Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the expected penetration for the meal package in February?
What is the expected penetration for the meal package in February?
- 10,000 meal packages
- 11,200 meal packages
- 13,800 meal packages
- 12,600 meal packages (correct)
How many first-time triers of the meal package were there in August?
How many first-time triers of the meal package were there in August?
- 14,400 first-time triers
- 21,000 first-time triers
- 6,600 first-time triers (correct)
- 18,000 first-time triers
What is the volume projection for February if both the frequency of purchase and units per purchase is 1?
What is the volume projection for February if both the frequency of purchase and units per purchase is 1?
- 12,600 packages (correct)
- 15,200 packages
- 10,000 packages
- 18,000 packages
How many new customers were added for the meal package in September?
How many new customers were added for the meal package in September?
What is the repeat customer rate expected for the new meal package?
What is the repeat customer rate expected for the new meal package?
What does a product portfolio comprise?
What does a product portfolio comprise?
Which factor is not considered a key decision in product portfolio management?
Which factor is not considered a key decision in product portfolio management?
In the BCG Matrix, which quadrant typically represents products with a high market growth rate and high relative market share?
In the BCG Matrix, which quadrant typically represents products with a high market growth rate and high relative market share?
What does the term 'Dog' refer to in the BCG Matrix?
What does the term 'Dog' refer to in the BCG Matrix?
How do decisions in product portfolio management evolve?
How do decisions in product portfolio management evolve?
What is the estimated trial rate for the new stapler based on the given percentages?
What is the estimated trial rate for the new stapler based on the given percentages?
What is the primary purpose of measuring growth rates?
What is the primary purpose of measuring growth rates?
How many first-time users are expected to try the stapler based on the adjusted trial rate?
How many first-time users are expected to try the stapler based on the adjusted trial rate?
Which of the following formulas represents year-on-year growth?
Which of the following formulas represents year-on-year growth?
How many total staplers are projected to be purchased by repeat buyers in the first year?
How many total staplers are projected to be purchased by repeat buyers in the first year?
What is the total projected volume of staplers in year one?
What is the total projected volume of staplers in year one?
What does CAGR stand for?
What does CAGR stand for?
What is needed to calculate the Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR)?
What is needed to calculate the Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR)?
What percentage of repeat buyers is expected in the first year?
What percentage of repeat buyers is expected in the first year?
What factors could potentially lead to inaccuracies in volume projections?
What factors could potentially lead to inaccuracies in volume projections?
What was the year-on-year growth percentage for Apple in 2008?
What was the year-on-year growth percentage for Apple in 2008?
What does a negative CAGR indicate?
What does a negative CAGR indicate?
How many occasions is each repeat buyer expected to purchase during the first year?
How many occasions is each repeat buyer expected to purchase during the first year?
What is the estimated awareness level for the stapler based on the company's beliefs?
What is the estimated awareness level for the stapler based on the company's beliefs?
Which years did the example provide Apple sales data for?
Which years did the example provide Apple sales data for?
What is the calculation result for the year-on-year growth of Apple sales in 2010?
What is the calculation result for the year-on-year growth of Apple sales in 2010?
What is one of the limitations of the McKinsey Grid compared to the BCG Matrix?
What is one of the limitations of the McKinsey Grid compared to the BCG Matrix?
Which is NOT a purpose of volume projections in sales forecasting?
Which is NOT a purpose of volume projections in sales forecasting?
How does the calculation for volume projection at time t incorporate first-time triers?
How does the calculation for volume projection at time t incorporate first-time triers?
In volume projections, what does the term 'frequency of purchase' refer to?
In volume projections, what does the term 'frequency of purchase' refer to?
What is the primary method for tracking market changes when using the McKinsey Grid?
What is the primary method for tracking market changes when using the McKinsey Grid?
What is a component of the volume projection formula for future sales?
What is a component of the volume projection formula for future sales?
Which statement correctly reflects a strategy for flat screen TVs within the McKinsey Grid?
Which statement correctly reflects a strategy for flat screen TVs within the McKinsey Grid?
Volume projections for existing products are primarily used for which of the following?
Volume projections for existing products are primarily used for which of the following?
What is the formula to calculate Volume Projection in time t?
What is the formula to calculate Volume Projection in time t?
How is Trial Volume in time t calculated?
How is Trial Volume in time t calculated?
What factors contribute to the Adjusted Trial Rate?
What factors contribute to the Adjusted Trial Rate?
What is the purpose of calculating the Repeat Volume in time t?
What is the purpose of calculating the Repeat Volume in time t?
Which weight is typically assigned to 'definites' in the Trial Rate calculation?
Which weight is typically assigned to 'definites' in the Trial Rate calculation?
How is the Number of Repeat Buyers in time t calculated?
How is the Number of Repeat Buyers in time t calculated?
What is the Repeat Volume in time t formula dependent on?
What is the Repeat Volume in time t formula dependent on?
What role does ACV play in volume projection calculations?
What role does ACV play in volume projection calculations?
Flashcards
Product Portfolio
Product Portfolio
A collection of products and businesses that a company manages.
BCG Matrix
BCG Matrix
A tool used to analyze a company's product portfolio based on market growth rate and relative market share.
Stars
Stars
Products with a high market share in a high-growth market. Requires significant investment.
