Podcast
Questions and Answers
What age group exhibits a bimodal distribution for Hodgkin’s Lymphomas?
What age group exhibits a bimodal distribution for Hodgkin’s Lymphomas?
- 5-10 years and 20-30 years
- 15-20 years and elderly (correct)
- 0-5 years and 35-40 years
- 20-25 years and 60-70 years
Which of the following is the most common clinical feature of Hodgkin’s Lymphomas?
Which of the following is the most common clinical feature of Hodgkin’s Lymphomas?
- Cervical lymph node enlargement (correct)
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- Weight gain
- Coughing
Which of the following symptoms are referred to as B symptoms in Hodgkin’s Lymphomas?
Which of the following symptoms are referred to as B symptoms in Hodgkin’s Lymphomas?
- Joint pain and swelling
- Fatigue and shortness of breath
- Fever, night sweats, and weight loss (correct)
- Nausea and vomiting
What characteristic is associated with the Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin’s Lymphomas?
What characteristic is associated with the Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin’s Lymphomas?
Which subtype of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma is most commonly associated with young individuals?
Which subtype of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma is most commonly associated with young individuals?
What variant is identified in Non-Classical Hodgkin’s Lymphoma?
What variant is identified in Non-Classical Hodgkin’s Lymphoma?
What specific feature can be observed in Reed-Sternberg cells associated with CMV inclusions?
What specific feature can be observed in Reed-Sternberg cells associated with CMV inclusions?
In which gender is Hodgkin’s Lymphoma more prevalent in non-classical types?
In which gender is Hodgkin’s Lymphoma more prevalent in non-classical types?
What type of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) is usually seen in children?
What type of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) is usually seen in children?
Which genetic mutation is associated with T-ALL?
Which genetic mutation is associated with T-ALL?
Which marker is NOT typically associated with B-ALL?
Which marker is NOT typically associated with B-ALL?
What is a common feature of hand mirror cells observed in ALL?
What is a common feature of hand mirror cells observed in ALL?
What does the presence of mediastinal involvement indicate in T-ALL compared to B-ALL?
What does the presence of mediastinal involvement indicate in T-ALL compared to B-ALL?
What peripheral smear finding is commonly associated with iron deficiency anemia?
What peripheral smear finding is commonly associated with iron deficiency anemia?
Which type of anemia is characterized by macrocytic red blood cells?
Which type of anemia is characterized by macrocytic red blood cells?
Bite cells on a peripheral smear are often indicative of which condition?
Bite cells on a peripheral smear are often indicative of which condition?
Which condition is associated with spherocytes in a peripheral blood smear?
Which condition is associated with spherocytes in a peripheral blood smear?
What type of cell is indicated by blunted projections and is associated with chronic renal failure?
What type of cell is indicated by blunted projections and is associated with chronic renal failure?
Target cells on a peripheral smear can be indicative of which of the following conditions?
Target cells on a peripheral smear can be indicative of which of the following conditions?
Which type of anemia is primarily caused by the lack of central pallor in red blood cells?
Which type of anemia is primarily caused by the lack of central pallor in red blood cells?
Spurr cells are associated with which condition?
Spurr cells are associated with which condition?
What is the characteristic appearance of megaloblasts observed in bone marrow aspiration?
What is the characteristic appearance of megaloblasts observed in bone marrow aspiration?
In the primary hemostasis process, what role does von Willebrand factor (vWF) play?
In the primary hemostasis process, what role does von Willebrand factor (vWF) play?
Which disease is associated with a deficiency of the GpIb-IX complex?
Which disease is associated with a deficiency of the GpIb-IX complex?
What is the first step in primary hemostasis?
What is the first step in primary hemostasis?
Which factor is referred to as the Christmas factor in the coagulation pathway?
Which factor is referred to as the Christmas factor in the coagulation pathway?
What type of factor is the Hageman factor (Factor XII)?
What type of factor is the Hageman factor (Factor XII)?
Which condition is characterized by a defect in platelet aggregation due to a lack of GpIIb-IIIa?
