Podcast
Questions and Answers
What defines the primary protein structure?
What defines the primary protein structure?
- The presence of hydrogen bonds between polypeptide chains
- The three-dimensional shape of the protein
- The number, type, and sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain (correct)
- The sequence of nucleotides in DNA
Which bond is primarily responsible for maintaining the primary structure of proteins?
Which bond is primarily responsible for maintaining the primary structure of proteins?
- Hydrogen bond
- Disulfide bridge
- Ionic bond
- Peptide bond (correct)
How many amino acids are present in one complete turn of an alpha-helix?
How many amino acids are present in one complete turn of an alpha-helix?
- 10
- 5
- 3.6 (correct)
- 4
What characterizes the formation of beta-pleated sheets?
What characterizes the formation of beta-pleated sheets?
Which statement is true about the super secondary structures in proteins?
Which statement is true about the super secondary structures in proteins?
What is the typical characteristic of the helix-turn-helix (HTH) motif?
What is the typical characteristic of the helix-turn-helix (HTH) motif?
What primarily stabilizes an alpha-helix structure in proteins?
What primarily stabilizes an alpha-helix structure in proteins?
Which element is not involved in hydrogen bonding within protein structures?
Which element is not involved in hydrogen bonding within protein structures?
What is the primary factor that leads to the formation of tertiary structure in proteins?
What is the primary factor that leads to the formation of tertiary structure in proteins?
Which type of bond is formed between the sulfur atoms of cysteine residues in proteins?
Which type of bond is formed between the sulfur atoms of cysteine residues in proteins?
Which forces are NOT involved in stabilizing tertiary protein structures?
Which forces are NOT involved in stabilizing tertiary protein structures?
What characterizes the quaternary structure of proteins?
What characterizes the quaternary structure of proteins?
Which of the following is an example of an oligomeric protein?
Which of the following is an example of an oligomeric protein?
What type of bonds predominantly stabilize the quaternary structures of proteins?
What type of bonds predominantly stabilize the quaternary structures of proteins?
Which of the following statements is true regarding secondary and tertiary structures of proteins?
Which of the following statements is true regarding secondary and tertiary structures of proteins?
Which of the following proteins consists of a dimeric structure?
Which of the following proteins consists of a dimeric structure?
Which structural feature is essential for the formation of secondary protein structures like α-helix and β-pleated sheets?
Which structural feature is essential for the formation of secondary protein structures like α-helix and β-pleated sheets?
What is the consequence of a change in the amino acid sequence within the primary protein structure?
What is the consequence of a change in the amino acid sequence within the primary protein structure?
Which of the following describes a characteristic of the helix-turn-helix (HTH) motif?
Which of the following describes a characteristic of the helix-turn-helix (HTH) motif?
In a typical α-helix, how many amino acids are involved in one complete turn?
In a typical α-helix, how many amino acids are involved in one complete turn?
Which type of protein structure refers to the combination of α-helices and β-sheets forming specific patterns?
Which type of protein structure refers to the combination of α-helices and β-sheets forming specific patterns?
What stabilizes the β-pleated sheet structure in proteins?
What stabilizes the β-pleated sheet structure in proteins?
Which end of the polypeptide chain is referred to as the N-terminal end?
Which end of the polypeptide chain is referred to as the N-terminal end?
What defines the primary structure of a protein?
What defines the primary structure of a protein?
What is the primary factor that leads to the formation of quaternary protein structure?
What is the primary factor that leads to the formation of quaternary protein structure?
Which forces control the tertiary structure of proteins?
Which forces control the tertiary structure of proteins?
Which type of bond is primarily responsible for stabilizing the tertiary structure of proteins?
Which type of bond is primarily responsible for stabilizing the tertiary structure of proteins?
In the context of protein structure, what is a domain?
In the context of protein structure, what is a domain?
Which of the following statements is true about protein oligomeric structure?
Which of the following statements is true about protein oligomeric structure?
What type of protein structure is characterized by interactions between oppositely charged side chains of amino acids?
What type of protein structure is characterized by interactions between oppositely charged side chains of amino acids?
Which of these is true about hemoglobin regarding protein structure?
Which of these is true about hemoglobin regarding protein structure?
Which bonds primarily stabilize the quaternary structure of proteins?
