Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the glomerular wall?
What is the primary function of the glomerular wall?
- To act as an ultrafilter for the blood (correct)
- To store nutrients
- To regulate blood pressure
- To synthesize proteins
What is the function of the filtration slits?
What is the function of the filtration slits?
- To form a barrier for filtration (correct)
- To regulate blood flow
- To aid in absorption
- To filter out large molecules
What is the purpose of the Bowman's space?
What is the purpose of the Bowman's space?
- To store the ultrafiltrate (correct)
- To filter out waste products
- To aid in absorption
- To regulate blood pressure
What is the name of the structure that surrounds the glomerulus?
What is the name of the structure that surrounds the glomerulus?
What is the function of the peritubular capillaries?
What is the function of the peritubular capillaries?
What is the name of the system that regulates blood pressure?
What is the name of the system that regulates blood pressure?
What is the function of the efferent arteriole?
What is the function of the efferent arteriole?
What is the name of the membrane that the plasma filtrate must pass through?
What is the name of the membrane that the plasma filtrate must pass through?
What is the primary function of the kidneys?
What is the primary function of the kidneys?
How many nephrons are present in each kidney?
How many nephrons are present in each kidney?
What are the two types of nephrons?
What are the two types of nephrons?
What is the function of cortical nephrons?
What is the function of cortical nephrons?
What is the location of the kidneys in the human body?
What is the location of the kidneys in the human body?
What is the approximate length of an adult human kidney?
What is the approximate length of an adult human kidney?
What are the four components of the urinary system?
What are the four components of the urinary system?
What is the first step in urine formation?
What is the first step in urine formation?
What is the primary function of the filtration process in the glomerular capillaries?
What is the primary function of the filtration process in the glomerular capillaries?
What is the role of transport proteins in the nephron cells?
What is the role of transport proteins in the nephron cells?
What is the term for the fluid that is filtered out of the blood in the glomerular capillaries?
What is the term for the fluid that is filtered out of the blood in the glomerular capillaries?
What is the main function of tubular reabsorption?
What is the main function of tubular reabsorption?
What is the term for the process by which the kidney regulates the amount of water in the body?
What is the term for the process by which the kidney regulates the amount of water in the body?
What is the role of the kidney in maintaining overall health?
What is the role of the kidney in maintaining overall health?
What is the term for the process by which the kidney produces a hormone that stimulates the production of red blood cells?
What is the term for the process by which the kidney produces a hormone that stimulates the production of red blood cells?
What is the term for the process by which the kidney removes waste products from the body?
What is the term for the process by which the kidney removes waste products from the body?
What percentage of blood pumped by the heart goes to the kidneys?
What percentage of blood pumped by the heart goes to the kidneys?
What is the primary function of peritubular capillaries?
What is the primary function of peritubular capillaries?
Where does the final urinary composition take place?
Where does the final urinary composition take place?
What is the location of vasa recta?
What is the location of vasa recta?
What is the function of vasa recta?
What is the function of vasa recta?
What is the total renal blood flow for an average body size of 1.73m2?
What is the total renal blood flow for an average body size of 1.73m2?
What is the range of total renal plasma flow?
What is the range of total renal plasma flow?
What is the composition of urine?
What is the composition of urine?
Where is water removed by osmosis?
Where is water removed by osmosis?
What is the purpose of the countercurrent mechanism?
What is the purpose of the countercurrent mechanism?
What is the major function of tubular secretion?
What is the major function of tubular secretion?
What is the site for the removal of non-filtered substances?
What is the site for the removal of non-filtered substances?
What is the final step in the concentration of the filtrate?
What is the final step in the concentration of the filtrate?
What is the main factor that affects reabsorption in the collecting duct?
What is the main factor that affects reabsorption in the collecting duct?
Which of the following is NOT a major constituent of urine?
Which of the following is NOT a major constituent of urine?
What is the role of the ascending loop of Henle in the nephron?
What is the role of the ascending loop of Henle in the nephron?
What is the purpose of the shield of negativity in the glomerular filtration barrier?
