Podcast
Questions and Answers
What does PNS stand for?
What does PNS stand for?
Peripheral Nervous System
How many pairs of nerves are in the PNS?
How many pairs of nerves are in the PNS?
43
What type of messages do cranial nerves transmit?
What type of messages do cranial nerves transmit?
- Neither Motor nor Sensory
- Motor or Sensory (correct)
- Motor only
- Sensory only
All cranial nerves originate from the midbrain.
All cranial nerves originate from the midbrain.
What is the function of the olfactory nerve (I)?
What is the function of the olfactory nerve (I)?
What is the function of the optic nerve (II)?
What is the function of the optic nerve (II)?
What is the function of the oculomotor nerve (III)?
What is the function of the oculomotor nerve (III)?
What is the function of the trochlear nerve (IV)?
What is the function of the trochlear nerve (IV)?
What is the function of the trigeminal nerve (V)?
What is the function of the trigeminal nerve (V)?
What is the function of the abducent nerve (VI)?
What is the function of the abducent nerve (VI)?
What is the function of the facial nerve (VII)?
What is the function of the facial nerve (VII)?
What is the function of the vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)?
What is the function of the vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)?
What is the function of the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)?
What is the function of the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)?
What is the function of the vagus nerve (X)?
What is the function of the vagus nerve (X)?
What is the function of the accessory nerve (XI)?
What is the function of the accessory nerve (XI)?
What is the function of the hypoglossal nerve (XII)?
What is the function of the hypoglossal nerve (XII)?
The somatic nervous system controls voluntary movement.
The somatic nervous system controls voluntary movement.
The autonomic nervous system is responsible for controlling involuntary functions like breathing and heart rate.
The autonomic nervous system is responsible for controlling involuntary functions like breathing and heart rate.
What is the neurotransmitter released by somatic motor neurons?
What is the neurotransmitter released by somatic motor neurons?
What is the function of the sympathetic nervous system?
What is the function of the sympathetic nervous system?
Sympathetic and parasympathetic effects are always opposite in all organs.
Sympathetic and parasympathetic effects are always opposite in all organs.
The adrenal medulla is a part of the sympathetic nervous system.
The adrenal medulla is a part of the sympathetic nervous system.
What are the two main neurotransmitters released by the autonomic nervous system?
What are the two main neurotransmitters released by the autonomic nervous system?
Norepinephrine is the same thing as noradrenaline.
Norepinephrine is the same thing as noradrenaline.
Nicotinic receptors are found at the neuromuscular junction of skeletal muscles.
Nicotinic receptors are found at the neuromuscular junction of skeletal muscles.
Muscarinic receptors are found in the postganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system.
Muscarinic receptors are found in the postganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system.
What is the name of the toxin produced by certain mushrooms that is an agonist for muscarinic receptors?
What is the name of the toxin produced by certain mushrooms that is an agonist for muscarinic receptors?
What is the name of the antagonist for muscarinic receptors?
What is the name of the antagonist for muscarinic receptors?
Flashcards
What are the two main branches of the autonomic nervous system?
What are the two main branches of the autonomic nervous system?
The autonomic nervous system is divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches, each controlling different bodily functions.
What is the function of the sympathetic nervous system?
What is the function of the sympathetic nervous system?
The sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for stressful situations, often described as 'fight or flight'. It increases heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration, diverting blood to muscles and preparing for action.
What is the function of the parasympathetic nervous system?
What is the function of the parasympathetic nervous system?
The parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for 'rest and digest' functions, promoting relaxation and digestion. It slows heart rate, lowers blood pressure, and increases digestion.
What are the two main neurotransmitters of the autonomic nervous system?
What are the two main neurotransmitters of the autonomic nervous system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are cholinergic receptors?
What are cholinergic receptors?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the two main types of cholinergic receptors?
What are the two main types of cholinergic receptors?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are adrenergic receptors?
What are adrenergic receptors?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the effects of sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation on pupils?
