Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the average depth of the free gingiva?
What is the average depth of the free gingiva?
- 3 to 6 mm
- 1 to 3 cm
- 0.5 to 2 mm (correct)
- 2 to 5 mm
What is the function of the periodontal ligament?
What is the function of the periodontal ligament?
- To produce saliva
- To connect the gums to the teeth
- To support the teeth (correct)
- To protect the teeth from decay
What is the characteristic of the attached gingiva?
What is the characteristic of the attached gingiva?
- It is translucent and pigmented
- It is mobile and soft
- It is thin and fragile
- It is firm and immovable (correct)
What is the color of the alveolar mucosa?
What is the color of the alveolar mucosa?
What is the purpose of the gingival sulcus?
What is the purpose of the gingival sulcus?
What is the feature of a healthy gingival sulcus?
What is the feature of a healthy gingival sulcus?
What is the shape of the gingival papilla in the anterior teeth?
What is the shape of the gingival papilla in the anterior teeth?
What is the relationship between skin pigmentation and gingival color?
What is the relationship between skin pigmentation and gingival color?
What is the composition of the alveolar mucosa?
What is the composition of the alveolar mucosa?
What is the attachment unit that supports the teeth?
What is the attachment unit that supports the teeth?
What type of mucosa is found on the hard palate?
What type of mucosa is found on the hard palate?
Which type of mucosa is thin, nonkeratinized, and easily injured?
Which type of mucosa is thin, nonkeratinized, and easily injured?
What is another name for free gingiva?
What is another name for free gingiva?
Which part of the mouth is lined with alveolar mucosa?
Which part of the mouth is lined with alveolar mucosa?
What type of collagen fibers make up the underlying mucosa of masticatory mucosa?
What type of collagen fibers make up the underlying mucosa of masticatory mucosa?
Why would alveolar mucosa not be considered part of the periodontium?
Why would alveolar mucosa not be considered part of the periodontium?
What is the junctional epithelium continuous with?
What is the junctional epithelium continuous with?
What does the junctional epithelium attach to on the tooth surface?
What does the junctional epithelium attach to on the tooth surface?
What covers the tooth and stays attached throughout its eruption?
What covers the tooth and stays attached throughout its eruption?
Where does the junctional epithelium end up after the tooth has erupted?
Where does the junctional epithelium end up after the tooth has erupted?
What prevents bacteria from embedding below the gingival tissues during tooth eruption?
What prevents bacteria from embedding below the gingival tissues during tooth eruption?
What is the main function of the attachment apparatus?
What is the main function of the attachment apparatus?
What is the name of the bone between the teeth?
What is the name of the bone between the teeth?
What is the purpose of the periodontal ligament (PDL)?
What is the purpose of the periodontal ligament (PDL)?
What type of fibers connect the tooth to the bone in the PDL?
What type of fibers connect the tooth to the bone in the PDL?
What is the main component of the PDL?
What is the main component of the PDL?
What is the purpose of the gingival sulcus?
What is the purpose of the gingival sulcus?
What is the function of the Sharpey's fibers in the PDL?
What is the function of the Sharpey's fibers in the PDL?
What is the function of the fluids within the spaces of the PDL?
What is the function of the fluids within the spaces of the PDL?
What is the purpose of the transseptal group of fibers in the PDL?
What is the purpose of the transseptal group of fibers in the PDL?
What is the difference between the sulcular gingiva and the marginal gingiva?
What is the difference between the sulcular gingiva and the marginal gingiva?
What is the primary function of the junctional epithelium during tooth eruption?
What is the primary function of the junctional epithelium during tooth eruption?
What is the primary component of the dentogingival junction?
What is the primary component of the dentogingival junction?
Where does the junctional epithelium eventually attach to as the tooth erupts?
Where does the junctional epithelium eventually attach to as the tooth erupts?
What is the purpose of the gingival sulcus?
What is the purpose of the gingival sulcus?
What is the primary function of the Sharpey's fibers in the periodontal ligament (PDL)?
What is the primary function of the Sharpey's fibers in the periodontal ligament (PDL)?
What is the main characteristic of the masticatory mucosa?
What is the main characteristic of the masticatory mucosa?
Which part of the gingiva extends from the gingival margin to the base of the gingival sulcus?
Which part of the gingiva extends from the gingival margin to the base of the gingival sulcus?
What is the primary function of the underlying mucosa in the masticatory mucosa?
What is the primary function of the underlying mucosa in the masticatory mucosa?
Which type of mucosa is continuous with the lining of the cheeks and lips?
Which type of mucosa is continuous with the lining of the cheeks and lips?
What is the primary difference between the masticatory mucosa and the alveolar mucosa?
What is the primary difference between the masticatory mucosa and the alveolar mucosa?
Which statement is true about the alveolar mucosa?
Which statement is true about the alveolar mucosa?
What is the average depth of the free gingiva around a fully erupted tooth?
What is the average depth of the free gingiva around a fully erupted tooth?
What is the shape of the gingival papilla in the anterior teeth?
What is the shape of the gingival papilla in the anterior teeth?
What is the main function of the periodontal ligament (PDL)?
What is the main function of the periodontal ligament (PDL)?
What is the characteristic of the attached gingiva?
What is the characteristic of the attached gingiva?
What is the relationship between skin pigmentation and gingival color?
What is the relationship between skin pigmentation and gingival color?
What is the purpose of the gingival sulcus?
What is the purpose of the gingival sulcus?
What is the composition of the alveolar mucosa?
