Podcast
Questions and Answers
What occurs during systole in the heart?
What occurs during systole in the heart?
- The left ventricle contracts and forces blood into the aorta. (correct)
- The heart is relaxed and filling with blood.
- The heart muscle is undergoing oxygen deprivation.
- The right ventricle ejects blood into the pulmonary artery.
What is hypoperfusion commonly referred to as?
What is hypoperfusion commonly referred to as?
- Hyperemia
- Cardiac arrest
- Shock (correct)
- Systolic failure
Which of the following is NOT a potential cause of shock?
Which of the following is NOT a potential cause of shock?
- Increased physical activity (correct)
- Pump failure
- Large blood loss
- Vessel adjustment failure
What does adequate perfusion ensure for cells?
What does adequate perfusion ensure for cells?
What can result from impaired oxygen delivery due to shock?
What can result from impaired oxygen delivery due to shock?
What is the primary function of the pelvis?
What is the primary function of the pelvis?
Which bone is located on the thumb side of the forearm?
Which bone is located on the thumb side of the forearm?
Which muscle type is characterized as striated and facilitates voluntary movement?
Which muscle type is characterized as striated and facilitates voluntary movement?
Where does the Achilles tendon connect?
Where does the Achilles tendon connect?
What is the role of cardiac muscle?
What is the role of cardiac muscle?
Which bone connects to the elbow and is located on the pinky side?
Which bone connects to the elbow and is located on the pinky side?
What are phalanges in context of human anatomy?
What are phalanges in context of human anatomy?
What is a common area for sprains?
What is a common area for sprains?
Which part of the spine is located in the neck?
Which part of the spine is located in the neck?
How many pairs of ribs are considered true ribs?
How many pairs of ribs are considered true ribs?
What type of joint allows for rotation of nearly 360 degrees?
What type of joint allows for rotation of nearly 360 degrees?
Where is the xiphoid process located?
Where is the xiphoid process located?
Which joint connects the clavicle to the sternum?
Which joint connects the clavicle to the sternum?
What is the role of synovial fluid in joints?
What is the role of synovial fluid in joints?
Which spine section is fused with the pelvis?
Which spine section is fused with the pelvis?
Which of the following is not a type of rib?
Which of the following is not a type of rib?
Which muscle is responsible for flexing the lower leg?
Which muscle is responsible for flexing the lower leg?
What type of muscle movement is defined as movement that one cannot control?
What type of muscle movement is defined as movement that one cannot control?
Which of the following muscles plays a role in the flexion of the spine?
Which of the following muscles plays a role in the flexion of the spine?
What is the primary action of the Gastrocnemius muscle?
What is the primary action of the Gastrocnemius muscle?
What movement is characterized by pointing the foot downward?
What movement is characterized by pointing the foot downward?
Which structure acts as a protective flap for the trachea during swallowing?
Which structure acts as a protective flap for the trachea during swallowing?
What is the primary function of the intercostal muscles?
What is the primary function of the intercostal muscles?
Which term describes the action of moving an extremity back to the side of the body?
Which term describes the action of moving an extremity back to the side of the body?
What is the normal heart rate range for an adult?
What is the normal heart rate range for an adult?
Which valve connects the right atrium to the right ventricle?
Which valve connects the right atrium to the right ventricle?
Which structure is commonly referred to as the pacemaker of the heart?
Which structure is commonly referred to as the pacemaker of the heart?
What is the primary function of the chordae tendineae in the heart?
What is the primary function of the chordae tendineae in the heart?
What is the definition of cardiac output?
What is the definition of cardiac output?
During what phase do the electrical charges on the muscle cell surfaces change from positive to negative?
During what phase do the electrical charges on the muscle cell surfaces change from positive to negative?
Which vessels deliver deoxygenated blood to the right atrium?
Which vessels deliver deoxygenated blood to the right atrium?
What is the purpose of the pulmonary veins in the circulatory system?
