Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is NOT a principle fiber type found in the periodontal ligament?
Which of the following is NOT a principle fiber type found in the periodontal ligament?
- Apical (correct)
- Transseptal
- Alveolar Crest
- Horizontal
What is the main function of the epithelial rests of Malassez found within the periodontal ligament?
What is the main function of the epithelial rests of Malassez found within the periodontal ligament?
- Contribute to the formation of cementum
- Remain dormant and are capable of forming a new periodontal ligament if the original periodontal ligament is damaged (correct)
- Contribute to the development of the pulp
- Secrete collagen fibers for periodontal ligament formation
- Act as undifferentiated mesenchymal cells for tissue repair
Which of the following statements accurately reflects the role of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) in the periodontal ligament (PDL)?
Which of the following statements accurately reflects the role of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) in the periodontal ligament (PDL)?
- GAGs are primarily responsible for the calcification of cementum.
- GAGs are primarily involved in the attachment of PDL fibers to the tooth surface.
- GAGs primarily facilitate the diffusion of nutrients and waste products within the PDL. (correct)
- GAGs primarily provide structural support and tensile strength to the PDL.
- GAGs primarily provide the bulk of the collagen fibers found in the PDL.
Which of these is associated with the production of the entire attachment apparatus of the tooth, including cementum, periodontal ligament, and bone?
Which of these is associated with the production of the entire attachment apparatus of the tooth, including cementum, periodontal ligament, and bone?
What is the primary reason for the variability in the thickness of the periodontal ligament as seen on radiographs?
What is the primary reason for the variability in the thickness of the periodontal ligament as seen on radiographs?
Which of the following characteristics correctly describes the nature of cementum?
Which of the following characteristics correctly describes the nature of cementum?
What consequence can occur due to the removal of the cementum layer during scaling and root planing?
What consequence can occur due to the removal of the cementum layer during scaling and root planing?
What is the role of the alveolar process in relation to teeth?
What is the role of the alveolar process in relation to teeth?
What type of bone is described as being adjacent to the periodontal ligament and containing Sharpey’s fibers?
What type of bone is described as being adjacent to the periodontal ligament and containing Sharpey’s fibers?
What process describes the changes in the shape and resistance of bone over time?
What process describes the changes in the shape and resistance of bone over time?
What is the distance between the crest of the alveolar bone and the cemento-enamel junction in young adults?
What is the distance between the crest of the alveolar bone and the cemento-enamel junction in young adults?
What is the term for isolated areas where the root is denuded of bone?
What is the term for isolated areas where the root is denuded of bone?
What are the two main types of tissue that cover the outer surface and the internal cavities of the bone?
What are the two main types of tissue that cover the outer surface and the internal cavities of the bone?
What percentage of teeth lack a cemento-enamel junction (CEJ)?
What percentage of teeth lack a cemento-enamel junction (CEJ)?
What is the primary inorganic component of cementum?
What is the primary inorganic component of cementum?
Which type of cementum does not incorporate cells in its formation?
Which type of cementum does not incorporate cells in its formation?
At which location is cementum typically thinnest?
At which location is cementum typically thinnest?
Which type of cementum predominantly contains cellular remnants and lies near the cementodentinal junction?
Which type of cementum predominantly contains cellular remnants and lies near the cementodentinal junction?
What percentage of the cementum typically overlaps the cervical end of the enamel?
What percentage of the cementum typically overlaps the cervical end of the enamel?
Which statement about cementum is accurate regarding its resistance to resorption?
Which statement about cementum is accurate regarding its resistance to resorption?
Which of the following structures is primarily responsible for the anchorage of the tooth?
Which of the following structures is primarily responsible for the anchorage of the tooth?
What characteristic shapes do the cell bodies of cementocytes have?
What characteristic shapes do the cell bodies of cementocytes have?
What is the ideal depth of the gingival sulcus in healthy gingiva?
What is the ideal depth of the gingival sulcus in healthy gingiva?
What is the width of the attached gingiva at the maxillary incisor?
What is the width of the attached gingiva at the maxillary incisor?
Which of these is NOT a part of the gingiva?
Which of these is NOT a part of the gingiva?
What is the typical thickness of the free gingiva?
What is the typical thickness of the free gingiva?
What is the difference between the marginal gingiva and the attached gingiva?
