Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the anatomical location of the hypoglossal canal?
What is the anatomical location of the hypoglossal canal?
- Between the Occipital and Temporal bones (correct)
- Anterior to the occipital lobe
- Superior to the medulla
- Inferior to the pons
What would be the observed behavior of the tongue if there is damage to the right hypoglossal nerve?
What would be the observed behavior of the tongue if there is damage to the right hypoglossal nerve?
- The tongue will retract backward
- The tongue will deviate to the left
- The tongue will deviate to the right (correct)
- The tongue will point straight ahead
Which cranial nerve does not connect to the brainstem?
Which cranial nerve does not connect to the brainstem?
- CN I (correct)
- CN V
- CN VII
- CN IX
Where does cranial nerve XII originate?
Where does cranial nerve XII originate?
At which anatomical landmark does cranial nerve III originate?
At which anatomical landmark does cranial nerve III originate?
Which cranial nerve is responsible for vision?
Which cranial nerve is responsible for vision?
What is the function of the vestibulocochlear nerve?
What is the function of the vestibulocochlear nerve?
Which of the following cranial nerves does not contribute to sensory information?
Which of the following cranial nerves does not contribute to sensory information?
How many cranial nerves are present in the human body?
How many cranial nerves are present in the human body?
Which cranial nerve is associated with taste from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue?
Which cranial nerve is associated with taste from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue?
What type of nerve is the vagus nerve classified as?
What type of nerve is the vagus nerve classified as?
Which Roman numeral corresponds to the trigeminal nerve?
Which Roman numeral corresponds to the trigeminal nerve?
The oculomotor nerve is primarily responsible for which of the following functions?
The oculomotor nerve is primarily responsible for which of the following functions?
Which cranial nerve is associated with the olfactory system?
Which cranial nerve is associated with the olfactory system?
What structure do optic nerve fibers synapse with before being transmitted to the visual cortex?
What structure do optic nerve fibers synapse with before being transmitted to the visual cortex?
What is the primary function of the oculomotor nerve (CN III)?
What is the primary function of the oculomotor nerve (CN III)?
Which of the following extrinsic eye muscles is NOT supplied by the oculomotor nerve (CN III)?
Which of the following extrinsic eye muscles is NOT supplied by the oculomotor nerve (CN III)?
What does the term ' trochlea' refer to in relation to cranial nerve IV?
What does the term ' trochlea' refer to in relation to cranial nerve IV?
Which cranial nerve is responsible for the sensory perception of vision?
Which cranial nerve is responsible for the sensory perception of vision?
Which anatomical feature is associated with the olfactory nerve?
Which anatomical feature is associated with the olfactory nerve?
Which structure do the optic nerve fibers connect to after crossing at the optic chiasma?
Which structure do the optic nerve fibers connect to after crossing at the optic chiasma?
What primary function is associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve?
What primary function is associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve?
Which nerve is responsible for the gag reflex?
Which nerve is responsible for the gag reflex?
Which anatomical structures does the vagus nerve primarily interact with?
Which anatomical structures does the vagus nerve primarily interact with?
What type of function does the accessory nerve primarily serve?
What type of function does the accessory nerve primarily serve?
Where do the accessory nerve fibers originate from?
Where do the accessory nerve fibers originate from?
Which receptors in the carotid sinus are associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve?
Which receptors in the carotid sinus are associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve?
What is a unique characteristic of the accessory nerve?
What is a unique characteristic of the accessory nerve?
Which muscle is not primarily innervated by the accessory nerve?
Which muscle is not primarily innervated by the accessory nerve?
Which cranial nerve is responsible for the sense of smell?
Which cranial nerve is responsible for the sense of smell?
What type of function is associated with the Trigeminal nerve?
What type of function is associated with the Trigeminal nerve?
Which mnemonic helps to remember the functions of cranial nerves?
Which mnemonic helps to remember the functions of cranial nerves?
What does CN VII (Facial nerve) primarily control?
What does CN VII (Facial nerve) primarily control?
Which cranial nerve exits through the Foramen Magnum?
Which cranial nerve exits through the Foramen Magnum?
Which cranial nerve is purely sensory?
Which cranial nerve is purely sensory?
Which of the following cranial nerves is responsible for eye movement?
Which of the following cranial nerves is responsible for eye movement?
Which cranial nerve is associated with the function of balance and hearing?
Which cranial nerve is associated with the function of balance and hearing?
What is the function of the Vagus nerve?
What is the function of the Vagus nerve?
Which of the following foramen does the Trigeminal nerve exit through?
Which of the following foramen does the Trigeminal nerve exit through?
What is the primary function of the Hypoglossal nerve?
What is the primary function of the Hypoglossal nerve?
What mnemonic helps to remember the foramina through which cranial nerves exit?
What mnemonic helps to remember the foramina through which cranial nerves exit?
Which cranial nerve is primarily responsible for mastication (chewing)?
Which cranial nerve is primarily responsible for mastication (chewing)?
What is the main action performed by the superior oblique muscle?
What is the main action performed by the superior oblique muscle?
Which nerve is primarily responsible for the cutaneous supply in the face?
Which nerve is primarily responsible for the cutaneous supply in the face?
The mnemonic SO4LR6 helps to remember the innervation of which cranial nerves?
The mnemonic SO4LR6 helps to remember the innervation of which cranial nerves?
Which cranial nerve is responsible for the muscles of facial expression?
Which cranial nerve is responsible for the muscles of facial expression?
What is the primary function of the vestibular branch of the vestibulocochlear nerve?