Question Marks
Question Marks
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cash Cows
Cash Cows
Signup and view all the flashcards
Market Penetration
Market Penetration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Volume Projection
Volume Projection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Repeat Customer Rate
Repeat Customer Rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
First-time Triers
First-time Triers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Frequency of Purchase
Frequency of Purchase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trial Volume
Trial Volume
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trial Population
Trial Population
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trial Rate
Trial Rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Awareness
Awareness
Signup and view all the flashcards
ACV (All Commodity Volume)
ACV (All Commodity Volume)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Repeat Volume
Repeat Volume
Signup and view all the flashcards
Repeat Rate
Repeat Rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Growth Rate
Growth Rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Year-on-Year (YoY) Growth
Year-on-Year (YoY) Growth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR)
Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Growth Rate Construction
Growth Rate Construction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Using Secondary Data & Past Experiences
Using Secondary Data & Past Experiences
Signup and view all the flashcards
McKinsey Grid
McKinsey Grid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Market Attractiveness
Market Attractiveness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Company Strength
Company Strength
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seek Niches
Seek Niches
Signup and view all the flashcards
Consider Acquisitions
Consider Acquisitions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Volume Projection for an Existing Product
Volume Projection for an Existing Product
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adjusted Trial Rate
Adjusted Trial Rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Repeat Buyers
Repeat Buyers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Total Projected Volume
Total Projected Volume
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Analysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Product and Portfolio Management
- Product portfolio is a collection of products and businesses.
- Key decisions include allocating resources (cash, expertise, time) across products and deciding whether to invest or divest in them.
- Market changes, product evolutions, and shifts in customer preferences affect these decisions.
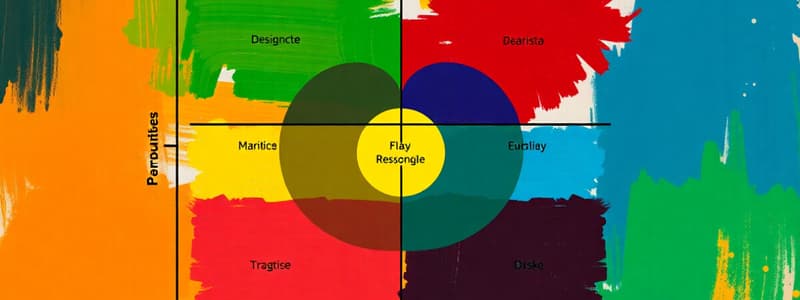
Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrix
- This matrix is used to evaluate the attractiveness of a product in relation to relative market share strength.
- It uses a 2x2 matrix with market growth rate (vertical axis) and relative market share (horizontal axis).
- Four quadrants represent different product categories:
- Star: High market growth rate, high relative market share.
- Cash Cow: Low market growth rate, high relative market share.
- Dog: Low market growth rate, low relative market share.
- Question Mark: High market growth rate, low relative market share.
BCG Matrix – Limitations
- Market attractiveness depends on factors beyond growth rate, including competitive intensity and market size.
- Strength depends on attributes beyond market share, such as R&D and marketing capabilities.
- Market share is a cost-based advantage indicator.
- Cut-off values on the matrix axes are arbitrary.
- Synergies between products are not accounted for.
GE/McKinsey Portfolio Planning Grid
- This grid analyzes market attractiveness and business strength.
- Market attractiveness factors include market growth, market size, profit margins, competitive intensity, market entry barriers, cyclicality of product life cycle and environmental impact.
- Business strength factors include market share, product quality, R&D capabilities, marketing capabilities, brand awareness, production capabilities, and cost efficiency.
- This matrix differs from BCG by including broader attributes.
Evaluating Attractiveness: Flat Screen TVs
- The document provides a detailed analysis on the attractiveness and market position of Flat Screen TVs.
- Critical criteria like market growth, market size, competitive intensity, profit margins, and market entry barriers were considered to assess attractiveness.
- The document provides a step by step assessment of these specific factors and evaluation methods.
Evaluating Strength: Flat Screen TVs
- The study documents steps to evaluate the relative competitive strength of flat-screen TVs.
- Factors analyzed include market share, research and development capabilities, marketing capabilities, distribution, and production capabilities.
- The documents detail the factors, evaluation process and outcome for each one of these factors.
McKinsey Grid: Flat screen TVs
- A visual representation of consumer electronic company's flat screen TVs using a two-axis matrix showing market attractiveness versus relative competitive strength.
- Provides a visual overview of which products are performing well and which are not.
Volume Projections: Purpose
- Forecasting sales by understanding customer intentions, with data from surveys and market research.
- Crucial during early product development to set a product launch schedule.
- Proper penetration in the market means considering both new ('triers') and existing ('repeat') customers.
Volume Projection for an Existing Product: Construction
- This section details the volume projection methodology.
- New penetration is a function of existing penetration, repeat rate and new customers.
Volume Projection for a New Product: Construction
- This section lays out the construction method for new product volume projections.
- The method considers trial volume and repeat volume.
- Key terms such as trial population, trial rate, awareness, and ACV are defined.
Volume Projections: Caution
- Volume projections need crucial assumptions (e.g., customer expectations or awareness).
- Sensitivity analysis is essential to test the robustness of these assumptions.
- Determining trial and repeat rates can be challenging.
- Secondary data and past product experiences are helpful.
Growth Rates: Purpose
- Measuring growth patterns (monthly, seasonal, yearly) and periods.
- Understanding business success or failure is often tied to growth.
Growth Rates: Construction
- Calculate year-on-year growth using the formula: (Value in t - Value in t-1) / Value in t-1
- Calculate compound annual growth rate to find average growth over a given period.
Growth Rates: Example
- This section provides an example of calculating year-on-year and compound annual growth rates for Apple sales.
Growth Rates: Cautions
- Adjusting growth rates for various influencing factors like store expansion, salesperson numbers, or new market expansions is vital.
- Focusing on 'same-store sales' growth is a significantly more useful metric for analyzing retail growth
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.