Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of cementum?
What is the primary function of cementum?
- To provide sensation to the tooth
- To attach the tooth to the periodontal ligament
- To produce dentin
- To seal the open dentinal tubules (correct)
What is the width range of the periodontal ligament?
What is the width range of the periodontal ligament?
- 0.5 to 1 mm
- 1 to 2 mm
- 0.15 to 0.38 mm (correct)
- 0.05 to 0.1 mm
What is the main component of alveolar bone?
What is the main component of alveolar bone?
- Cementum
- Dentin
- Mineralized organic matrix
- Specialized connective tissue (correct)
What is the function of the periodontal ligament?
What is the function of the periodontal ligament?
What is the function of acellular cementum?
What is the function of acellular cementum?
What is the function of cellular cementum?
What is the function of cellular cementum?
What is the classification of cementum based on location?
What is the classification of cementum based on location?
What is the attachment apparatus of the tooth?
What is the attachment apparatus of the tooth?
What is the main function of the jaw bones?
What is the main function of the jaw bones?
What is the alveolar process divisible into on an anatomic basis?
What is the alveolar process divisible into on an anatomic basis?
What surrounds the root of the tooth and gives attachment to principal fibers of the periodontal ligament?
What surrounds the root of the tooth and gives attachment to principal fibers of the periodontal ligament?
What is the term for the isolated areas in which the root is denuded of bone and marginal bone is intact?
What is the term for the isolated areas in which the root is denuded of bone and marginal bone is intact?
What is the term for the denuded areas that extend through the marginal bone?
What is the term for the denuded areas that extend through the marginal bone?
What is the portion of the jaw located apically but unrelated to the teeth?
What is the portion of the jaw located apically but unrelated to the teeth?
What is the main function of the gingivae?
What is the main function of the gingivae?
What is the gingival sulcus?
What is the gingival sulcus?
What is the function of the gingival fibers?
What is the function of the gingival fibers?
What is the color of the gingivae in health?
What is the color of the gingivae in health?
What is the part of the periodontium that supports the fibers of the periodontal ligament?
What is the part of the periodontium that supports the fibers of the periodontal ligament?
What is the location of the gingival margin in health?
What is the location of the gingival margin in health?
What is the anatomical division of the gingivae?
What is the anatomical division of the gingivae?
What is the characteristic of the gingival sulcus in a fully erupted tooth?
What is the characteristic of the gingival sulcus in a fully erupted tooth?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
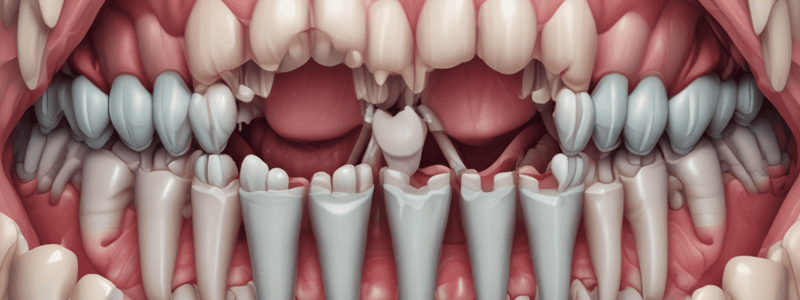
Periodontium
- Consists of investing and supporting tissues of the tooth: gingivae, periodontal ligament, cementum, and alveolar bone
- Divided into two parts: gingivae and attachment apparatus (periodontal ligament, cementum, and alveolar bone)
Gingivae
- Part of oral mucosa that covers alveolar processes of jaws and surrounds necks of teeth
- In health, gingivae are pink, firm, and have a knife-edge appearance, scalloped around teeth
- May be pigmented in certain ethnic groups
- Gingival margin is a few millimeters coronal to cement-enamel junction
- Gingival sulcus (or crevice) is a shallow groove, 0.5-3 mm in depth around a fully erupted tooth
- Gingival tissues are keratinized and appear paler pink than non-keratinized oral epithelium
Clinical Features
- Normal gingivae cover alveolar bone and tooth root to a level just coronal to cement-enamel junction
- Gingivae are divided anatomically into marginal, attached, and interdental areas
Gingival Fibers
- Functions:
- Stabilize attached gingivae to alveolar process
- Stabilize attached gingivae to tooth
- Help maintain epithelial seal to tooth
- Provide stability to tooth
- Provide rigidity to withstand forces of mastication
- Help maintain marginal/free gingivae firmly against tooth and adjacent attached gingivae
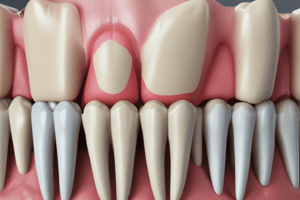
Periodontal Ligament
- Soft, specialized connective tissue situated between cementum covering root of tooth and bone forming socket wall
- Width ranges from 0.15 to 0.38 mm
- Constituents:
- Periodontal ligament fibers
- Cellular elements
- Ground substances (glycosaminoglycans and glycoproteins)
Cementum
- Calcified, avascular, mesenchymal tissue forming the outer covering of anatomic root
- Functions:
- Provides attachment to collagen fibers of periodontal ligament to root
- Covers root surface, sealing open dentinal tubules, preventing dentinal sensitivity
- Aids in maintaining teeth in functional occlusion
- Contributes to process of repair after damage to root surface
- Classification:
- According to location: radicular and coronal cementum
- According to cells present: acellular and cellular cementum
- According to fibers present: not specified
Alveolar Bone
- Portion of maxilla and mandible that forms and supports tooth sockets (alveoli)
- Specialized connective tissue with mineralized organic matrix
- Main function is to distribute and reabsorb forces generated by mastication and other tooth contact
- Consists of:
- Alveolar bone proper: thin lamella of bone surrounding root of tooth and giving attachment to principal fibers of periodontal ligament
- Supporting alveolar bone: surrounds alveolar bone proper and gives support to socket
- Cortical plates: compact bone forming outer and inner plates of alveolar bone
- Spongy bone (trabecular or cancellous bone): fills area between plates and alveolar bone proper
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.