levels through increased insulin release.
Which hormone is stimulated by low blood pressure and acts on the kidneys to increase sodium reabsorption?
Which hormone is stimulated by low blood pressure and acts on the kidneys to increase sodium reabsorption?
- Cortisol
- Epinephrine
- Aldosterone (correct)
- Oxytocin
Which cell type produces T3 and T4 in the thyroid gland?
Which cell type produces T3 and T4 in the thyroid gland?
- Follicular cells (correct)
- Chief cells
- Chromaffin cells
- Parafollicular cells
What triggers the release of epinephrine and norepinephrine from the adrenal medulla?
What triggers the release of epinephrine and norepinephrine from the adrenal medulla?
What effect does calcitonin have on bones?
What effect does calcitonin have on bones?
What is the primary function of the interstitial cells in the ovaries?
What is the primary function of the interstitial cells in the ovaries?
Which layer of the uterus is primarily responsible for contractions during labor?
Which layer of the uterus is primarily responsible for contractions during labor?
In the uterine tubes, which type of cell is responsible for moving the oocyte toward the uterus?
In the uterine tubes, which type of cell is responsible for moving the oocyte toward the uterus?
What role does the endometrium play during the menstrual cycle?
What role does the endometrium play during the menstrual cycle?
Which structure connects the ovary to the pelvic wall?
Which structure connects the ovary to the pelvic wall?
What is the primary function of the ovarian ligament?
What is the primary function of the ovarian ligament?
Which layer provides outer protection and support for the uterine structure?
Which layer provides outer protection and support for the uterine structure?
How many segments make up the urethra in individuals assigned male at birth?
How many segments make up the urethra in individuals assigned male at birth?
What type of epithelium does the urethra in individuals assigned female at birth transition to?
What type of epithelium does the urethra in individuals assigned female at birth transition to?
Which structure collects urine from the kidneys and transports it to the urinary bladder?
Which structure collects urine from the kidneys and transports it to the urinary bladder?
Which of the following is NOT one of the structural layers that protect the kidneys?
Which of the following is NOT one of the structural layers that protect the kidneys?
What is the first blood vessel that blood passes through on its way to the kidneys?
What is the first blood vessel that blood passes through on its way to the kidneys?
During the storage phase of the urination process, what role does the sympathetic nervous system play?
During the storage phase of the urination process, what role does the sympathetic nervous system play?
Which structure is primarily responsible for the filtration of blood in the kidneys?
Which structure is primarily responsible for the filtration of blood in the kidneys?
What type of connective tissue forms the fibrous capsule surrounding the kidneys?
What type of connective tissue forms the fibrous capsule surrounding the kidneys?
What are retroperitoneal organs specifically described as?
What are retroperitoneal organs specifically described as?
What type of hormone is derived from cholesterol?
What type of hormone is derived from cholesterol?
Which gland secretes hormones directly into the bloodstream?
Which gland secretes hormones directly into the bloodstream?
Which hormone is released by the anterior pituitary and stimulates cortisol production?
Which hormone is released by the anterior pituitary and stimulates cortisol production?
What is the main function of Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH)?
What is the main function of Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH)?
Which of the following describes the nature of polypeptides?
Which of the following describes the nature of polypeptides?
What triggers the release of Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)?
What triggers the release of Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)?
The typical response of the anterior pituitary to releasing hormones from the hypothalamus is to:
The typical response of the anterior pituitary to releasing hormones from the hypothalamus is to:
Which hormone is involved in the physiological response during uterine stretching or breastfeeding?
Which hormone is involved in the physiological response during uterine stretching or breastfeeding?
What is a primary role of the hormones produced by the hypothalamus?
What is a primary role of the hormones produced by the hypothalamus?
Which of the following correctly defines endocrine glands?
Which of the following correctly defines endocrine glands?
What is the primary function of the glomerulus in the nephron?
What is the primary function of the glomerulus in the nephron?
Which type of nephron is primarily located in the renal cortex and has a shorter nephron loop?
Which type of nephron is primarily located in the renal cortex and has a shorter nephron loop?
What is the role of macula densa cells within the nephron?
What is the role of macula densa cells within the nephron?
Which structure collects the filtrate from the glomerular capsule?
Which structure collects the filtrate from the glomerular capsule?
What type of epithelium lines the distal convoluted tubule?
What type of epithelium lines the distal convoluted tubule?
What is the significance of the juxtamedullary nephrons?
