Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the percentage of teeth where cementum meets the cervical end of enamel in a knife edge-to-edge pattern?
What is the percentage of teeth where cementum meets the cervical end of enamel in a knife edge-to-edge pattern?
- 20%
- 30% (correct)
- 60%
- 10%
What type of cementum is deposited on the enamel surface by differentiated mesenchymal cells?
What type of cementum is deposited on the enamel surface by differentiated mesenchymal cells?
- Afibrillar cementum (correct)
- Fibrillar cementum
- Acellular cementum
- Cellular cementum
What is the result of cementum not meeting enamel, where a zone of root dentin appears devoid of cementum?
What is the result of cementum not meeting enamel, where a zone of root dentin appears devoid of cementum?
- Dental hypersensitivity (correct)
- Tooth decay
- Gingivitis
- Periodontitis
What is the percentage of teeth where cementum overlaps enamel?
What is the percentage of teeth where cementum overlaps enamel?
What is the characteristic of the dentin surface in deciduous teeth upon which cementum is deposited?
What is the characteristic of the dentin surface in deciduous teeth upon which cementum is deposited?
How many phases does cementogenesis take place?
How many phases does cementogenesis take place?
What is the characteristic of the growth of cementum?
What is the characteristic of the growth of cementum?
What is the term for the uncalcified matrix secreted by cementoblasts during cementogenesis?
What is the term for the uncalcified matrix secreted by cementoblasts during cementogenesis?
What happens to cementoblasts after reaching full thickness?
What happens to cementoblasts after reaching full thickness?
What is the term for abnormal thickening of cementum?
What is the term for abnormal thickening of cementum?
What is the function of cementum in case of root fracture or resorption?
What is the function of cementum in case of root fracture or resorption?
What is the term for calcified oval or round nodules found in the PDL?
What is the term for calcified oval or round nodules found in the PDL?
What is the reason why cementum is more resistant to resorption?
What is the reason why cementum is more resistant to resorption?
What is the term for the fusion of cementum to alveolar bone with obliteration of PDL?
What is the term for the fusion of cementum to alveolar bone with obliteration of PDL?
What is the function of cementum in binding the tooth root to the alveolar bone?
What is the function of cementum in binding the tooth root to the alveolar bone?
What happens to the permeability of cementum with aging?
What happens to the permeability of cementum with aging?
What is the primary function of cementoblasts?
What is the primary function of cementoblasts?
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding cementocytes?
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding cementocytes?
What is the significance of Salter lines in cementum?
What is the significance of Salter lines in cementum?
Which type of cementum is typically found on the apical half of the root?
Which type of cementum is typically found on the apical half of the root?
What is a key characteristic that distinguishes intermediate cementum from cellular and acellular cementum?
What is a key characteristic that distinguishes intermediate cementum from cellular and acellular cementum?
Why is cementum considered an avascular tissue?
Why is cementum considered an avascular tissue?
What type of cementum is formed when mesenchymal cells differentiate into cementoblasts and deposit cementum on the enamel surface?
What type of cementum is formed when mesenchymal cells differentiate into cementoblasts and deposit cementum on the enamel surface?
Which type of cementum is characterized by the presence of intrinsic fibers?
Which type of cementum is characterized by the presence of intrinsic fibers?
Which type of cementum is characterized by the presence of cementocytes within lacunae?
Which type of cementum is characterized by the presence of cementocytes within lacunae?
Which of the following is NOT a type of cementum based on fibrillar content?
Which of the following is NOT a type of cementum based on fibrillar content?
What is the primary component of acellular cementum?
What is the primary component of acellular cementum?
Which of the following is TRUE regarding the location of acellular cementum?
Which of the following is TRUE regarding the location of acellular cementum?
What is the significance of the reduced enamel epithelium in the formation of cementum?
What is the significance of the reduced enamel epithelium in the formation of cementum?
What is the primary function of Sharpey's fibers in cementum?
What is the primary function of Sharpey's fibers in cementum?
Which of the following statements regarding the formation of cementum is TRUE?
Which of the following statements regarding the formation of cementum is TRUE?
What is the Cementoenamel Junction (CEJ)?
What is the Cementoenamel Junction (CEJ)?
What is the primary function of cementum in the periodontium?
What is the primary function of cementum in the periodontium?
Which of the following statements about the thickness of cementum is correct?
Which of the following statements about the thickness of cementum is correct?
What is the primary chemical composition of cementum?
What is the primary chemical composition of cementum?
Which type of collagen is primarily found in the bulk of cementum?
Which type of collagen is primarily found in the bulk of cementum?
What distinguishes cellular cementum from acellular cementum?
What distinguishes cellular cementum from acellular cementum?
What is the coloration of cementum relative to other dental hard tissues?
What is the coloration of cementum relative to other dental hard tissues?
What happens to cementum's permeability with age?
What happens to cementum's permeability with age?
What are Sharpey's fibers in relation to cementum?
