Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary anatomical structure that connects the pituitary gland to the hypothalamus?
What is the primary anatomical structure that connects the pituitary gland to the hypothalamus?
- Foramen magnum
- Pituitary stalk (correct)
- Sella turcica
- Optic chiasm
Which division of the pituitary gland is derived from ectodermal tissue?
Which division of the pituitary gland is derived from ectodermal tissue?
- Anterior pituitary (correct)
- Hypothalamic stalk
- Posterior pituitary
- Pars intermedia
In terms of physiological functions, which hormone is primarily associated with growth and metabolic processes?
In terms of physiological functions, which hormone is primarily associated with growth and metabolic processes?
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone
- Luteinizing hormone
- Growth hormone (correct)
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone
What structural feature is found between the anterior and posterior pituitary glands?
What structural feature is found between the anterior and posterior pituitary glands?
How do the anterior and posterior pituitary glands differ fundamentally in terms of their embryological origin?
How do the anterior and posterior pituitary glands differ fundamentally in terms of their embryological origin?
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland?
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland?
What is the average weight range of the pituitary gland in grams?
What is the average weight range of the pituitary gland in grams?
Which physiological factor may trigger the secretion of growth hormone?
Which physiological factor may trigger the secretion of growth hormone?
Which cells in the anterior pituitary are not secretory and serve as precursors to chromophil cells?
Which cells in the anterior pituitary are not secretory and serve as precursors to chromophil cells?
What percentage of chromophil cells in the anterior pituitary are classified as somatotropes?
What percentage of chromophil cells in the anterior pituitary are classified as somatotropes?
Which of the following anterior pituitary hormones is classified as a glycoprotein?
Which of the following anterior pituitary hormones is classified as a glycoprotein?
Which type of cell in the anterior pituitary secretes prolactin?
Which type of cell in the anterior pituitary secretes prolactin?
Which option correctly identifies the classification of ACTH based on its related peptides?
Which option correctly identifies the classification of ACTH based on its related peptides?
Which anterior pituitary cells primarily secrete adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)?
Which anterior pituitary cells primarily secrete adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)?
Which type of staining property distinguishes acidophilic cells from basophilic cells?
Which type of staining property distinguishes acidophilic cells from basophilic cells?
Which hormone primarily stimulates the release of growth hormone?
Which hormone primarily stimulates the release of growth hormone?
What percentage of anterior pituitary cells are classified as chromophobe cells?
What percentage of anterior pituitary cells are classified as chromophobe cells?
What is the major function of the first 24 amino acids of ACTH?
What is the major function of the first 24 amino acids of ACTH?
Which of the following statements about the anterior pituitary hormones is true?
Which of the following statements about the anterior pituitary hormones is true?
What role does the hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system serve?
What role does the hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system serve?
Which hormone is associated with analgesic properties and is present in the brain and gastrointestinal tract?
Which hormone is associated with analgesic properties and is present in the brain and gastrointestinal tract?
Which of the following is not a releasing hormone secreted by the hypothalamus?
Which of the following is not a releasing hormone secreted by the hypothalamus?
What characterizes the first five hormones of the anterior pituitary?
What characterizes the first five hormones of the anterior pituitary?
What is the primary action of prolactin-inhibitory hormone (PIH)?
What is the primary action of prolactin-inhibitory hormone (PIH)?
Flashcards
Pituitary Gland
Pituitary Gland
A small, pea-sized endocrine gland located at the base of the brain, responsible for producing and releasing hormones that regulate various bodily functions.
Anterior Pituitary
Anterior Pituitary
The front portion of the pituitary gland, responsible for producing and releasing hormones that control various bodily functions, including growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
Posterior Pituitary
Posterior Pituitary
The back portion of the pituitary gland, responsible for storing and releasing hormones produced by the hypothalamus, such as oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone.
What is ACTH?
What is ACTH?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the functional part of ACTH?
What is the functional part of ACTH?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is beta-endorphin?
What is beta-endorphin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does the hypothalamus control the anterior pituitary?
How does the hypothalamus control the anterior pituitary?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do hypothalamic hormones reach the anterior pituitary?
How do hypothalamic hormones reach the anterior pituitary?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are tropic hormones?