What is the significance of the juxtamedullary nephrons?
What occurs in the papillary ducts of the collecting system?
What occurs in the papillary ducts of the collecting system?
What mechanism does the parasympathetic system utilize during urination?
What mechanism does the parasympathetic system utilize during urination?
Which part of the nephron directly connects the renal corpuscle to the collecting system?
Which part of the nephron directly connects the renal corpuscle to the collecting system?
What is the main purpose of the filtration process in the glomerular capillaries?
What is the main purpose of the filtration process in the glomerular capillaries?
What hormone is primarily responsible for maintaining the uterus during pregnancy?
What hormone is primarily responsible for maintaining the uterus during pregnancy?
Which structure connects the body of the uterus to the cervix?
Which structure connects the body of the uterus to the cervix?
Which cell type in the uterine tubes secretes mucus to nourish the oocyte?
Which cell type in the uterine tubes secretes mucus to nourish the oocyte?
What is the primary histological feature of the endometrium during the menstrual cycle?
What is the primary histological feature of the endometrium during the menstrual cycle?
Which ligament anchors the ovary to the uterus?
Which ligament anchors the ovary to the uterus?
What is a function of the myometrium layer of the uterus?
What is a function of the myometrium layer of the uterus?
What role does the broad ligament serve in the female reproductive system?
What role does the broad ligament serve in the female reproductive system?
What is the primary role of the posterior pituitary?
What is the primary role of the posterior pituitary?
Which hormone primarily aids in increasing blood glucose levels?
Which hormone primarily aids in increasing blood glucose levels?
How does the anterior pituitary receive hormone signals?
How does the anterior pituitary receive hormone signals?
What is one of the functions of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)?
What is one of the functions of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)?
What distinguishes the autonomic nervous system from the endocrine system?
What distinguishes the autonomic nervous system from the endocrine system?
Which hormone is responsible for stimulating contractions during childbirth?
Which hormone is responsible for stimulating contractions during childbirth?
What effect does aldosterone primarily have on the kidneys?
What effect does aldosterone primarily have on the kidneys?
What is the main target for the hormone calcitonin?
What is the main target for the hormone calcitonin?
Which hormone is released in response to high blood glucose levels?
Which hormone is released in response to high blood glucose levels?
Which functional change occurs in the endometrium during the uterine cycle?
Which functional change occurs in the endometrium during the uterine cycle?
What is the primary function of the Leydig cells in the male reproductive system?
What is the primary function of the Leydig cells in the male reproductive system?
What is the primary role of cortisol in the body?
What is the primary role of cortisol in the body?
Which cells in the pancreas secrete glucagon?
Which cells in the pancreas secrete glucagon?
What distinguishes the basal layer of the endometrium during the menstrual cycle?
What distinguishes the basal layer of the endometrium during the menstrual cycle?
Which pathway does sperm follow from the testes to ejaculation?
Which pathway does sperm follow from the testes to ejaculation?
What triggers the release of parathyroid hormone (PTH)?
What triggers the release of parathyroid hormone (PTH)?
What type of cells produce T3 and T4 in the thyroid gland?
What type of cells produce T3 and T4 in the thyroid gland?
What is the main role of the prostate gland in male reproductive physiology?
What is the main role of the prostate gland in male reproductive physiology?
Where does sperm maturation primarily take place?
Where does sperm maturation primarily take place?
What is the effect of epinephrine on the body during stress?
What is the effect of epinephrine on the body during stress?
Which of the following hormones lowers blood calcium levels?
Which of the following hormones lowers blood calcium levels?
What type of epithelium is primarily found in the functional layer of the endometrium?
What type of epithelium is primarily found in the functional layer of the endometrium?
What is the primary purpose of sperm mixing with seminal fluid in the ejaculatory duct?
What is the primary purpose of sperm mixing with seminal fluid in the ejaculatory duct?
Which of the following statements about the basal layer of the endometrium is true?
Which of the following statements about the basal layer of the endometrium is true?
Which layer of connective tissue provides the primary structural support for the kidneys?
Which layer of connective tissue provides the primary structural support for the kidneys?
What segment of the urethra is not found in individuals assigned female at birth?
What segment of the urethra is not found in individuals assigned female at birth?
Which structure is shared between the urinary and reproductive tracts in individuals assigned male at birth?
Which structure is shared between the urinary and reproductive tracts in individuals assigned male at birth?