What is the difference between the marginal gingiva and the attached gingiva?
What is the shape of the interdental gingiva?
What is the shape of the interdental gingiva?
What is the purpose of the free gingival groove?
What is the purpose of the free gingival groove?
What is the term for the junction between the attached gingiva and the alveolar mucosa?
What is the term for the junction between the attached gingiva and the alveolar mucosa?
What is the primary function of the junctional epithelium?
What is the primary function of the junctional epithelium?
Which of the following cell types is most abundant in the gingival epithelium?
Which of the following cell types is most abundant in the gingival epithelium?
What is the approximate ratio of melanocytes to keratinocytes in the gingival epithelium?
What is the approximate ratio of melanocytes to keratinocytes in the gingival epithelium?
Which type of epithelium is found in the sulcular epithelium?
Which type of epithelium is found in the sulcular epithelium?
What is the unique feature of the junctional epithelium that allows it to function as a seal?
What is the unique feature of the junctional epithelium that allows it to function as a seal?
Which of the following statements about the turn-over rate of different types of epithelium in the oral cavity is true?
Which of the following statements about the turn-over rate of different types of epithelium in the oral cavity is true?
What is the primary function of the Langerhans cells found in the gingival epithelium?
What is the primary function of the Langerhans cells found in the gingival epithelium?
What is the function of the rete pegs found in the oral epithelium?
What is the function of the rete pegs found in the oral epithelium?
In the context of periodontal health, the interdental col is considered a weak point as it is comprised of non-keratinized epithelium. How does this characteristic contribute to the initiation of periodontal disease?
In the context of periodontal health, the interdental col is considered a weak point as it is comprised of non-keratinized epithelium. How does this characteristic contribute to the initiation of periodontal disease?
What is the primary cell type found in the gingival connective tissue, responsible for the production of collagen fibers?
What is the primary cell type found in the gingival connective tissue, responsible for the production of collagen fibers?
The periodontal ligament (PDL) is a highly cellular and vascular connective tissue that surrounds the tooth root. How does the width of the PDL space vary depending on the tooth's function?
The periodontal ligament (PDL) is a highly cellular and vascular connective tissue that surrounds the tooth root. How does the width of the PDL space vary depending on the tooth's function?
What is the function of Sharpey's fibers in the periodontal ligament?
What is the function of Sharpey's fibers in the periodontal ligament?
Gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) plays a crucial role in maintaining periodontal health. Which of the following is NOT a protective role attributed to GCF?
Gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) plays a crucial role in maintaining periodontal health. Which of the following is NOT a protective role attributed to GCF?
The turnover rate of the junctional epithelium (JE) is typically between 1 and 6 days. What is the significance of this rapid turnover rate in the context of periodontal health?
The turnover rate of the junctional epithelium (JE) is typically between 1 and 6 days. What is the significance of this rapid turnover rate in the context of periodontal health?
What is the correct order of the histological layers found in the gingiva, starting from the outermost layer?
What is the correct order of the histological layers found in the gingiva, starting from the outermost layer?
The mucogingival junction (MGJ) is a distinct boundary between two types of oral mucosa. Which two types of oral mucosa are separated by the MGJ?
The mucogingival junction (MGJ) is a distinct boundary between two types of oral mucosa. Which two types of oral mucosa are separated by the MGJ?
Flashcards
Epithelial components of gingiva
Epithelial components of gingiva
Gingiva consists of oral, sulcular, and junctional epithelium.
Turnover rate of gingival epithelium
Turnover rate of gingival epithelium
Gingival epithelium turnover occurs every 10 to 12 days.
Oral epithelium
Oral epithelium
Primary barrier of the gingiva; stratified squamous, keratinized or parakeratinized.