What is the primary function of the vestibular branch of the vestibulocochlear nerve?
Through which foramina does the trigeminal nerve (CN V) exit the skull?
Through which foramina does the trigeminal nerve (CN V) exit the skull?
Which cranial nerve is responsible for supplying the anterior two-thirds of the tongue?
Which cranial nerve is responsible for supplying the anterior two-thirds of the tongue?
What type of function is primarily associated with the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)?
What type of function is primarily associated with the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)?
Flashcards
Autonomic Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System
The part of the nervous system that controls involuntary bodily functions, like heart rate, digestion, and breathing.
Sympathetic Nervous System
Sympathetic Nervous System
The part of the autonomic nervous system that activates the 'fight-or-flight' response, preparing the body for action.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Parasympathetic Nervous System
The part of the autonomic nervous system that promotes 'rest and digest' functions, conserving energy and calming the body.
Cranial Nerve
Cranial Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Olfactory Nerve (I)
Olfactory Nerve (I)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Optic Nerve (II)
Optic Nerve (II)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oculomotor Nerve (III)
Oculomotor Nerve (III)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trochlear Nerve (IV)
Trochlear Nerve (IV)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cribriform Plate
Cribriform Plate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Optic Canal
Optic Canal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Optic Chiasma
Optic Chiasma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superior Orbital Fissure
Superior Orbital Fissure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscles NOT Supplied by CN III
Muscles NOT Supplied by CN III
Signup and view all the flashcards
CN I
CN I
Signup and view all the flashcards
CN II
CN II
Signup and view all the flashcards
CN III
CN III
Signup and view all the flashcards
CN IV
CN IV
Signup and view all the flashcards
CN V
CN V
Signup and view all the flashcards
CN VI
CN VI
Signup and view all the flashcards
CN VII
CN VII
Signup and view all the flashcards
CN VIII
CN VIII
Signup and view all the flashcards
CN IX
CN IX
Signup and view all the flashcards
CN X
CN X
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypoglossal Nerve (XII)
Hypoglossal Nerve (XII)
Signup and view all the flashcards
CN XI
CN XI
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypoglossal Canal
Hypoglossal Canal
Signup and view all the flashcards
CN XII
CN XII
Signup and view all the flashcards
Jugular Foramen Location
Jugular Foramen Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypoglossal Nerve Lesion
Hypoglossal Nerve Lesion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brainstem Origins of Cranial Nerves
Brainstem Origins of Cranial Nerves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX)
Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gag Reflex
Gag Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vagus Nerve (X)
Vagus Nerve (X)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Baroreceptors
Baroreceptors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chemoreceptors
Chemoreceptors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Accessory Nerve (XI)
Accessory Nerve (XI)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sternocleidomastoid
Sternocleidomastoid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trapezius
Trapezius
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superior Oblique Action
Superior Oblique Action
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trigeminal Nerve (V)
Trigeminal Nerve (V)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trigeminal Nerve Branches
Trigeminal Nerve Branches
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trigeminal Nerve Exit Points
Trigeminal Nerve Exit Points
Signup and view all the flashcards
Abducens Nerve (VI)
Abducens Nerve (VI)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Facial Nerve (VII)
Facial Nerve (VII)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (VIII)
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (VIII)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
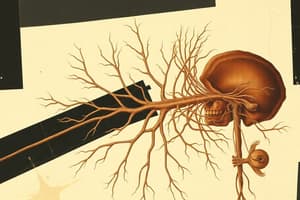
Peripheral Nervous System: Cranial Nerves and Special Senses
- The lecture covers the peripheral nervous system, focusing on cranial nerves and special senses.
- Students should be able to define, identify, describe, spell, determine the function, and understand the relationships among the autonomic, sympathetic, and parasympathetic nervous systems, motor nerves, sensory nerves, somatic, visceral nerves, cranial nerves, olfactory nerve, optic nerve, oculomotor nerve, trochlear nerve, trigeminal nerve, abducens nerve, facial nerve, vestibulocochlear nerve, glossopharyngeal nerve, vagus nerve, and spinal accessory nerve, and hypoglossal nerve.
- Students need to know Roman numerals I through XII.
- Students should be able to describe and label the cranial nerves, from their brainstem origin to their target organs.
- Students should be able to describe the functions of the cranial nerves, especially focusing on how each nerve contributes to sensory information.
- Students should also be able to describe the motor functions of the cranial nerves.
- Learn at least 1 topic of personal interest, such as vision, smell, taste, hearing, or balance, detailing the anatomy and physiology.
Cranial Nerve Mnemonics
- A mnemonic device for remembering cranial nerve names is "Oh, Once One Takes The Anatomy Final, Very Good Vacations Are Heavenly!"
- Another mnemonic for cranial nerve functions is "Some Say Marry Money, But My Brother Says Big “Brains” Mean More."
- Other mnemonics exist for remembering the locations of origin and exits of the cranial nerves (e.g., "Carl Only Swims South").
Cranial Nerve Details
- Detailed information on each cranial nerve (I-XII), including their names, functions, and the foramina they exit. For example, the olfactory nerve doesn't connect to the brainstem, the optic nerve passes through the optic canal, the oculomotor nerve's function includes moving most extrinsic eye muscles, the trochlear nerve is involved in superior oblique muscle movement.
- Knowledge of the specific nerves' origins, target organs, functions, (sensory or motor) is critical.
- The specifics of each nerve's sensory and/or motor functions are essential.
- Understanding of the foramina (bony openings) through which the nerves exit the skull.
- Knowledge of any related clinical or medical applications (e.g., the trigeminal nerve's relation to dentistry.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.