Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the Dentogingival fiber group?
What is the primary function of the Dentogingival fiber group?
- Maintain relationships of adjacent teeth
- Secure alignment of teeth in arch
- Attach gingiva to bone
- Provide gingival support (correct)
Which fiber group is responsible for maintaining the contour and position of the free marginal gingiva?
Which fiber group is responsible for maintaining the contour and position of the free marginal gingiva?
- Circular Group (correct)
- Intergingival
- Alveologingival
- Transseptal
What is a characteristic of V-shaped Stillman’s cleft?
What is a characteristic of V-shaped Stillman’s cleft?
- It has a slit-like form
- It appears as a rolled cleft
- It has a blunted appearance
- It is broader at the top and narrows down (correct)
What structural feature distinguishes the thickness of the periodontal ligament in different age groups?
What structural feature distinguishes the thickness of the periodontal ligament in different age groups?
Which group of fibers originates from the crest of alveolar process and inserts into the cervical cementum?
Which group of fibers originates from the crest of alveolar process and inserts into the cervical cementum?
What is the primary function of the periodontal ligament?
What is the primary function of the periodontal ligament?
Which of the following descriptions best fits bulbous gingival contours?
Which of the following descriptions best fits bulbous gingival contours?
What does the Transseptal fiber group primarily serve to protect?
What does the Transseptal fiber group primarily serve to protect?
How does the thickness of the periodontal ligament vary with age?
How does the thickness of the periodontal ligament vary with age?
What is the primary role of the Circular Group fibers in the periodontium?
What is the primary role of the Circular Group fibers in the periodontium?
What happens if epithelium grows into the area of cementum resorption?
What happens if epithelium grows into the area of cementum resorption?
What is the primary function of osteoblasts?
What is the primary function of osteoblasts?
Which developmental anomaly is associated with cementogenesis?
Which developmental anomaly is associated with cementogenesis?
What is hypercementosis also known as?
What is hypercementosis also known as?
What results from disuse atrophy in supporting bone?
What results from disuse atrophy in supporting bone?
What causes bone resorption on the mesial side of teeth?
What causes bone resorption on the mesial side of teeth?
What can cause cemental spikes?
What can cause cemental spikes?
How does increased functional demand affect bone density?
How does increased functional demand affect bone density?
Which of the following describes dehiscence?
Which of the following describes dehiscence?
What occurs during mesial drift of teeth?
What occurs during mesial drift of teeth?
What is the normal color of healthy gingiva?
What is the normal color of healthy gingiva?
Which mucosa is characterized as loosely connected and movable?
Which mucosa is characterized as loosely connected and movable?
What is the primary function of the gingiva?
What is the primary function of the gingiva?
Where is stippling found in the oral mucosa?
Where is stippling found in the oral mucosa?
What describes the interdental papilla?
What describes the interdental papilla?
What is observed in the gingival sulcus?
What is observed in the gingival sulcus?
What is the papillary contour of normal gingiva like?
What is the papillary contour of normal gingiva like?
How does the consistency of healthy gingiva present?
How does the consistency of healthy gingiva present?
What feature distinguishes specialized mucosa?
What feature distinguishes specialized mucosa?
What causes stippling in the attached gingiva?
What causes stippling in the attached gingiva?
What is the primary function of the periodontal ligament?
What is the primary function of the periodontal ligament?
Which type of cementum is primarily formed after the tooth reaches the occlusal plane?
Which type of cementum is primarily formed after the tooth reaches the occlusal plane?
Which cell type in the periodontal ligament is primarily responsible for collagen production?
Which cell type in the periodontal ligament is primarily responsible for collagen production?
What distinguishes acellular cementum from cellular cementum in terms of formation?
What distinguishes acellular cementum from cellular cementum in terms of formation?
What is a common consequence of ankylosis in teeth?
What is a common consequence of ankylosis in teeth?
Which is NOT a primary function of the periodontal ligament?
Which is NOT a primary function of the periodontal ligament?
What material primarily makes up the inorganic content of cementum?
What material primarily makes up the inorganic content of cementum?
Which developmental stage sees a significant increase in the thickness of cementum?
Which developmental stage sees a significant increase in the thickness of cementum?
What role do osteoclasts play in the periodontal environment?
What role do osteoclasts play in the periodontal environment?
What can lead to cemental caries?
What can lead to cemental caries?
Which of the following accurately describes Sharpey's fibers?
Which of the following accurately describes Sharpey's fibers?
What is the major component of acellular cementum?
What is the major component of acellular cementum?
How does the periodontal ligament contribute to the sensory function?
How does the periodontal ligament contribute to the sensory function?
Which group of fibers runs from cementum to bone at a diagonal angle?
Which group of fibers runs from cementum to bone at a diagonal angle?
What is the primary purpose of the junctional epithelium?
What is the primary purpose of the junctional epithelium?
Which of the following characterizes the sulcular epithelium?
Which of the following characterizes the sulcular epithelium?
What does active eruption involve?
What does active eruption involve?
Which type of eruption is considered pathologic by some authors?
Which type of eruption is considered pathologic by some authors?
What is biologic width?
What is biologic width?
What is the function of gingival connective tissue?
What is the function of gingival connective tissue?
What is the characteristic of junctional epithelial cells compared to keratinized cells?
What is the characteristic of junctional epithelial cells compared to keratinized cells?
What is a primary component of the gingival connective tissue?
What is a primary component of the gingival connective tissue?
How does attrition affect clinical crown length during active eruption?
How does attrition affect clinical crown length during active eruption?
Which gingival principal fibers encircle the tooth?
Which gingival principal fibers encircle the tooth?
What is one of the main roles of the biologic width?
What is one of the main roles of the biologic width?
What primarily influences the rate of continuous tooth eruption?