What is the purpose of the pulmonary veins in the circulatory system?
Which plane divides the body into anterior and posterior sections?
Which plane divides the body into anterior and posterior sections?
What term describes a position towards the surface of the tissues of the body?
What term describes a position towards the surface of the tissues of the body?
Which body position involves lying face down?
Which body position involves lying face down?
In which direction is the lateral movement moving?
In which direction is the lateral movement moving?
What is the primary function of the skeletal system?
What is the primary function of the skeletal system?
Which part of the skeleton consists of the skull, spinal column, and thoracic cage?
Which part of the skeleton consists of the skull, spinal column, and thoracic cage?
What is the meaning of the term 'distal'?
What is the meaning of the term 'distal'?
Which structure is described as the large opening at the base of the skull where the spinal cord leaves the brain?
Which structure is described as the large opening at the base of the skull where the spinal cord leaves the brain?
What is the position called when an individual is lying on their back?
What is the position called when an individual is lying on their back?
What does the term 'apex' refer to in human anatomy?
What does the term 'apex' refer to in human anatomy?
Flashcards
Standard Anatomical Position
Standard Anatomical Position
The standard position used for anatomical descriptions. Patient is standing upright, facing forward, arms at sides, and palms facing forward
Topographic Anatomy
Topographic Anatomy
Refers to the anatomical regions, including superficial landmarks, used in physical assessments
Frontal Plane
Frontal Plane
Divides the body into front and back halves. Front part is called anterior, back is posterior.
Sagittal Plane
Sagittal Plane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transverse Plane
Transverse Plane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Distal
Distal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proximal
Proximal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superficial
Superficial
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deep
Deep
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anterior or Ventral
Anterior or Ventral
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cervical Spine
Cervical Spine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thoracic Spine
Thoracic Spine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lumbar Spine
Lumbar Spine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thorax
Thorax
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sternum
Sternum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Joints
Joints
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symphysis Joints
Symphysis Joints
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ball-and-Socket Joint
Ball-and-Socket Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femur
Femur
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ulna
Ulna
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patella
Patella
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tibia
Tibia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Smooth Muscle
Smooth Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Iliac Crest
Iliac Crest
Signup and view all the flashcards
Voluntary Movement
Voluntary Movement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Involuntary Movement
Involuntary Movement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biceps
Biceps
Signup and view all the flashcards
Triceps
Triceps
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pectoral
Pectoral
Signup and view all the flashcards
Latissimus Dorsi
Latissimus Dorsi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rectus Abdominis
Rectus Abdominis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tibialis Anterior
Tibialis Anterior
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is stroke volume?
What is stroke volume?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Cardiac Output?
What is Cardiac Output?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Depolarization?
What is Depolarization?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Repolarization?
What is Repolarization?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Atrioventricular Node?
What is the Atrioventricular Node?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Bundle of HIS?
What is the Bundle of HIS?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the Purkinje Fibers?
What are the Purkinje Fibers?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Sinoatrial Node?
What is the Sinoatrial Node?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Systolic Pressure
Systolic Pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diastolic Pressure
Diastolic Pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Perfusion
Perfusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypoperfusion
Hypoperfusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Shock
Shock
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Human Anatomy
- Directional Analysis: Study of anatomical directions and terms to describe locations and relationships within the body.
Standard Anatomical Position
- A reference position with the body erect, facing forward, arms at the sides, and palms facing forward.
Body Planes & Directions
- Frontal (Coronal) Plane: Divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) portions.
- Sagittal Plane: Divides the body into left and right portions. The midline is an imaginary line down the center. Lateral refers to moving away from the midline.
- Transverse Plane: Divides the body into superior (top) and inferior (bottom) portions.
Directional Terms
- Distal: Away from the point of attachment.
- Proximal: Toward the point of attachment.
- Deep: Further into the tissues of the body.
- Superficial: Toward the surface of the body.
