Podcast
Questions and Answers
What components are included in the periodontium?
What components are included in the periodontium?
- Cementum
- Alveolar bone
- Periodontal ligament
- All of the above (correct)
What is the composition of cementum?
What is the composition of cementum?
65% mineralized, 23% organic, 12% water
Cementum is highly vascular and contains nerves.
Cementum is highly vascular and contains nerves.
False (B)
How does cementum receive nutrition?
How does cementum receive nutrition?
What are cementoblasts responsible for?
What are cementoblasts responsible for?
Which of the following best describes the appearance of cementum when exposed?
Which of the following best describes the appearance of cementum when exposed?
What is the primary function of Sharpey's fibers?
What is the primary function of Sharpey's fibers?
Cementum develops from the __________.
Cementum develops from the __________.
What forms the dentinocemental junction (DCJ)?
What forms the dentinocemental junction (DCJ)?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Periodontium
- Comprises supporting soft and hard tissues associated with teeth.
- Plays a critical role in anchoring teeth to alveolar bone.
- Components include cementum, alveolar bone, periodontal ligament, and specific tissue elements.
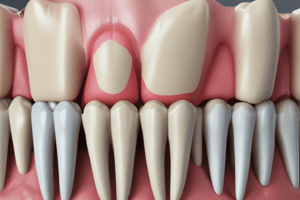
Cementum
- Acts as a connector between teeth and alveolar bone via periodontal ligament.
- Fully covers the root surface, providing stability.
- Classified as a hard tissue, exhibiting thickness variations across different areas.
- Thickest at the apex and interradicular regions; thinnest at the cementoenamel junction (CEJ).
- Avascular and lacks nerve supply, receiving nutrients from periodontal ligament cells.
- Capable of continuous formation throughout an individual's life.
- Composition: 65% mineralized (inorganic), 23% organic, 12% water; primarily consists of calcium hydroxyapatite.
- Similar in composition to bone, with a dull pale yellow appearance when exposed.
- Texture feels grainy upon instrumentation.
Development of Cementum
- Originates from the dental sac after Hertwig's root sheath disintegration.
- Undifferentiated cells from the sac induce differentiation into cementoblasts upon contact with the root surface.
- The process of cementogenesis involves laying down cementoid, leading to maturation and calcification of cementum.
- Once fully formed, the dentinocemental junction (DCJ) is established.
Microscopic Appearance of Cementum
- Composed of a mineralized fibrous matrix with embedded cells.
- Contains Sharpey's fibers, which are collagen fibers inserted at a right angle into both cementum and alveolar bone, acting as a ligament.
- Intrinsic nonperiodontal fibers, organized in a parallel manner to the DCJ, are also present.
Cells of Cementum
- Cementocytes (entrapped cementoblasts) reside in lacunae and have canaliculi for intercellular communication.
- Lacks nerves and does not radiate outward.
- Cementocyte processes are oriented towards the periodontal ligament.
Cementoblasts
- Align along the cementum surface within the periodontal ligament and form new cementum layers as necessary.
Cementoenamel Junction Patterns
- Transitional interfaces at the cementoenamel junction can include overlapping cementum with enamel in certain situations.
Cementum Histology
- Understanding of cementum histology is essential for recognizing its functional and structural significance in dental health.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.