What is the composition of the alveolar mucosa?
What is the attachment unit that supports the teeth?
What is the attachment unit that supports the teeth?
What is the feature of a healthy gingival sulcus?
What is the feature of a healthy gingival sulcus?
What is the color of the alveolar mucosa?
What is the color of the alveolar mucosa?
What is another name for free gingiva?
What is another name for free gingiva?
What is the main function of the Sharpey's fibers in the Periodontal Ligament (PDL)?
What is the main function of the Sharpey's fibers in the Periodontal Ligament (PDL)?
Which group of fibers attaches one tooth to another across the interproximal space?
Which group of fibers attaches one tooth to another across the interproximal space?
What is the function of the gingival sulcus in relation to the tooth?
What is the function of the gingival sulcus in relation to the tooth?
What is the primary role of cementoblasts in the attachment apparatus?
What is the primary role of cementoblasts in the attachment apparatus?
Why do multirooted teeth have interradicular bone?
Why do multirooted teeth have interradicular bone?
What is the purpose of the oblique group of fibers in the PDL?
What is the purpose of the oblique group of fibers in the PDL?
How do Sharpey's fibers contribute to maintaining healthy occlusal stresses?
How do Sharpey's fibers contribute to maintaining healthy occlusal stresses?
Which type of fiber is known for attaching from the cervical area of the tooth to the alveolar crest?
Which type of fiber is known for attaching from the cervical area of the tooth to the alveolar crest?
What is one of the functions of fibroblasts in the Periodontal Ligament (PDL)?
What is one of the functions of fibroblasts in the Periodontal Ligament (PDL)?
How do Sharpey's fibers contribute to preventing a tooth from being pushed into the bone?
How do Sharpey's fibers contribute to preventing a tooth from being pushed into the bone?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
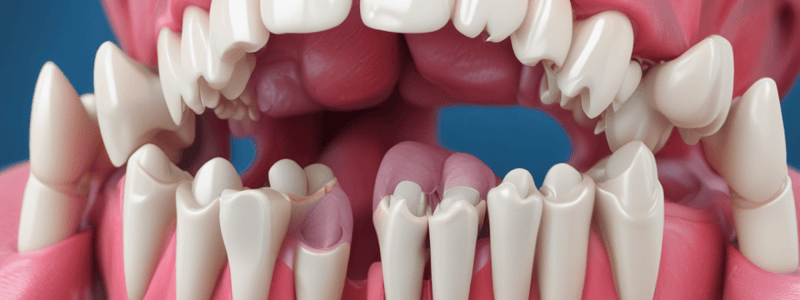
Gingival Depth and Characteristics
- Average depth of free gingiva around a fully erupted tooth is approximately 1-2 mm.
- Healthy gingival sulcus should measure 1-3 mm in depth, free from inflammation.
- Free gingiva is also referred to as marginal gingiva, which serves as a barrier to protect underlying tissues.
Functions of Periodontal Structures
- Periodontal ligament (PDL) functions to support the teeth, absorb shock during chewing, and maintain tooth position.
- Sharpey's fibers anchor the PDL to the cementum of the tooth and the alveolar bone, preventing unwanted movement.
- Main function of the attachment apparatus is to secure the teeth within the alveolar bone.
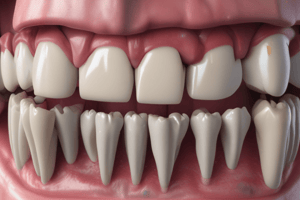
Gingiva and Mucosal Color
- Alveolar mucosa is typically a pink to reddish color, contrasting with the more opaque coral pink of the attached gingiva.
- Skin pigmentation influences gingival color; darker skin types often have darker gingiva due to melanin production.
Gingival Anatomy and Functions
- Gingival papilla in anterior teeth is pyramidal in shape, aiding in the esthetics and function during mastication.
- The purpose of the gingival sulcus is to provide a space for gingival health by allowing the passage of fluids while acting as a barrier to bacteria.
Mucosal Types and Properties
- Hard palate is lined with masticatory mucosa, which is keratinized and robust.
- Alveolar mucosa is classified as nonkeratinized and is easily susceptible to injury.
- Masticatory mucosa, including attached gingiva, features a higher keratinized protective layer.
Collagen and Fiber Composition
- Underlying mucosa of masticatory mucosa primarily consists of dense collagen fibers which offer strength and resilience.
- PDL's primary component is connective tissue rich in collagen fibers that provide stability to teeth.
Junctional Epithelium
- Junctional epithelium is continuous with the gingival epithelium and attaches to the tooth surface at the cementoenamel junction.
- This structure plays a crucial role during tooth eruption, providing a physical barrier to bacteria and contributing to the overall health of the periodontal tissues.
Interradicular and Transseptal Fiber Functions
- Interradicular bone is present in multirooted teeth, providing structural support and separation between roots.
- Transseptal fibers connect adjacent teeth across interproximal spaces, maintaining their alignment and supporting natural dental arch integrity.
PDL and Blood Supply Functions
- Fluids within the PDL spaces serve to transport nutrients and remove waste products, supporting overall periodontal health.
- Oblique group of fibers within the PDL help to resist vertical forces and stabilize the teeth during chewing.
Overall Periodontal Health
- Healthy gingival sulcus maintains an optimal environment, supporting overall periodontal health and preventing disease progression.
- Fibroblasts within the PDL assist in the maintenance and repair of connective tissue, ensuring continued support to the teeth and surrounding structures.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.