What is the correct order of blood flow through the kidneys starting from the abdominal aorta?
What is the correct order of blood flow through the kidneys starting from the abdominal aorta?
During the storage phase of urination, which system's action maintains the bladder's relaxed state?
During the storage phase of urination, which system's action maintains the bladder's relaxed state?
How many distinct segments does the urethra contain in individuals assigned male at birth?
How many distinct segments does the urethra contain in individuals assigned male at birth?
What type of epithelium lines the urethra in individuals assigned male at birth after the transitional stage?
What type of epithelium lines the urethra in individuals assigned male at birth after the transitional stage?
What type of fat provides protective padding for the kidneys?
What type of fat provides protective padding for the kidneys?
What is the final structure that urine passes through before exiting the body?
What is the final structure that urine passes through before exiting the body?
What anatomical feature is responsible for the filtration of blood within the kidney?
What anatomical feature is responsible for the filtration of blood within the kidney?
Flashcards
Oocyte Production
Oocyte Production
The process of producing eggs (oocytes) for fertilization. This is one of the primary functions of the ovaries.
Estrogen
Estrogen
Hormones secreted by the ovaries that support sexual and reproductive development. It is responsible for female characteristics like breast development and menstrual cycles.
Progesterone
Progesterone
A hormone produced by the ovaries that mainly prepares the uterus for pregnancy. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the uterine lining during pregnancy.
Follicles
Follicles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endometrium
Endometrium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myometrium
Myometrium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fundus
Fundus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Voiding Phase
Voiding Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nephron
Nephron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerulus
Glomerulus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bowman's Capsule
Bowman's Capsule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Tubule
Renal Tubule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Descending Tubule
Descending Tubule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nephron Loop
Nephron Loop
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ascending Tubule
Ascending Tubule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Collecting System
Collecting System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testosterone Production
Testosterone Production
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urethra Anatomy (Sex Differences)
Urethra Anatomy (Sex Differences)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal Urethral Sphincter
Internal Urethral Sphincter
Signup and view all the flashcards
External Urethral Sphincter
External Urethral Sphincter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Organs of the Urinary System
Organs of the Urinary System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Retroperitoneal Organs
Retroperitoneal Organs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Protection
Kidney Protection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Flow through the Kidney
Blood Flow through the Kidney
Signup and view all the flashcards
Storage Phase of Urination
Storage Phase of Urination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Receptor Binding
Receptor Binding
Signup and view all the flashcards
Signal Activation
Signal Activation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Response Generation
Response Generation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amines
Amines
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polypeptides
Polypeptides
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glycoproteins
Glycoproteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Steroids
Steroids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endocrine Glands
Endocrine Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exocrine Glands
Exocrine Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Releasing Hormones
Releasing Hormones
Signup and view all the flashcards
T3/T4 (Triiodothyronine and Thyroxine)
T3/T4 (Triiodothyronine and Thyroxine)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mineralocorticoids (e.g., Aldosterone)
Mineralocorticoids (e.g., Aldosterone)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucocorticoids (e.g., Cortisol)
Glucocorticoids (e.g., Cortisol)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Insulin and Glucagon
Insulin and Glucagon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oocyte Maturation
Oocyte Maturation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovarian Follicles
Ovarian Follicles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uterine Fundus
Uterine Fundus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uterine Isthmus
Uterine Isthmus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cervix
Cervix
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basal Layer
Basal Layer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functional Layer
Functional Layer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testes
Testes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epididymis
Epididymis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vas Deferens
Vas Deferens
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ejaculatory Ducts
Ejaculatory Ducts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prostate Gland
Prostate Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Leydig Cells
Leydig Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urethra
Urethra
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibrous Capsule
Fibrous Capsule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Voiding Phase of Urination
Voiding Phase of Urination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urine Formation
Urine Formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucagon
Glucagon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypothalamus-Pituitary Complex
Hypothalamus-Pituitary Complex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypophyseal Portal System
Hypophyseal Portal System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior Pituitary
Posterior Pituitary
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anterior Pituitary
Anterior Pituitary
Signup and view all the flashcards
TRH (Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone)
TRH (Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aldosterone
Aldosterone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cortisol
Cortisol
Signup and view all the flashcards
Insulin
Insulin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Calcitonin
Calcitonin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Insulin
Insulin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Learning Outcomes
- State the functions and histological features of ovaries, uterine tubes, and the uterus.