What are the effects of sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation on pupils?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
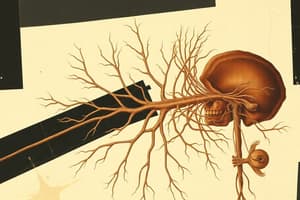
Cranial Nerves & Peripheral Nervous System
- The peripheral nervous system (PNS) transmits signals between the central nervous system (CNS) and receptors/effectors throughout the body.
- Axons are bundled together to form nerves.
- The PNS comprises 43 pairs of nerves: 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves. These connect to the spinal cord.
- Cranial nerves primarily connect the brain/brainstem to the head and neck. They carry motor or sensory or both types of messages.
- Cranial nerves (except olfactory and optic) arise from the midbrain, pons, or medulla oblongata.
Cranial Nerve Functions
- Olfactory (I): Sensory, smell
- Optic (II): Sensory, vision
- Oculomotor (III): Motor, extraocular eye movement (superior, medial, and inferior lateral), pupillary constriction, and upper eyelid elevation.
- Trochlear (IV): Motor, extraocular eye movement (inferior medial)
- Trigeminal (V): Both, sensory (face and head, corneal reflex), motor (chewing, biting, lateral jaw movements).
- Abducens (VI): Motor, extraocular eye movement (lateral)
- Facial (VII): Both, sensory (taste anterior 2/3 of tongue), motor (facial muscle movement, including expression).
- Vestibulocochlear (VIII): Sensory, hearing and balance
- Glossopharyngeal (IX): Both, sensory (throat, taste posterior 1/3 tongue), motor (swallowing)
- Vagus (X): Both, sensory (throat, larynx, thoracic and abdominal viscera), motor (palate movement, swallowing, gag reflex, and activity of thoracic/abdominal viscera - heart, lungs, and GI tract)
- Accessory (XI): Motor, shoulder movement, head rotation
- Hypoglossal (XII): Motor, tongue movement
Somatic Nervous System
- The somatic portion of the PNS carries signals from the CNS to skeletal muscle cells.
- Axons in this system are large, myelinated, and pass directly to target muscles without synapses.
- The neurotransmitter released by these neurons is acetylcholine.
- Excitation of motor neurons causes muscle contractions.
- Muscle relaxation occurs through the inhibition of motor neurons within the spinal cord.
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- The ANS controls involuntary actions in internal organs.
- It's typically comprised of two neuron chains (pre and postganglionic) connecting the CNS to effector cells (e.g cardiac muscle, smooth muscles glands).
- The synapse between the two neurons occurs outside the CNS in structures called ganglia.
- There are two main branches: sympathetic and parasympathetic.
Autonomic Nervous System Divisions
- Sympathetic Division:
- Fibers originate from the thoracic (chest) and lumbar regions of the spinal cord.
- Often called thoracolumbar division.
- Associated with "fight or flight" responses.
- Parasympathetic Division:
- Fibers originate from the brainstem and sacral portion of the spinal cord.
- Often called craniosacral division.
- Associated with maintaining homeostasis (e.g., digestion).
ANS Neurotransmitters
- The main neurotransmitters of the ANS are acetylcholine and norepinephrine.
- Acetylcholine is used by preganglionic neurons in both sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions, and by postganglionic neurons in the parasympathetic system.
- Norepinephrine is released by postganglionic sympathetic neurons except for those connecting to sweat glands.
Autonomic Receptors
- Cholinergic receptors bind acetylcholine.
- Nicotinic receptors are found at neuromuscular junctions of skeletal muscle, postganglionic neurons, and neurons in the brain.
- Muscarinic receptors are found at neuromuscular junctions of cardiac and smooth muscle, glands, and some sympathetic neurons.
- Adrenergic receptors respond to norepinephrine and epinephrine.
- Different adrenergic receptor subtypes (α1, α2, β1, β2, β3) impact target effectors differently.
ANS Physiological Effects
- Physiological effects depend on whether sympathetic or parasympathetic activities are dominant.
- Effects can be localized or widespread (eg. heart rate increases during stress via widespread sympathetic response).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.