Which condition is characterized by a defect in platelet aggregation due to a lack of GpIIb-IIIa?
What denotes stable clot formation in the hemostasis process?
What denotes stable clot formation in the hemostasis process?
What is the shelf life of CPD-A anticoagulant?
What is the shelf life of CPD-A anticoagulant?
Which blood component is stored at a temperature of 2-6°C?
Which blood component is stored at a temperature of 2-6°C?
What is the primary use of fresh frozen plasma (FFP)?
What is the primary use of fresh frozen plasma (FFP)?
Which component is most prone to bacterial contamination?
Which component is most prone to bacterial contamination?
What changes occur in the life span of transfused red blood cells (RBCs)?
What changes occur in the life span of transfused red blood cells (RBCs)?
How much does one unit of random donor platelets increase platelet count?
How much does one unit of random donor platelets increase platelet count?
What is the storage temperature for cryoprecipitate?
What is the storage temperature for cryoprecipitate?
Which infection is NOT screened for in blood products?
Which infection is NOT screened for in blood products?
Study Notes
Peripheral Smear Findings
- Macrocytic RBCs: Can be seen in liver disease, hypothyroidism, megaloblastic anemia (B12/folate deficiency), or due to cytotoxic drugs. Macro ovalocytes can also be seen.
- Pencil Cells: Associated with iron deficiency anemia.
- Bite Cells: Indicator of G6PD deficiency.
- Spherocytes: Absence of central pallor. Common in hereditary spherocytosis, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, blood transfusion reactions, and burns.
- Burr Cell/Echinocyte: Blunt projections, present in chronic renal failure, uremia, and liver disease.
- Spur Cell/Acanthocyte: Pointed spicules, seen in abetalipoproteinemia.
- Sickle Cells: A characteristic feature of sickle cell anemia.
- Target Cell/Codocyte: Seen in thalassemia, liver disease, and iron deficiency anemia.
Hodgkin’s Lymphomas (HL)
- Bimodal Distribution: Most common between ages 15-20 years and in elderly individuals.
- Common Feature: Cervical lymph node enlargement is the most common finding.
- B Symptoms: Fever (Pel Ebstein: waxing and waning fever), night sweats, and weight loss.
- Mediastinal Involvement: Common in nodular sclerosing HL, can also be seen in T-ALL.
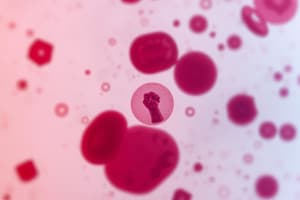
- Reed-Sternberg (RS) Cells: Characterized by large binucleate cells with prominent eosinophilic macronucleoli.
- Lacunar RS Cell: Large empty spaces seen in the cytoplasm.
- Popcorn/LH RS Cell: Lymphohistiocytic variant with nucleoli appearing like "popcorn”
- Owl's Eye Appearance: Large binucleate cells with prominent eosinophilic macronucleoli. Note: Also seen in CMV inclusions.
- Types of HL: - Classical HL: - Nodular Sclerosis (M/C): Most common globally. - Mixed Cellularity (M/C in India): - Lymphocyte Rich (Mostly HIV associated): - ** Lymphocyte Depleted:** - Non-Classical HL: - Nodular Lymphocyte Predominant HL (NLPHL): M:F = >F, more common in younger patients, Lacunar RS cell variants
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
- FAB Classification: Based on morphology (L1, L2, L3). Difficult to differentiate ALL-L2 from AML.
- WHO Classification:
- B-ALL: More common, better prognosis, commonly seen in children.
- T-ALL: Less common, poorer prognosis, more common in adults, mediastinal involvement present.
- Loss of Function Mutations (B-ALL):
- PAX5.
- NOTCH 1 gene.
- E2A.
- RUN X1.
- EBF gene.
- t(12;21)
- Gain of Function Mutations (T-ALL):
- E2A.
- RUN X1.
- EBF gene.
- Loss of Function Mutations (B-ALL):
- Peripheral Smear: >20% lymphoblasts present
- Hand Mirror Cells: Cytoplasmic protrusion seen in ALL.