Sulcular epithelium
Sulcular epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Junctional epithelium
Junctional epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Keratinization
Keratinization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Melanocytes
Melanocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lining mucosa
Lining mucosa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oral Mucosa
Oral Mucosa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gingiva
Gingiva
Signup and view all the flashcards
Marginal Gingiva
Marginal Gingiva
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gingival Sulcus
Gingival Sulcus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Attached Gingiva
Attached Gingiva
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gingival crevicular fluid
Gingival crevicular fluid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interdental col
Interdental col
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interdental Gingiva
Interdental Gingiva
Signup and view all the flashcards
Masticatory mucosa
Masticatory mucosa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mucogingival Junction
Mucogingival Junction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Free Gingival Thickness
Free Gingival Thickness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Periodontal ligament
Periodontal ligament
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sharpey's fibers
Sharpey's fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Collagen type I
Collagen type I
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cementum Composition
Cementum Composition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Types of Cementum
Types of Cementum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acellular Cementum
Acellular Cementum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cellular Cementum
Cellular Cementum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cementoenamel Junction (CEJ)
Cementoenamel Junction (CEJ)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cementum Function
Cementum Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cementum and Orthodontics
Cementum and Orthodontics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intermediate Cementum
Intermediate Cementum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scaling and root planing
Scaling and root planing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cementum loss effects
Cementum loss effects
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cemental deposition
Cemental deposition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveolar process
Alveolar process
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cortical bone
Cortical bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lamina dura
Lamina dura
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fenestrations
Fenestrations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Remodeling
Remodeling
Signup and view all the flashcards
Calcification process
Calcification process
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteopontin
Osteopontin
Signup and view all the flashcards
PDL cellular elements
PDL cellular elements
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ground substance of PDL
Ground substance of PDL
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functions of PDL
Functions of PDL
Signup and view all the flashcards
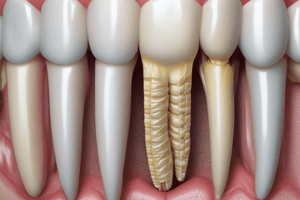
Cementum
Cementum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cementum characteristics
Cementum characteristics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Clinical Correlations of Periodontal Anatomy
- This presentation covers the clinical and microscopic features of the periodontium.
- The periodontium is a complex structure that includes the gingiva, periodontal ligament, cementum, and alveolar process.
Contents
- Oral Mucosa and Gingiva: This section details various types of oral mucosa (masticatory, specialized, lining) and focuses on the gingiva, its definition, anatomical divisions (marginal, attached, interdental), and the gingival sulcus.
- Periodontal Ligament: Describes the periodontal ligament (PDL) as a complex connective tissue that surrounds the tooth root and connects it to the alveolar bone. It includes its average width (0.2mm), variations in width related to tooth function, and the principle fibers (Sharpey's).
- Cementum: Details cementum as a specialized, calcified tissue that covers the tooth root. It classifies it as either Acellular or Cellular and discusses its clinical significance and role in tooth anchorage.
- Alveolar Process: Discusses the alveolar process's role in forming tooth sockets (alveoli) and providing attachment to the periodontal ligament. It includes histological features, radiographic appearance, and clinical considerations like dehiscences, fenestrations and remodeling.
Oral Mucosa
- Oral mucosa is categorized into masticatory, specialized, and lining mucosa.
- Masticatory mucosa covers areas subjected to significant stress, such as the gingiva and hard palate.
- Specialized mucosa has distinct characteristics, such as the dorsum of the tongue.
- Lining mucosa covers internal surfaces of the oral cavity, like the cheeks, lips, and soft palate.
Gingiva
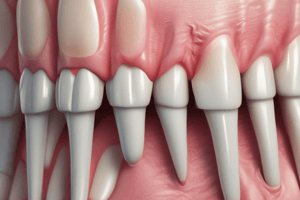
- Gingiva is the oral mucosa covering the alveolar processes and surrounding the tooth neck.
- Anatomically, the gingiva is divided into marginal, attached, and interdental gingiva.
- Marginal gingiva is the free gingiva, it is unattached to the tooth.
- Free gingival thickness is 1.56mm +/- 0.39mm
- Attached gingiva is tightly bound to the tooth, spanning the area from the free gingival groove apical to the mucogingival junction.
- Interdental gingiva occupies the embrasure between adjacent teeth, with shapes varying according to contact with adjacent teeth.
Gingival Sulcus
- A shallow crevice around the tooth, bordered by the tooth surface and the gingival margin epithelium.
- Ideal sulcus depth is 0mm, with a typical range of 1-3mm in healthy gingiva.
- The probing depth generally overestimates the actual sulcus depth due to probe penetration through inflamed tissues.
Attached Gingiva
- Attached gingiva is resilient, thick and tightly bound
- Mucogingival junction - the intersection between the attached gingiva and oral mucosa.
