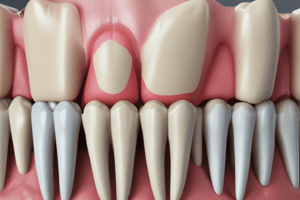
Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary role of the cemento-dentinal junction?
What is the primary role of the cemento-dentinal junction?
- To facilitate the movement of nerves into the tooth
- To separate dentin from enamel
- To regulate blood supply to the tooth
- To serve as a medium for collagen fiber attachment (correct)
How does the width of the cemento-dentinal junction change with age?
How does the width of the cemento-dentinal junction change with age?
- It decreases over time
- It fluctuates with dental health
- It increases significantly
- It remains relatively stable (correct)
What is a key feature of intermediate cementum?
What is a key feature of intermediate cementum?
- It contains characteristic features of dentin
- It contains cellular remnants of Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath (correct)
- It is predominantly found in incisors
- It is a well-defined zone at the cemento-dentinal junction
What function does cementum provide at the surface of sensitive root dentin?
What function does cementum provide at the surface of sensitive root dentin?
What aspect does continuous deposition of cementum facilitate?
What aspect does continuous deposition of cementum facilitate?
Which type of cementum is primarily responsible for the repair of the root surface?
Which type of cementum is primarily responsible for the repair of the root surface?
What characterizes anatomic repair of cementum?
What characterizes anatomic repair of cementum?
What type of cemental resorption is characterized by its origin from within the tooth structure?
What type of cemental resorption is characterized by its origin from within the tooth structure?
Cementum is more resistant to resorption than which of the following?
Cementum is more resistant to resorption than which of the following?
Which of the following is a local factor that can lead to cementum resorption?
Which of the following is a local factor that can lead to cementum resorption?
What happens to the periodontal ligament (PDL) space during functional repair?
What happens to the periodontal ligament (PDL) space during functional repair?
Which of the following systemic factors is associated with cementum resorption?
Which of the following systemic factors is associated with cementum resorption?
What is a key reason for cementum's resistance to resorption compared to bone?
What is a key reason for cementum's resistance to resorption compared to bone?
What is the primary role of the enzyme associated with the ALPL gene?
What is the primary role of the enzyme associated with the ALPL gene?
Which of the following is a common oral sign of hypophosphatasia?
Which of the following is a common oral sign of hypophosphatasia?
Which treatment is NOT typically used for managing hypophosphatasia?
Which treatment is NOT typically used for managing hypophosphatasia?
What is the hallmark radiographic finding in Paget disease?
What is the hallmark radiographic finding in Paget disease?
Which of the following conditions is characterized by overgrowth of body parts in children?
Which of the following conditions is characterized by overgrowth of body parts in children?
What type of bone involvement is primarily associated with Paget disease?
What type of bone involvement is primarily associated with Paget disease?
Which clinical feature is typically associated with acromegaly?
Which clinical feature is typically associated with acromegaly?
Which of the following statements about hypercementosis is correct?
Which of the following statements about hypercementosis is correct?
Which benign neoplasm is characterized by a large mass of cementum or cementum-like tissue on the tooth root?
Which benign neoplasm is characterized by a large mass of cementum or cementum-like tissue on the tooth root?
At what age is Cementoblastoma most commonly diagnosed?
At what age is Cementoblastoma most commonly diagnosed?
Which site is most commonly affected by Cementifying fibroma?
Which site is most commonly affected by Cementifying fibroma?
What is the primary treatment for a well-defined Cementoblastoma?
What is the primary treatment for a well-defined Cementoblastoma?
How can excessive removal of healthy cementum during root planning affect periodontal health?
How can excessive removal of healthy cementum during root planning affect periodontal health?
What characterizes the radiographic finding of Cementoblastoma?
What characterizes the radiographic finding of Cementoblastoma?
Cementifying fibroma is primarily composed of which types of tissue?
Cementifying fibroma is primarily composed of which types of tissue?
In which population is Cementifying fibroma most frequently diagnosed?
In which population is Cementifying fibroma most frequently diagnosed?
What is the primary function of cementum?
What is the primary function of cementum?
What describes the cellular composition of acellular cementum?
What describes the cellular composition of acellular cementum?
Which type of cementum forms after a tooth reaches the occlusal plane?