What is the purpose of the shield of negativity in the glomerular filtration barrier?
What is the main factor that affects glomerular filtration?
What is the main factor that affects glomerular filtration?
What is the function of podocytes in the glomerular filtration process?
What is the function of podocytes in the glomerular filtration process?
What is the effect of increased hydrostatic pressure on glomerular filtration?
What is the effect of increased hydrostatic pressure on glomerular filtration?
What is the primary function of the glomerular filtration barrier?
What is the primary function of the glomerular filtration barrier?
What is the relationship between renal blood flow and body size?
What is the relationship between renal blood flow and body size?
What percentage of the blood pumped by the heart goes to the kidneys?
What percentage of the blood pumped by the heart goes to the kidneys?
Where does the reabsorption of essential nutrients take place?
Where does the reabsorption of essential nutrients take place?
What is the function of the peritubular capillaries?
What is the function of the peritubular capillaries?
What is the final step in urine formation?
What is the final step in urine formation?
What is the driving force behind the filtration process in the glomerular capillaries?
What is the driving force behind the filtration process in the glomerular capillaries?
What is the location of the vasa recta?
What is the location of the vasa recta?
What is the function of the vasa recta?
What is the function of the vasa recta?
Which process involves the movement of water and some filtered molecules back into the blood in the peritubular capillaries?
Which process involves the movement of water and some filtered molecules back into the blood in the peritubular capillaries?
What is the total renal blood flow for an average body size of 1.73m2?
What is the total renal blood flow for an average body size of 1.73m2?
What is the primary function of tubular secretion?
What is the primary function of tubular secretion?
What is the composition of urine?
What is the composition of urine?
What is the term for the fluid that is filtered out of the blood in the glomerular capillaries?
What is the term for the fluid that is filtered out of the blood in the glomerular capillaries?
What is the primary function of the renal blood flow?
What is the primary function of the renal blood flow?
Which process is responsible for the formation of urine?
Which process is responsible for the formation of urine?
What is the main function of the glomerular capillaries?
What is the main function of the glomerular capillaries?
What is the term for the process by which the kidney regulates the amount of water in the body?
What is the term for the process by which the kidney regulates the amount of water in the body?
Study Notes
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS) & Basement Membrane
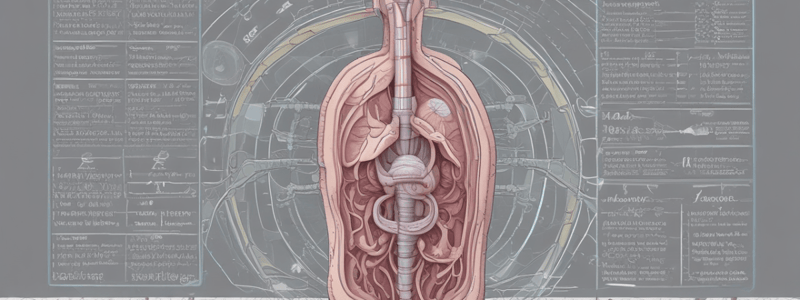
- The glomerular filtration barrier has three cellular layers: capillary wall membrane, basement membrane, and podocytes.
- Podocytes form an elaborate network of small slits between them, referred to as filtration slits.
- The filtration barrier filters the blood, creating an ultrafiltrate.
Glomerulus
- The glomerulus acts as an ultrafilter, very permeable to water.
- The pressure of the blood within the glomerulus forces water and dissolved solutes with a molecular weight of less than 70,000 through the semi-permeable capillary membrane and into Bowman's space.
- The remainder of the blood, including blood cells, plasma proteins, and large molecules, leaves the glomerulus via the efferent arteriole and enters the peritubular capillaries.
Bowman's Space
- The space formed between the capsule and the glomerulus.
- Plasma filtrate must pass through the three glomerular filtration barrier cellular layers.
Nephron
- The functional unit of the kidney.
- Approximately 1 to 1.5 million in number.
- Has two types: cortical nephrons (shorter loops of Henle) and juxtamedullary nephrons (longer loops of Henle).