What are Sharpey's fibers in relation to cementum?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Cementum
- Part of the periodontium, which is the investing and supporting attachment system of the teeth
- Consists of two soft tissues (gingiva and periodontal ligament) and two hard tissues (cementum and alveolar bone)
- A calcified, hard connective tissue derived from ectomesenchyme of the dental follicle, forming the outer covering of the anatomic root
- Begins at the cervical portion of the tooth at the cemento-enamel junction and continues to the apex
- Avascular and non-innervated
Physical Characteristics
- Color: Yellow, lighter than dentin but darker than enamel
- Hardness: Lesser than dentin
- Permeability: Permeable to inorganic ions and bacteria, which diminishes with age; cellular cementum is more permeable than acellular cementum
- Thickness: Thinnest at the cemento-enamel junction (20-50μm) and gradually thicker apically, ranging from 150-200μm or more
Chemical Composition
- 45-50% inorganic substances (calcium phosphate in the form of hydroxyapatite crystals)
- 50-55% organic substances (collagen fibers embedded in a ground substance, polysaccharides, and proteins)
- Contains the greatest amount of fluoride in mineralized tissues
Histological Structure of Cementum
- Two forms of collagen: collagen fibrils and collagen bundles
- Collagen fibrils constitute the main bulk of the organic material of cementum
- Collagen bundles represent the embedded portion of the principal fibers of the periodontal ligament, known as Sharpey's fibers
- Two types of cells functionally concerned with cementum: cementoblasts and cementocytes
- Cementoblasts line the root surface and contain numerous mitochondria and a well-developed Golgi complex; they become entrapped in the cementum matrix and form cementocytes
- Cementocytes are seen in lacunae in the cementum matrix and have numerous processes that may branch and anastomose with those of adjacent cementocytes
Types of Cementum
- Based on cellular content:
- Cellular cementum: contains cells called cementocytes in lacunae, more frequently found on the apical half of the root
- Intermediate cementum: a thin, amorphous layer of hard tissue approximately 10 microns thick, intermediate between cementum and dentin
- Acellular cementum: doesn't contain cells, present on the cervical third or half of the root
- Based on fibrillar content:
- Intrinsic fibers cementum: fibers derived from the synthetic and secretory activity of cementoblasts
- Extrinsic fibers cementum: fibers originate from the principal fibers of the periodontal ligament (Sharpey's fibers)
- Mixed fibers cementum: contains both intrinsic and extrinsic fibers
- Afibrillar cementum: lacks fibers, formed when the reduced enamel epithelium retracts from the cervical region of enamel, allowing mesenchymal cells to invade and differentiate into cementoblasts
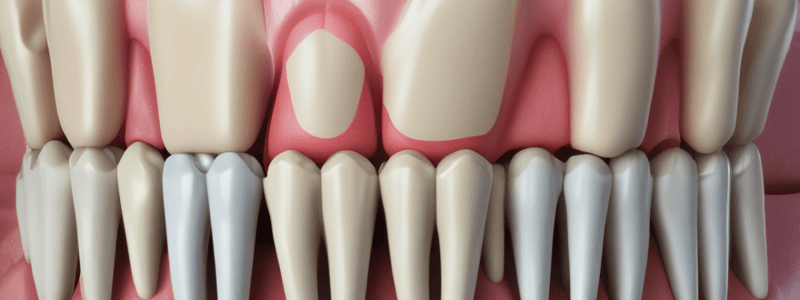
Cementoenamel Junction (CEJ)
- In approximately 60% of teeth, cementum overlaps the cervical end of enamel for a very narrow area at the CEJ
- In 30% of teeth, cementum meets the cervical end of enamel in a knife-edge-to-edge pattern
- In approximately 10% of teeth, cementum does not meet enamel, resulting in a zone of root dentin appearing devoid of cementum
Cementodentinal Junction
- The dentin surface upon which cementum is deposited is relatively smooth in permanent teeth
- The cementodentinal junction in deciduous teeth is sometimes scalloped
Cementogenesis
- Takes place in two phases: matrix formation and mineralization
- Three cell types responsible for cementogenesis: cementoblasts, cementocytes, and fibroblasts, all derived from ectomesenchymal cells
- Growth of cementum is a rhythmic process, with new cementoid formed and old one calcified
- Mineralization begins after forming the first layer of matrix, with mineral crystals deposited within and between collagen fibers
Clinical Considerations
- Hypercementosis: abnormal thickening of cementum, may occur in one tooth or all teeth, in local areas of one root or generalized to the whole root
- Cementum is more resistant to resorption from bone, making orthodontic therapy possible
- Fusion of cementum to alveolar bone with obliteration of the periodontal ligament is termed ankylosis
- Decrease in permeability of cementum with age
- Cementicles: calcified oval or round nodules found in the periodontal ligament, single or multiple, near the cemental surface
Functions of Cementum
- Furnishes a medium for the incorporation of the principal periodontal fibers, securing the binding of the tooth root to the alveolar bone
- Serves as a reparative tissue in case of root fracture or resorption
- Allows for functional adaptation of the tooth by cementum deposition at the apices, compensating for tooth loss occlusally by attrition
- Protects dentin by blocking the dentinal tubules
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.