- Anterior (Ventral): Front of the body.
- Posterior (Dorsal): Back of the body.
- Superior: Above a structure.
- Inferior: Below a structure.
- Medial: Toward the middle or center.
- Lateral: Away from the middle or center.
- Apex: Tip of a structure.
- Palmar: Palm of the hand.
- Plantar: Sole of the foot.
- Axillary: Armpit area.
Body Cavities
- Dorsal Cavity: Cranial cavity housing the brain, and spinal cavity housing the spinal cord; Ventral Cavity: Thoracic (heart, lungs), Abdominal (stomach, intestines), and Pelvic (bladder, reproductive organs) cavities.
Abdominal Quadrants
- RUQ (Right Upper Quadrant): Includes the liver, gallbladder, part of the colon, etc...
- LUQ (Left Upper Quadrant): Consists of the stomach, spleen, part of the colon, etc..
- RLQ (Right Lower Quadrant): Contains parts of the large intestine, small intestine, appendix, and female reproductiveorgans.
- LLQ (Left Lower Quadrant): Houses the large intestine, small intestine, and female reproductive organs.
Patient Positioning
- Supine: Lying on the back (face up)
- Prone: Lying on the stomach (face down)
- Trendelenburg: Lying on the back with the feet elevated above the head
- Reverse Trendelenburg: Lying on the back with the head elevated above the feet
- Fowler's/Semi or High: Lying on the back with the head elevated at a 30-45-degree angle.
- Lithotomy: Lying on the back with legs raised and supported, often used for gynecological procedures.
- Shock Position: Lying on the back with legs elevated and a cushion or elevated surface beneath the hips, often used for patients in shock.
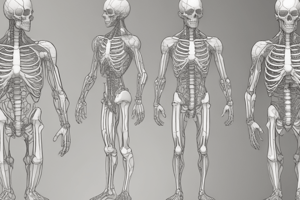
Skeletal System Overview
- Axial Skeleton: The foundational skeleton composed of the skull, spinal column, and thoracic cage.
- Appendicular Skeleton: The arms, legs, and their connection points, along with the pelvis. Also includes joints/articulations.
Cranium
- Foramen Magnum: Large opening at the base of the skull where the spinal cord emerges.
- Occipital Bone: Bone at the back of the skull. Also refers to a specific muscle and major arteries.
- Temporal Bones: Bones on the sides of the skull.
- Parietal Bones: Bones on the top of the skull.
- Frontal Bone: Bone at the front of the skull.
- Maxilla: Upper jaw bone.
- Mandible: Lower jaw bone.
- Zygomatic Bones: Cheekbones.
- Nasal Bones: Bones forming the bridge of the nose.
- Orbitals: Eye sockets.
- Mastoids: Bones behind the ears.
Spinal Column
- Vertebrae: Stacked spinal bones that support posture and protect the spinal cord. Contains Cervical (Neck), Thoracic (Chest), Lumber (Lower back), Sacral, and Coccyx (Tailbone) spines.
- Specific sections of the vertebral column are listed above
Thorax (Rib Cage)
- Ribs: Twelve pairs of ribs. True ribs (1-7 attach directly to sternum), False Ribs (8-10 attach indirectly), Floating Ribs (11-12 do not connect) make the thoracic cavity.
- Sternum: Breastbone; located in the middle of the thoracic cavity, composed of Manubrium (Upper), Body (Middle), and Xiphoid Process (Lower) portions.
Joints (Articulations)
- Symphysis: Joints with very limited motion, connected by fibrous connective tissue (e.g., pubic symphysis).
- Sacroiliac Joint: Joins the Ilium to the Sacrum in the pelvis.
- Articular Cartilage: Covers the ends of bones at joints to reduce friction.
- Synovial Membrane & Fluid: Fluid within a joint capsule that lubricates and cushions movement.