Urinary System & Renal Function
- The kidneys filter the blood, remove waste, and excrete waste in the urine.
- The kidneys are located between the twelfth thoracic and third lumbar vertebrae, one on each side of the vertebral column.
- Adult human kidney measures roughly 12.5 cm (length), 6 cm (width), and 2.5 cm (depth).
- Four components of the urinary system: kidney, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
Functions of the Kidney
- Acid-base balance
- Water balance
- Electrolyte balance
- Toxin removal
- Blood pressure regulation
- Erythropoietin production
- Vitamin D metabolism
Urine Formation
- A. Filtration
- Blood pressure in the glomerular capillaries forces fluid and small molecules out of the blood, referred to as the filtrate.
- The filtration process is non-selective and separates based only on the size or molecular charge.
- B. Tubular Reabsorption
- Cells present in the nephron contain transport proteins that move water and filtered molecules back into the blood in the peritubular capillaries.
- Most filtered water and useful solutes are returned to the blood by the time the filtrate has been modified into urine.
- C. Tubular Secretion
- The movement of non-filtered substances from the blood into the filtrate.
- Certain tubule cells transport additional solutes from the blood into the filtrate.
Renal Blood Flow
- Renal artery supplies blood to the kidney.
- Human kidneys receive approximately 25% of the blood pumped through the heart at all times.
- Peritubular capillaries surround the proximal and distal convoluted tubule.
- Renal blood flow is approximately 1200 mL/min.
- Total renal plasma flow ranges from 600 – 700 mL/min.
Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion
- Sodium and Chloride are reabsorbed in the ascending loop of Henle.
- Water is removed by osmosis in the descending loop of Henle.
- Countercurrent mechanism – the absorption of water from the descending loop and reabsorption of solutes without water in the ascending loop.
Collecting Duct Concentration
- Final concentration of the filtrate through the reabsorption of water begins in the distal convoluted tubule and continues in the collecting ducts.
- Reabsorption depends on the osmotic gradient in the medulla and ADH (Vasopressin).
Main Constituents of Urine
- Water
- Urea
- Uric acid
- Creatinine
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Chloride
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Phosphates
- Sulfates
Kidney Function and Structure
- The renal artery supplies blood to the kidney, which receives approximately 25% of the blood pumped by the heart at all times.
- The peritubular capillaries surround the proximal and distal convoluted tubules and reabsorb essential nutrients present in the proximal convoluted tubule.
Glomerular Filtration
- The glomerular filtration barrier consists of three layers: endothelial cells, basement membrane, and podocytes.
- The glomerular filtration barrier contains a shield of negativity that repels molecules with positive charge, even if they are small enough to pass through the barrier.
- The filtration process is affected by several factors, including cellular structure of the capillary walls and Bowman's capsule, hydrostatic pressure, oncotic pressure, and blood pressure in the glomerular capillaries.
Functions of the Kidney
- The kidney performs seven main functions: acid-base balance, water balance, electrolyte balance, toxin removal, blood pressure regulation, erythropoietin production, and vitamin D metabolism.
Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion
- Cells in the nephron contain transport proteins that move water and some filtered molecules back into the blood in the peritubular capillaries.
- The process of reabsorption prevents the loss of important solutes from the body, and most filtered water and useful solutes are returned to the blood by the time the filtrate has been modified into urine.
- Tubular secretion involves the transport of additional solutes from the blood into the filtrate, and some of these solutes may not have been filtered by the filtration membrane.
Renal Blood Flow
- The total renal blood flow is approximately 1200 mL/min, and total renal plasma flow ranges from 600-700 mL/min.
- Normal values for renal blood flow and renal function tests depend on body size.
- Vasa recta are located adjacent to the ascending and descending loops of Henle in the juxtamedullary nephrons and maintain an osmotic gradient (salt concentration) in the medulla.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
This quiz covers the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone system (RAAS) and the filtration mechanism in the renal system, including the role of podocytes and the basement membrane. Test your knowledge of the filtration process and the structures involved.