Which type of cementum forms after a tooth reaches the occlusal plane?
What is the thickness range of the thinnest part of cementum?
What is the thickness range of the thinnest part of cementum?
What is the primary inorganic component of cementum?
What is the primary inorganic component of cementum?
How does the permeability of cellular cementum compare to acellular cementum?
How does the permeability of cellular cementum compare to acellular cementum?
What distinguishes acellular afibrillar cementum from other types?
What distinguishes acellular afibrillar cementum from other types?
What type of fibers does cellular mixed stratified cementum predominantly contain?
What type of fibers does cellular mixed stratified cementum predominantly contain?
What significant role does the cemento-enamel junction play in dental health?
What significant role does the cemento-enamel junction play in dental health?
Which type of cementum is characterized by regular formation and high calcification?
Which type of cementum is characterized by regular formation and high calcification?
What happens to the permeability of cementum with age?
What happens to the permeability of cementum with age?
Which cementum type forms primarily in the cervical third thickness of the tooth?
Which cementum type forms primarily in the cervical third thickness of the tooth?
How does the rate of formation differ between acellular and cellular cementum?
How does the rate of formation differ between acellular and cellular cementum?
What is the primary purpose of Guided Tissue Regeneration (GTR)?
What is the primary purpose of Guided Tissue Regeneration (GTR)?
Which factor primarily contributes to tooth sensitivity related to cementum?
Which factor primarily contributes to tooth sensitivity related to cementum?
What is a common method to reduce tooth sensitivity caused by exposed cementum?
What is a common method to reduce tooth sensitivity caused by exposed cementum?
Which of the following agents is not known to block the dentinal tubule to reduce sensitivity?
Which of the following agents is not known to block the dentinal tubule to reduce sensitivity?
Which statement accurately describes the role of cementum in dental health?
Which statement accurately describes the role of cementum in dental health?
What happens when gingiva recedes and cementum is exposed?
What happens when gingiva recedes and cementum is exposed?
What surgical option may be performed for severe cases of gum recession?
What surgical option may be performed for severe cases of gum recession?
Which of the following issues can arise due to irreversible damage to cementum?
Which of the following issues can arise due to irreversible damage to cementum?
Flashcards
Cementum
Cementum
Calcified, avascular tissue forming the outer layer of tooth roots, starting at the CEJ and extending to the apex.
Periodontal Ligament (PDL)
Periodontal Ligament (PDL)
Connective tissue that anchors the teeth to the bone.
Acellular Cementum
Acellular Cementum
Type of cementum formed before the tooth reaches its final position; characterized by a lack of cells.
Cellular Cementum
Cellular Cementum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cemento-enamel junction (CEJ)
Cemento-enamel junction (CEJ)
Signup and view all the flashcards
CEJ Overlap
CEJ Overlap
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cemento-dentinal junction
Cemento-dentinal junction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clinical Attachment Loss
Clinical Attachment Loss
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cementum Composition
Cementum Composition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cemento-dentinal Junction
Cemento-dentinal Junction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intermediate Cementum
Intermediate Cementum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cementogenesis
Cementogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Function of Cementum
Function of Cementum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clinical Significance of Cemento-dentinal Junction
Clinical Significance of Cemento-dentinal Junction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Root Canal Obturation
Root Canal Obturation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cemento-dentinal junction stability
Cemento-dentinal junction stability
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cementum Function
Cementum Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acellular Cementum
Acellular Cementum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cellular Cementum
Cellular Cementum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cementum Repair Types
Cementum Repair Types
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cementum Resorption Causes
Cementum Resorption Causes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cementum Resistance to Resorption
Cementum Resistance to Resorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Orthodontic Movement & Cementum
Orthodontic Movement & Cementum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vertical dimension
Vertical dimension
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cementifying Fibroma
Cementifying Fibroma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cementoblastoma
Cementoblastoma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dental Radiograph Signs (Cementifying Fibroma)
Dental Radiograph Signs (Cementifying Fibroma)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dental Radiograph Signs (Cementoblastoma)