- Differentiate between the layers of the uterine wall and specify changes during the uterine cycle.
- Recall the structures sperm passes through from formation to ejaculation.
- Recall cells/structures that produce testosterone.
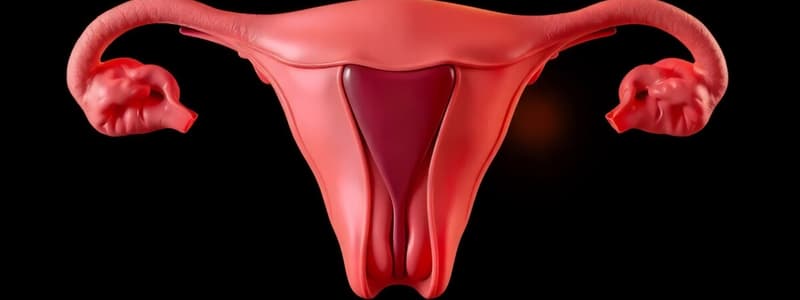
Ovaries
- Functions:
- Oocyte production for fertilization.
- Hormone secretion (estrogen and progesterone).
- Histological Features:
- Follicles containing oocytes at various stages.
- Interstitial cells secreting hormones (estrogen and progesterone).
- Support Structures:
- Ovarian ligament anchors the ovary to the uterus.
- Suspensory ligament connects the ovary to the pelvic wall.
- Mesovarium supports the ovary within the broad ligament.
Uterine Tubes (Fallopian Tubes)
- Functions:
- Oocyte transport from the ovary to the uterus.
- Fertilization site (typically where fertilization occurs).
- Histological Features:
- Mucosal layer with ciliated cells for oocyte movement and non-ciliated cells for nourishment.
- Muscularis layer for peristalsis.
Uterus
- Functions:
- Protection and nutrition for the developing embryo/fetus.
- Waste removal.
- Histological Features:
- Endometrium (innermost layer): Site of implantation and cycle changes.
- Myometrium (muscular layer): Contracts during labor.
- Perimetrium (outer serous layer).
- Regions:
- Fundus (upper portion above fallopian tubes).
- Body (main portion where embryo implants).
- Isthmus (narrow portion connecting body and cervix).
- Cervix (lower portion connecting to vagina), including the isthmus portion.
- Supporting structures include broad ligament, which is involved in anchoring the uterus, uterine tubes, and ovaries. Supporting structures also include the pelvic floor muscles.
Structures Passed by Sperm (Formation to Ejaculation)
- Testes: Location in scrotum, sperm production in seminiferous tubules.
- Epididymis: Sperm maturation and storage.
- Vas Deferens (Ductus Deferens): Transports sperm to ejaculatory ducts.
- Ejaculatory Ducts: Formed by union of vas deferens and seminal vesicle ducts.
- Prostate Gland: Adds fluid to semen for nourishment and protection from acidity.
- Urethra: Carries semen to external opening.
Cells Producing Testosterone
- Leydig cells (Interstitial cells): Located between seminiferous tubules in the testes, produce and secrete testosterone in response to luteinizing hormone (LH).
Urinary System
- Organs: Kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra.
- Kidney Structures: Renal artery and vein, nephrons (including glomerulus, glomerular capsule, proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule, collecting duct,), renal pelvis, capsule.
- Nephrons: Responsible for urine formation (filtration, reabsorption, and secretion). Filtrate is formed and passes through the convoluted tubules for further processing, which involves reabsorption and secretion.
- Urine Transport: From ureters to bladder for storage, then to the urethra for elimination. The pathway includes the renal pelvis, minor calyces, major calyces, then to the ureter.
- Kidney Protection: Surrounding structures and fat pads provide protection. These include the fibrous capsule (connective tissue); paranephric fat and renal fascia.
Endocrine System
- Hormones: Chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands.
- Hormone function: Regulate metabolism, growth, reproduction, internal stability, and other body functions.
- Hormone Classification: Amines, polypeptides, proteins, glycoproteins, steroids (e.g., cortisol, TSH, ADH, insulin).
- Hormone Action: Hormone binds to specific receptors (on or within target cells to cause effects.)
- Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamus, anterior pituitary, posterior pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid. adrenal cortex and medulla, pancreas, testes, ovaries, and other glands.
- Hormone Regulation: Negative feedback loops (e.g., regulate hormone levels).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.