- Investigations:
- Special Stain: PAS +ve (Dot and block)
- Markers:
- B-ALL: CD 19, CD 20, CD 22, PAX 5, TdT
- T-ALL: CD 1, CD 2, CD 3, CD 5, CD 7
- IOC: Flow Cytometry
- Note: AML-M6 is also PAS positive but shows diffuse positivity, while ALL shows block/dot positivity.
Bone Marrow Aspiration Findings
- Megaloblast: Erythroid precursors with sieve-like chromatin.
- Note: Folic acid deficiency anemia is similar to B12 deficiency anemia but without neurological complications.
Hemostasis
- Interplay of 3 Components:
- Platelets: Normal count 1.5 - 4 lakhs/mL
- Vascular Endothelium
- Coagulation Cascade
- Primary Hemostasis
- Step 1: Platelet adhesion to endothelium. vWF (present on endothelium) binds to GpIb-IX (present on platelets).
- Step 2: Platelets aggregate to each other through factor GpIIb-IIIa on their surface, forming an unstable clot.
- Blood Clot: Aggregation of platelets, fibrin, and an unstable clot/thrombus.
- Stable clot/thrombus: A stable clot
- Platelet Aggregation Disorders:
- Deficiency of Factor:
- GpIb-IX: Bernard Soulier syndrome
- GpIIb-IIIa: Glanzmann thrombasthenia
- von Willebrand Factor: von Willebrand disease
- Deficiency of Factor:
Secondary Hemostasis
- Coagulation Pathway:
- XII: Hageman factor, a serine protease. (Intrinsic pathway)
- XI: Plasma thromboplastin, an antecedent serine protease. (Intrinsic pathway)
- IX: Christmas factor, a serine protease. (Intrinsic pathway)
- VII: Stable factor, a serine protease. (Extrinsic pathway)
- XIII: Fibrin stabilizing factor, a transglutaminase. (Both pathways)
- PL: Platelet membrane phospholipid. (Both pathways)
Blood Banking
-
Anticoagulants Used:
- CPD (Citrate PO43- dextrose): 21 days shelf life
- CPD-A (Citrate PO43 dextrose adenine): 35 days shelf life
- SAG-M (Sodium adenine glucose mannitol): 42 days shelf life
-
Blood Components and Storage:
- Whole Blood:
- Volume: 350 mL or 200 mL.
- Shelf Life: 2-6 °C (based on anticoagulant).
- Use: Acute blood loss, fresh frozen plasma used for multiple coagulation factor deficiency.
- Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP):
- Volume: ≤ -18°C.
- Shelf Life: 1 year.
- Use: Hemophilia A (rich in factor VIII), von Willebrand disease, factor XIII deficiency, hypofibrinogenemia.
- Cryoprecipitate:
- Volume: 10-20 mL.
- Shelf Life: 1 year.
- Use: Hemophilia A, von Willebrand disease, factor XIII deficiency, hypofibrinogenemia.
- Random Donor Platelets:
- Volume: 50-70 mL.
- Storage Temperature: 20-24 °C with agitation.
- Shelf Life: 5 days.
- Use: Thrombocytopenia
- Single Donor Platelets:
- Volume: 200-300 mL.
- Storage Temperature: 20-24 °C with agitation.
- Shelf Life: 5 Days.
- Use: Thrombocytopenia
- Whole Blood:
-
Notes:
- 1 unit of blood increases Hb by 1 g% (in blood).
- 1 unit of random donor platelets increases platelets by 10,000/μL.
- 1 unit of single donor platelets increases platelets by 30,000/μL.
- Blood is screened for: HIV, Hepatitis B/C, malaria, and syphilis.
- Malaria can be transmitted by all blood products.
- Platelets are the component most prone to bacterial contamination.
- The lifespan of transfused RBCs is 50-60 days.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
This quiz covers key peripheral smear findings associated with various blood disorders, including macrocytic anemia and spherocytosis. Additionally, it explores Hodgkin's Lymphomas, focusing on their epidemiology and clinical features. Test your knowledge on these important topics in hematology.