- Ball-and-Socket Joint: Allows for almost 360 degrees of rotation (shoulder, hip)
- Hinge Joint: Allows flexion and extension (elbow, knee, fingers).
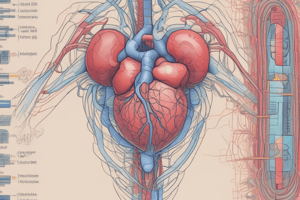
Cardiovascular System
- The Pump: The heart (located in the thoracic cavity between the lungs) contracts approximately 100,000 times per day and pumps about 2,000 gallons of blood. Contains four tissue layers.
- Pericardium, Epicardium, Myocardium, Endocardium
- Chambers include Atria and Ventricles
- Valves include Tricuspid, Mitral (Bicuspid), Pulmonary Semilunar, and Aortic
- Heart has four tissue layers
- Arteries: The vessels that carry blood away from the heart (e.g., aorta, coronary arteries, carotid arteries, renal arteries).
- Veins: The vessels that return blood to the heart. The vena cava (superior and inferior) return blood to the heart. Other key veins include pulmonary veins & coronary veins.
- Capillaries: Tiny vessels that connect arterioles to venules, allowing for nutrient and gas exchange.
- Blood: A connective tissue carrying oxygen and nutrients and removing waste. Contains erythrocytes (Red blood cells), leukocytes (White blood cells), platelets, and plasma.
- Blood Pressure: The force exerted against the walls of the arteries. Systolic (during contraction) and Diastolic (relaxation).
Respiratory System
- Upper Airway: Nasopharynx (behind nasal cavity), Oropharynx(behind the mouth), Pharynx (back of throat), Mouth, Epiglottis, Larynx.
- Lower Airway: Trachea (windpipe), Bronchi (branches), Bronchioles (smaller branches), Alveoli (sacs for gas exchange).
- Ventilation and Respiration: Movement of air into and out of the lungs and the exchange of gasses between the air and blood.
- Lungs: Divided into lobes, they inflate and deflate due to diaphragm and intercostal muscles.
- Surfaces include visceral and parietal pleura.
Muscular System
- Categories, location (anterior/posterior, etc), main actions.
- Example: Biceps brachii (anterior humerus), flexion of forearm.
- Muscle Types: Skeletal (voluntary), Smooth (involuntary), Cardiac (heart).
- Major muscle groups
- Movement types: Abduction, Adduction, Circumduction, Rotation, Dorsiflexion, Plantar flexion, Pronation, Supination, Flexion, and Extension.
Nervous System
- Central Nervous System (CNS): Brain and spinal cord
- Cerebrum, Cerebellum, Brain Stem, Reticular Activating System, Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): All the nerves outside the CNS
- Somatic nervous system (voluntary movement), Autonomic Nervous System (involuntary) with further branches.
Integumentary System
- Layers:
- Epidermis (outermost, protective layer)
- Dermis (middle, with structures like hair follicles, sweat glands, nerves)
- Hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue, with adipose tissue, blood vessels)
- Skin Eruptions: Macules, Papules, Vesicles, Pustules, Crusts, Wheals, Cysts, and Ulcers.
- Burns: Classified by degree (first, second, third, fourth).
Digestive System
- Basic Function: Processes food for nutrient absorption and waste removal. Includes mechanical and chemical digestion, with digestive organs located in abdominal quadrants.
Endocrine System
- Mechanism: Chemical signaling and control using hormones
- Important Glands: Adrenal, Ovaries, Testes, Pancreas, Pituitary, and Thyroid
Lymphatic System
- Mechanism: Support to circulatory and immune systems
- Key Components: Lymph, Lymph vessels, Lymph nodes, Spleen, and Thymus
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
This quiz focuses on the physiological processes of the heart during systole and the concepts related to shock and hypoperfusion. Test your understanding of what constitutes adequate perfusion and the consequences of impaired oxygen delivery. Perfect for students studying cardiovascular physiology or related health sciences.