Which bonds primarily stabilize the quaternary structure of proteins?
Flashcards
Tertiary Structure
Tertiary Structure
The three-dimensional structure of a protein formed by interactions between amino acid side chains.
Forces in Tertiary Structure
Forces in Tertiary Structure
The interaction between amino acid side chains that contribute to the tertiary structure.
Quaternary Protein Structure
Quaternary Protein Structure
A protein with more than one polypeptide chain (subunit) assembled in a specific arrangement.
Dimer
Dimer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tetramer
Tetramer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subunits (Monomers)
Subunits (Monomers)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Domain
Domain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bonds in Quaternary Structure
Bonds in Quaternary Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary Protein Structure
Primary Protein Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
α-Helix
α-Helix
Signup and view all the flashcards
β-pleated Sheets
β-pleated Sheets
Signup and view all the flashcards
Super Secondary Structures (Motifs)
Super Secondary Structures (Motifs)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Helix-turn-helix (HTH)
Helix-turn-helix (HTH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impact of change in amino acid sequence
Impact of change in amino acid sequence
Signup and view all the flashcards
N-terminal End
N-terminal End
Signup and view all the flashcards
C-terminal End
C-terminal End
Signup and view all the flashcards
Importance of Amino Acid Sequence
Importance of Amino Acid Sequence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Protein Structure
- Proteins are comprised of numerous amino acids connected by peptide bonds, creating a polypeptide chain.
- The order, type, and sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain define the primary structure.
- Any modification in an amino acid sequence can cause a physiological defect.
- The primary structure is characterized by the peptide bond connecting the amino and carboxyl groups of amino acids.
- N-terminal end represents the free amino group of the first amino acid.
- C-terminal end signifies the free carboxyl group of the last amino acid.
- The primary structure determines the subsequent structures.
Secondary Protein Structure
- Secondary structure involves the folding of the polypeptide chain.
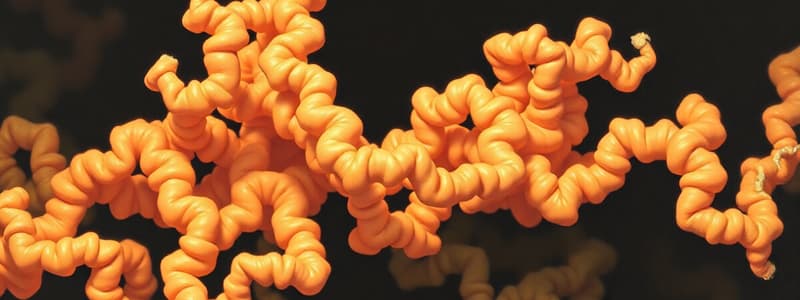
- Alpha-helix: A right-handed coiled helix stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the carbonyl oxygen of one peptide bond and the amino hydrogen of the fourth. Each turn in an alpha helix contains 3.6 amino acid residues. Hydrogen bonds are parallel to the helix axis.
- Beta-pleated sheets: Hydrogen bonds form between adjacent polypeptide chain segments, creating a pleated structure.
- Secondary structures are common in globular proteins.
- The folding process is spontaneous.
Super Secondary Structures (Motifs)
- Super-secondary structures emerge from the combination of alpha-helices and beta-sheets.
- Helix-turn-helix (HTH): Two alpha-helices connected by a short turn motif. It's a structural motif essential for DNA-binding proteins.
Tertiary Protein Structure
- Tertiary structure encapsulates the three-dimensional arrangement of a polypeptide chain.
- The interactions between R-groups (side chains) of amino acids dictate this folding pattern. Forces controlling tertiary structure include:
- Hydrogen bonds: between polar side chains
- Hydrophobic forces : between non-polar side chains
- Electrostatic forces (ionic bonds, salt bridges): between oppositely charged side chains
- Disulfide bonds: between cysteine residues.
- Proteins fold into a stable 3D conformation called a domain.
Quaternary Protein Structure
- Quaternary structure describes the arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains (subunits) in a protein.
- The arrangement is stabilized by non-covalent bonds (hydrogen or ionic bonds).
- Examples of oligomeric proteins with quaternary structure include hemoglobin (Hb), creatine kinase (CK), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), which consist of multiple protein subunits interacting together.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.