What primarily influences the rate of continuous tooth eruption?
What is the relationship between passive eruption and gingival inflammation?
What is the relationship between passive eruption and gingival inflammation?
What type of fibers connect the tooth to the alveolus?
What type of fibers connect the tooth to the alveolus?
What is the typical length range for junctional epithelium?
What is the typical length range for junctional epithelium?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Gingiva and Periodontium Overview
- Oral mucosa encompasses all soft tissues within the mouth.
- Divided into three areas:
- Masticatory mucosa (gingiva, hard palate)
- Lining mucosa (alveolar mucosa, other membranes)
- Specialized mucosa (dorsum of tongue)
Surface Characteristics of Gingiva
- Normal healthy gingiva presents as coral pink.
- Papillary contour: pointed, filling interproximal spaces; typically blunt in older individuals.
- Marginal contour appears scalloped in a mesiodistal view, sloping coronally.
- Texture is stippled, giving it an “orange peel” appearance, found only in attached gingiva.
- Firmly consistent, tightly bound to teeth and underlying bone.
Mucogingival Junction
- Acts as the demarcation between attached gingiva and alveolar mucosa.
- Remains stable throughout life; absent on palate due to the firm binding of mucosa to bone.
Alveolar Mucosa and Interdental Papilla
- Alveolar mucosa located apically to attached gingiva, characterized by loose connection and mobility.
- Interdental papilla occupies space between neighboring teeth, critical for early periodontal disease diagnosis. Its shape varies:
- Anterior: pyramidal
- Posterior: peaked with gingival col
Gingival Sulcus
- Depth ranges from 2-3 mm.
- Bounded by the tooth surface, junctional epithelium (JE), and sulcus epithelium.
Tooth Eruption
- Continuous tooth eruption occurs throughout life with two types:
- Active eruption involves upward movement of the tooth towards the occlusal plane.
- Passive eruption results in the exposure of the crown due to separation of the JE.
Biologic Width
- Defined as the distance from the alveolar bone crest to the margins of the periodontal attachment (total of 3 mm):
- Gingival sulcus: 1 mm
- Junctional epithelium: 1 mm
- Alveolar crest fibers: 1 mm
Gingival Connective Tissue
- Composed of lamina propria containing collagen, reticular fibers, and some elastic fibers.
- Structured in two layers: papillary layer and reticular layer.
Junctional Epithelium
- A cuff-like band of non-keratinized epithelium around the tooth, ranging from 0.025 to 1.35 mm in length.
- Provides a seal at the base of the sulcus, with varying permeability to fluids and inflammatory cells.
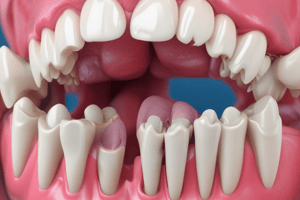
Principal Fibers of Gingiva
- Dentogingival: Provide gingival support.
- Alveologingival: Attach gingiva to underlying bone.
- Circular Group: Maintain contour of marginal gingiva.
- Other groups (transseptal, dentoperiosteal, semicircular, transgingival, intergingival) serve specific functions in tooth alignment and support.
Periodontal Ligament (PDL)
- Fibrous connective tissue attaching teeth to alveolar bone.
- Thickness ranges from 0.1 to 0.25 mm, varying with age and eruption stage.
- Contains principal fibers grouped by direction and function, including alveolar crest group, horizontal group, oblique group, and others.
cellular Types in PDL and Cementum
- Undifferentiated mesenchymal cells can develop into various cell types like fibroblasts and osteoblasts.
- Main functions of PDL include mechanical support, formation, nutrition, and sensory perception.
Cementum Classification
- Classified as acellular or cellular, with significant distinctions in formation timing, composition, and presence of cementocytes.
- Acellular cementum is primarily composed of Sharpey’s fibers and forms before teeth reach occlusal plane.
- Cellular cementum forms post-eruption and features incremental lines indicating growth phases, with cementocytes residing within.
Ankylosis and Root Resorption
- Ankylosis involves fusion of cementum and alveolar bone with obliteration of PDL, potentially leading to functional issues.
- Root resorption, primarily physiologic, occurs in deciduous teeth and can happen due to inflammation or trauma.### Cementum Repair
- Epithelium growth into resorption areas hinders cementum repair.
Enamel-Cementum Relationship
- Space between enamel and cementum with dentin exposure is 5-10%.
- End-to-end relationship between enamel and cementum is observed in 30% of cases.
- Cementum overlaps enamel in 60-65% of cases.
Developmental Anomalies
- Anomalies in cementogenesis may include:
- Enamel projections
- Enamel pearls
- Hypercementosis
- Cementicles
Hypercementosis
- Also referred to as cementum hyperplasia.
- Can occur in teeth that lack antagonists due to excessive eruption.
- Teeth with periapical irritation from pulp disease may develop hypercementosis to compensate for fibrous attachment loss.
Physiologic Mesial Drift
- Continuous migration of teeth in a mesial direction observed.
- Bone resorption on the mesial side of the alveolus coincides with tooth positioning.
- Bone formation occurs on the distal side, indicating activity alteration.
- Compression leads to bone resorption while tension accelerates bone formation.
Supporting (Basal) Bone
- Resorption caused by reduced functional requirements of the alveolar bone.
- Loss of occlusal function results in disuse atrophy of bone structure.
Disuse Atrophy
- Increased functional demand enhances bone density, while excessive demands lead to decreased density.
Defects in the Alveolar Process
- Dehiscence refers to a dipping of the crestal margin, resulting in root exposure.
Cemental Spikes
- A form of hypercementosis characterized by clumping of cementicles and calcification of Sharpey’s fibers.
- Can result from excessive tension due to orthodontic appliances or occlusal forces.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.