What are tropic hormones?
Signup and view all the flashcards
List some tropic hormones.
List some tropic hormones.
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does prolactin do?
What does prolactin do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the anterior pituitary called and why?
What is the anterior pituitary called and why?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Name the parts of the anterior pituitary.
Name the parts of the anterior pituitary.
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are chromophobe cells?
What are chromophobe cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are chromophil cells?
What are chromophil cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are acidophilic cells?
What are acidophilic cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are basophilic cells?
What are basophilic cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are acidophilic tumors?
What are acidophilic tumors?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How are anterior pituitary hormones classified?
How are anterior pituitary hormones classified?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Objectives
- Students should be able to describe the pituitary gland's structure and its relationship to function.
- Define the anterior pituitary cell types and their control mechanisms.
- Define growth hormone effects on growth and metabolism, and how IGF-I mediates its actions.
- List growth hormone secretion stimuli and their underlying causes.
- Understand abnormal pituitary function and growth hormone conditions, and their treatments.
Pituitary Gland
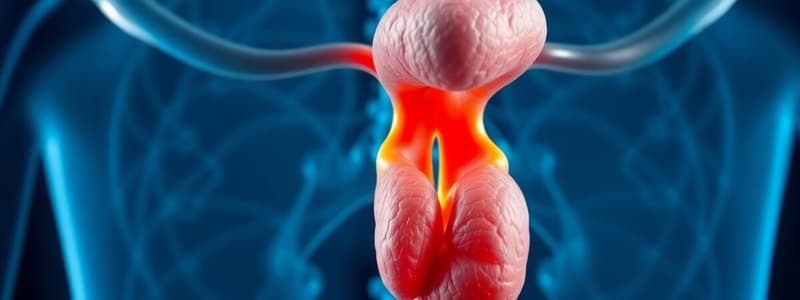
- The pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is a small endocrine gland (1 cm diameter, 0.5-1g weight).
- Located in the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone at the base of the skull.
- Connected to the hypothalamus by the pituitary stalk (hypophyseal stalk).
- Divided into two parts:
- Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis)
- Posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis)
- Both divisions are close together, but have different developments, structures, and functions.
- Pars intermedia is a small, relatively avascular structure between the divisions.
Pituitary Gland Anatomy
- Anterior and posterior pituitary divisions develop from different embryonic sources.
- Anterior pituitary is ectodermal, arising from Rathke's pouch.
- Posterior pituitary is neuroectodermal, arising from the hypothalamus.
- These two divisions grow towards each other, merging midway between the buccal cavity and brain.
Anterior Pituitary (Adenohypophysis)
- Also known as the 'master gland', regulating other endocrine glands.
- Composed of three parts: Pars distalis, Pars tuberalis, and Pars intermedia.
Histology of Anterior Pituitary
- Two main cell types:
- Chromophobe cells: Do not stain well, comprise 50% of anterior pituitary cells, thought to be precursor cells to chromophil cells.
- Chromophil cells: Darkly stain due to granules, classified by staining property or secretory nature.
- Classification by staining property:
- Acidophils (35%): Stain bright pink, include somatotropes and lactotropes.
- Basophils (15%): Stain deep blue, include corticotropes, thyrotropes, and gonadotropes.
- Classification by secretory nature:
- Somatotropes: Secrete growth hormone (GH).
- Corticotropes: Secrete adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH).
- Thyrotropes: Secrete thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
- Gonadotropes: Secrete follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH).
- Lactotropes: Secrete prolactin.
- Classification by staining property:
Regulation of Anterior Pituitary Secretion
- Hypothalamus controls the anterior pituitary by releasing and inhibiting hormones (neurohormones).
- These neurohormones are transported to the anterior pituitary via the hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal vessels.
Releasing and Inhibiting Hormones (Hypothalamus)
- Growth Hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH)
- Growth Hormone-releasing polypeptide (GHRP)
- Growth Hormone-inhibitory hormone (GHIH) or somatostatin
- Thyrotropic-releasing hormone (TRH)
- Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
- Prolactin-inhibitory hormone (PIH)
Hormones Secreted by Anterior Pituitary
- Growth hormone
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- Luteinizing hormone (LH)
- Prolactin
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.