Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are Paranasal Sinuses?
What are Paranasal Sinuses?
- Muscles that assist in swallowing
- Air-filled spaces within the bones of the face (correct)
- A part of the nasal cavity
- Tissues that filter air
What is the Nasal Cavity?
What is the Nasal Cavity?
- A hollow tube in the throat
- The entrance to the digestive tract
- The area for gas exchange in the lungs
- The space behind the nose (correct)
What does the term Nasopharynx refer to?
What does the term Nasopharynx refer to?
- The region where food passes down
- The part of the throat above the soft palate (correct)
- The lower part of the pharynx
- The area where ear and throat connect
What is the Oropharynx?
What is the Oropharynx?
What is the Laryngopharynx?
What is the Laryngopharynx?
What is the function of the Pharyngeal Tonsil?
What is the function of the Pharyngeal Tonsil?
What is the function of the Eustachian Tube?
What is the function of the Eustachian Tube?
What role do the Palatine Tonsils play?
What role do the Palatine Tonsils play?
What is the function of the Epiglottis?
What is the function of the Epiglottis?
What are Vocal Cords?
What are Vocal Cords?
What is the Esophagus?
What is the Esophagus?
Where is the Trachea located?
Where is the Trachea located?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
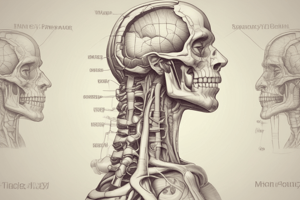
Pharynx and Related Structures
-
Paranasal Sinuses: Air-filled spaces located within the bones surrounding the nasal cavity, involved in reducing skull weight and producing mucus.
-
Nasal Cavity: The space behind the nose, lined with mucous membranes, plays a vital role in respiration and filtration of air.
-
Nasopharynx: The upper part of the pharynx, connecting the nasal cavity to the oropharynx, serves as a pathway for air movement and contains the pharyngeal tonsil.
-
Oropharynx: The middle section of the pharynx located behind the mouth, important for both respiratory and digestive functions, includes the palatine tonsils.
-
Laryngopharynx: The lower segment of the pharynx leading to the larynx and esophagus, involved in directing food and air to their respective pathways.
-
Pharyngeal Tonsil: Also known as adenoids, these lymphatic tissue located in the nasopharynx helps in immune defense against pathogens.
-
Eustachian Tube: Connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx, equalizing pressure in the ear and allowing drainage.
-
Palatine Tonsil: Lymphatic tissue located on either side of the oropharynx, plays a role in immune response.
-
Epiglottis: A flap of cartilage located at the upper laryngopharynx that prevents food from entering the trachea during swallowing.
-
Vocal Cords: Located in the lower laryngopharynx, they are essential for sound production and protecting the airway during swallowing.
-
Esophagus: A muscular tube located below the laryngopharynx, transporting food from the mouth to the stomach.
-
Trachea: Located below the esophagus, this tube conducts air to and from the lungs, lined with cartilage to maintain its structure.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.