Dental Radiograph Signs (Cementoblastoma)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cementoblastoma Age
Cementoblastoma Age
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cementifying Fibroma Age
Cementifying Fibroma Age
Signup and view all the flashcards
Root Planning and Scaling
Root Planning and Scaling
Signup and view all the flashcards
Excessive Cementum Removal
Excessive Cementum Removal
Signup and view all the flashcards
GTR (Guided Tissue Regeneration)
GTR (Guided Tissue Regeneration)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cementum Exposure
Cementum Exposure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tooth Sensitivity
Tooth Sensitivity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Desensitizing Agents
Desensitizing Agents
Signup and view all the flashcards
Restorative Procedures for Teeth
Restorative Procedures for Teeth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Soft Tissue Grafts
Soft Tissue Grafts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cementum function
Cementum function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cementum repair
Cementum repair
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clinical importance of cementum
Clinical importance of cementum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypophosphatasia (HPP)
Hypophosphatasia (HPP)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypophosphatasia Oral Manifestations
Hypophosphatasia Oral Manifestations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypophosphatasia Treatment
Hypophosphatasia Treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Paget's Disease
Paget's Disease
Signup and view all the flashcards
Paget's Disease Etiology
Paget's Disease Etiology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Paget's Disease Facial Bone Involvement
Paget's Disease Facial Bone Involvement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperpituitarism/Gigantism
Hyperpituitarism/Gigantism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperpituitarism/Acromegaly
Hyperpituitarism/Acromegaly
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperpituitarism Dental Features
Hyperpituitarism Dental Features
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypercementosis
Hypercementosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gigantism Dental Manifestations
Gigantism Dental Manifestations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Cementum Related Clinical Correlation
- Cementum is the calcified avascular mesenchymal tissue forming the outer layer of root surfaces.
- It begins at the cemento-enamel junction (CEJ) and continues to the apex.
- Cementum is part of the periodontium apparatus.
- It plays a key role in anchoring teeth to the bone via the periodontal ligament.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Structures of cementum
- Function
- Developmental anomalies
- Systemic conditions that influence cementum
- Clinical application
What is Cementum?
- Hardness is less than dentin.
- Color: light yellow, distinguishable from enamel (darker hue) and dentin (lighter).
- Thinnest at the cemento-enamel junction (20-50 µm), thickest towards the apex (150-200 µm).
- Cellular cementum permeability is greater than acellular cementum (more permeable from dentin and PDL side).
- With age, this permeability decreases.
Composition
- Primarily composed of organic and inorganic materials (50-55% organic, 45-50% inorganic).
- Inorganic component: calcium phosphate in the form of hydroxyapatite crystals.
- Organic component: collagen protein and polysaccharides (mainly collagen type I & III).
- Main collagen sources: Sharpey's fibers (extrinsic), and intrinsic fibers in the cementum matrix, both produced by fibroblasts.
Classification of Cementum
- Based on location: coronal or radicular.
- Based on cellularity: cellular or acellular.
- Based on fibers: extrinsic or intrinsic.
Acellular and Cellular Cementum
| Feature | Acellular Cementum (Primary) | Cellular Cementum (Secondary) |
|---|---|---|
| Formation | Before tooth reaches occlusal plane | Forms after tooth reaches occlusal plane |
| Cells | No cells | Contains cementocytes |
| Location | Cervical or half of root | Apical portion |
| Rate of formation | Slow | Faster |
| Calcification | More calcified | Less calcified |
| Fibers | Sharpey's fibers | Less fibers |
| Regularity | Regular | Irregular |
| Thickness | 30-50 µm | 1 to several µm |
| Function | Anchorage and attachment to PDL | Contribute to root length during growth, repair, and regeneration |
Presence or Absence of Fibers
- Fibrillar cementum: contains densely packed collagen fibrils.
- Afibrillar cementum: lacks dense collagen fibers.
- Categorized further as acellular afibrillar, acellular intrinsic fiber cementum, acellular extrinsic fibers, cellular mixed stratified cementum, and cellular intrinsic fiber cementum.
Structures in Cementum
- Cemento-enamel junction (CEJ): the junction between enamel and cementum.
- Types: overlapping, edge-to-edge, and gap.
- Clinical significance of CEJ: reference point for healthy individuals, calculate clinical attachment loss, & determine progression of periodontal disease.
- Cemento-dentinal junction (CDJ): the terminal apical area where cementum joins internal root canal dentin.
- Clinical significance: attachment medium for collagen fibers to alveolar bone, major source of repair for root surfaces.
