Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the three main types of neurons in the nervous system?
What are the three main types of neurons in the nervous system?
- Motor neurons, relay neurons, sensory neurons
- Sensory neurons, motor neurons, interneurons (correct)
- Afferent neurons, efferent neurons, interneurons
- Sensory neurons, motor neurons, inhibitory neurons
What does the autonomic nervous system primarily control?
What does the autonomic nervous system primarily control?
- Glandular activity and internal organ muscles (correct)
- Sensory information processing
- Voluntary muscle movements
- Skeletal muscle coordination
Which term refers to the central nervous system?
Which term refers to the central nervous system?
- Peripheral nervous system
- Afferent system
- Brain and spinal cord (correct)
- Autonomic system
What is the primary function of the somatic nervous system?
What is the primary function of the somatic nervous system?
How do motor neurons function within the nervous system?
How do motor neurons function within the nervous system?
Which of the following systems connects the CNS with the rest of the body?
Which of the following systems connects the CNS with the rest of the body?
What role do sensory neurons play in the nervous system?
What role do sensory neurons play in the nervous system?
Which statement correctly describes the autonomic nervous system?
Which statement correctly describes the autonomic nervous system?
What is the primary role of the sympathetic nervous system?
What is the primary role of the sympathetic nervous system?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the parasympathetic nervous system?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the parasympathetic nervous system?
What connects the peripheral nervous system to the brain?
What connects the peripheral nervous system to the brain?
Which division of the autonomic nervous system is responsible for the 'fight or flight' response?
Which division of the autonomic nervous system is responsible for the 'fight or flight' response?
What are the main components of the central nervous system?
What are the main components of the central nervous system?
How does the sympathetic nervous system affect heart rate?
How does the sympathetic nervous system affect heart rate?
What is the primary function of the parasympathetic nervous system during ordinary situations?
What is the primary function of the parasympathetic nervous system during ordinary situations?
Which part of the brain is NOT one of the four main lobes?
Which part of the brain is NOT one of the four main lobes?
What hormone released by the pituitary gland is primarily responsible for stimulating physical development?
What hormone released by the pituitary gland is primarily responsible for stimulating physical development?
Which gland is located in the upper torso and is important for developing T cells?
Which gland is located in the upper torso and is important for developing T cells?
What role does oxytocin play besides enabling contractions during childbirth?
What role does oxytocin play besides enabling contractions during childbirth?
Which gland is primarily responsible for regulating blood sugar levels?
Which gland is primarily responsible for regulating blood sugar levels?
What is the primary function of ascending neural fibers in the spinal cord?
What is the primary function of ascending neural fibers in the spinal cord?
Which hormone is secreted by the ovaries to promote female sex characteristics?
Which hormone is secreted by the ovaries to promote female sex characteristics?
What is the primary function of the thyroid gland?
What is the primary function of the thyroid gland?
Which of the following tasks is NOT performed by the spinal cord?
Which of the following tasks is NOT performed by the spinal cord?
How do descending neural fibers function in relation to motor control?
How do descending neural fibers function in relation to motor control?
What is the primary function of the adrenal glands?
What is the primary function of the adrenal glands?
What distinguishes hormonal signaling in the endocrine system from signaling in the nervous system?
What distinguishes hormonal signaling in the endocrine system from signaling in the nervous system?
Which gland is commonly involved in regulating sleep-wake cycles?
Which gland is commonly involved in regulating sleep-wake cycles?
What type of neurons connect to the spinal cord dorsally?
What type of neurons connect to the spinal cord dorsally?
Which of the following functions is NOT controlled by hormones in the endocrine system?
Which of the following functions is NOT controlled by hormones in the endocrine system?
Which gland is often referred to as the 'master gland' because it regulates other endocrine glands?
Which gland is often referred to as the 'master gland' because it regulates other endocrine glands?
What role does the hypothalamus play in the endocrine system?
What role does the hypothalamus play in the endocrine system?
Which symptom is associated with Cushing syndrome?
Which symptom is associated with Cushing syndrome?
What is a common treatment for Addison disease?
What is a common treatment for Addison disease?
Which of the following is NOT a symptom of diabetes?
Which of the following is NOT a symptom of diabetes?
What is a characteristic symptom of Cushing syndrome related to the skin?
What is a characteristic symptom of Cushing syndrome related to the skin?
Which statement accurately describes the relationship between Addison disease and dietary cravings?
Which statement accurately describes the relationship between Addison disease and dietary cravings?
What type of diabetes is characterized by insufficient insulin production?
What type of diabetes is characterized by insufficient insulin production?
Which of the following treatments can help manage diabetes?
Which of the following treatments can help manage diabetes?
Which symptom is common across both Cushing syndrome and diabetes?
Which symptom is common across both Cushing syndrome and diabetes?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
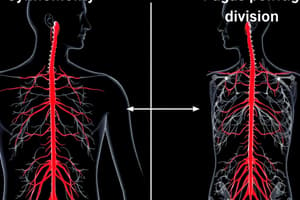
Peripheral Nervous System
- The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates internal organs including the heart, lungs, and digestive glands.
- The ANS has two main divisions: the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
- Sympathetic nervous system activates the fight or flight response, increasing heart rate, blood sugar, and energy for muscular strength.
- Parasympathetic nervous system conserves energy, lowering heart rate and blood pressure during ordinary situations.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
- The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, controlling most body functions.
- The brain can be divided into four lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital.
- Neurons in the brain cluster into neural networks for efficient communication.
Spinal Cord
- Acts as a two-way information highway between the CNS and peripheral nervous system.
- Responsible for conveying sensory information to the brain and controlling motor functions.
- Contains ascending neural fibers for sensory signals and descending fibers for motor control.
Neurons in the Nervous System
- Three main types of neurons: sensory (afferent), motor (efferent), and interneurons.
- Sensory neurons transmit information from the senses to the CNS.
- Motor neurons carry commands from the CNS to muscles and glands.
Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
- The SNS allows voluntary control of skeletal muscles.
- It connects the CNS with the rest of the body for motor functions.
Endocrine System
- The endocrine system regulates bodily functions through hormone secretion from glands.
- Hormones travel through the bloodstream, influencing processes like metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
Major Endocrine Glands
- Hypothalamus: Regulates sleep-wake cycles, temperature, and appetite.
- Pituitary Gland: Produces growth hormone and oxytocin, controlling growth and reproductive functions.
- Pineal Gland: Influential in regulating sleep-wake cycles.
- Thyroid Gland: Crucial for metabolism.
- Parathyroid Gland: Maintains calcium levels in blood and bones.
- Thymus: Produces hormones vital for T cell development until puberty.
- Adrenal Glands: Manage stress and regulate heart rate and blood pressure.
- Pancreas: Controls blood sugar levels through insulin and glucagon.
Connection Between Endocrine and Nervous Systems
- Both systems produce molecules acting on receptors throughout the body.
- The nervous system reacts swiftly, transmitting signals almost instantly.
Conditions Affecting the Endocrine System
- Cushing Syndrome: Symptoms include weight gain, weakened skin, and irregular periods; treatment varies based on the cause.
- Addison Disease: Characterized by low hormone production from adrenal glands, causing fatigue, weight loss, and cravings for salt; treatment includes hormone replacement.
- Diabetes: Involves poorly regulated blood sugar levels, leading to fatigue and frequent urination; management involves monitoring and lifestyle changes.
Learning Engagement
- Explore disorders of the endocrine system like diabetes and thyroid abnormalities, focusing on their physical and emotional impacts and potential treatments.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.