Intermediate Cementum
- Thin layer of hard tissue between cementum and dentin.
- Contains cellular remnants of Hertwig's epithelial root sheath.
- Predominantly seen in the apical two-thirds of molars and premolars.
- Does not exhibit the characteristics of dentin or cementum.
- Function: seals the surface of sensitive root dentin, attachment of cementum to dentin.
Function of Cementum
- Anchorage: Provides a medium for collagen fiber attachment, binding the tooth to the alveolar bone.
- Adaptation: Continuous cementum deposition adapts to tooth movement, maintaining vertical dimensions.
- Repair: Secondary (cellular) cementum responsible for repair and maintaining root surface integrity.
- Two types of repair: anatomic and functional.
Cementum Resorption
- Local Factors: Cysts, tumors, embedded teeth, trauma from occlusion, excessive orthodontic force, periapical or periodontal disease.
- Systemic Factors: Paget's disease, hypophosphatasia, calcium deficiency.
Cementum Resorption & Orthodontic Tooth Movement
- Cementum is more resistant to resorption than bone.
- Differences in vascularization & metabolism between cementum and bone affect resistance to pressure.
- Surface layers of cementum have higher fluoride content, leading to greater resistance to acidic dissolution.
- Bone resorption occurs on the pressure side and bone formation on the tension side during tooth movement.
Age Changes
- Cementum deposition is continuous throughout life, but slower in older age, particularly in the apical areas.
- Permeability decreases with age.
- Surface becomes irregular due to calcification.
Developmental Anomalies
- Hypercementosis: Thickening of cementum, potentially localized or generalized.
- Causes: teeth without antagonists, pulpal or periodontal infections.
- Clinical features: vital teeth insensitive to percussion, generalized thickening with nodular enlargement, large apical third roots, potential spikes.
- Radiographic appearance: thickened and dulled roots, apex rounding.
- Management: hypercementosis itself does not require treatment. Focus on the primary etiology, consider extraction / sectioning if needed.
- Cemental Tear: Detachment of cementum fragment.
- Etiology: acute trauma from occlusion.
- Clinical significance: a contributing factor to adult periodontitis.
- Cementicles: Globular mass of cellular cementum, less than 0.05mm.
- Types: free, sessile/attached, interstitial/embedded.
- Ankylosis: Fusion of cementum and alveolar bone.
- Etiology: chronic periapical infection, tooth reimplantation, and occlusal trauma.
- Clinical presentation: lack of physiological mobility, metallic sound upon percussion, infraocclusion, and radiographic appearance of bone filling the PDL space. No specific treatment.
- Concrescence: Fusion of teeth by cementum fusion.
- Etiology: traumatic injury, crowding of teeth during maturation.
Systemic Conditions Influencing Cementum
- Hypophosphatasia: Rare inherited metabolic disorder causing mutations in the ALPL gene, leading to deficient TNSALP activity, interfering with hydroxyapatite crystal formation.
- Oral signs (premature tooth loss, dental hypoplasia, alveolar bone deficiency) often precede skeletal symptoms.
- Treatment: enzyme replacement therapy, pain relief (NSAIDs), physical therapy, dental care (fluoride treatment, sealants), and prosthetics/implants, vitamin D & calcium supplements, and lifestyle modifications,
- Paget's Disease: Characterized by enhanced bone resorption.
- Clinical features: predominantly affecting middle-aged adults, involvement of facial bones (maxilla and mandible), widening of alveolar ridge, and loosening of teeth.
- Characteristic radiographic appearance: cotton-wool appearance of bone, generalized hypercementosis of teeth.
- Histologic appearance: jigsaw or mosaic pattern.
Clinical Importance and Applications
- Cementum and Periodontal Health: Root planning and scaling to remove calculus and infected or roughened cementum. Guided tissue regeneration uses barriers/growth factors to stimulate new cementum and periodontal ligament.
- Cementum and Tooth Sensitivity: Gingival recession, exposing cementum, can lead to tooth sensitivity. Desensitizing agents (potassium nitrate, fluoride compounds) can address this.
- Restorative Procedures: Covering exposed cementum with composite resin can protect the root surface.
- Soft Tissue Grafting: May be needed for severe gingival recession to cover exposed cementum.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.