- Width of attached gingiva varies between 1.8 - 4.5 mm in max & Man incisor and 1.9mm to 1.8 mm in premolar regions.
- Thickness of attached gingiva is 1.25mm (+/- 0.42mm).
Interdental Gingiva
- Occupies the gingival embrasure.
- Its form is pyramidal or col-shaped depending upon the contact relations with adjacent teeth.
Microscopic Features of Gingiva
- Gingiva comprises epithelial and connective tissue components.
- The epithelial components consist of oral epithelium, sulcular epithelium, and junctional epithelium.
- Turnover rates of epithelial cells in various regions of the oral cavity show significant variation.
- Keratinized epithelium characteristics differ from non-keratinized.
Oral Epithelium
- The primary function is a physical barrier.
- Stratified squamous, keratinized or parakeratinized.
Sulcular Epithelium
- Thin, non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium.
- Lacks rete pegs (finger-like projections).
- Semipermeable membrane.
Junctional Epithelium
- Collar-like attachment to the tooth.
- Stratified squamous, non-keratinized.
- Varies between 0.25 -1.25 mm in length.
- Widest at the coronal portion, gradually thinning towards the cement-enamel junction (CEJ).
Keratinization
- Keratinization is a series of biochemical and morphological events that occur in cells as they migrate from the basal layer.
- Keratinocytes constitute a predominant cell type (about 90%).
- Other cell types include melanocytes, Langerhans cells, and Merkel cells.
- These cells play varying but essential roles in the periodontium.
Gingival Connective Tissue
- Primarily composed of dense collagen fibers (type I and III).
- Classification is based on location and insertion.
- Functions to brace the marginal gingiva against masticatory forces, provide rigidity, and unite free marginal gingiva to cementum of adjacent teeth.
- Fibers are arranged in three groups: gingivodental, circular, and transseptal.
Cell Types in Gingival Connective Tissue
- Fibroblasts account for 65% of the volume
- Other connective tissue cells include neutrophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells, macrophages, and mast cells.
- Glycosaminoglycans, like dermatan sulfate, are crucial constituents of the ground substance.
Vascular Supply
- The gingival connective tissue receives its vascular supply from supraperiosteal arterioles, vessels of the periodontal ligament, and arterioles emerging from the crest of alveolar septa.
- A juxta-epithelial plexus is present adjacent to the papillary projections of the gingival epithelium.
Color
- Color variations are due to vascular supply, tissue thickness, keratinization, and pigment-containing cells.
- Lighter color is observed in individuals with fair complexions compared to those with swarthy, dark hair.
Size
- Gingival size is determined by the sum total of cellular and intercellular elements and their vascular supply.
- Alterations in gingival size are often associated with periodontal diseases.
Gingival Biotypes
- Ochsenbein and Miller highlighted the distinction between thick and thin gingiva in restorative treatment planning.
- Thick and flat biotypes account for 85%, while thin and scalloped biotypes make up 15%.
- Characteristics of thick and thin gingiva differ in architecture, soft tissue density, amount of attached gingiva, and response to trauma and disease.
Gingival Zenith
- Gingival zenith is the most apical point of the marginal gingival scallop.
- Locations of the zenith on various teeth are presented in the slides.
Surface Texture
- Gingival surface texture is often described as stippled, similar to the texture of an orange peel.
- Stippling is more prominent in the attached portion of gingiva compared to the marginal gingiva.
Passive Eruption
- Describes Gottlieb & Orban's stages of passive eruption, outlining the progression of the junctional epithelium (JE) relative to enamel and cementum during tooth eruption.
Connective Tissue Grafts
- Grafting is performed to create new gingiva when there is a deficiency.
- Gingival tissue is more stable relative to alveolar mucosa when attached to restorations.
Periodontal Probing
- Periodontal probing measurements may not accurately reflect the actual anatomic sulcus depth.
- The depth is often overestimated due to probing through inflamed tissues.
Gingival Crevicular Fluid
- Gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) is formed as an inflammatory exudate.
- It contains components like serum, structural cells, plasma proteins, electrolytes, inflammatory and immune cells.
- Plays a protective role through cleansing action, antibacterial action and adhesive properties.
Interdental Col
- The interdental col is not a strong bacterial barrier.
- It is covered by non-keratinized epithelium, making it a potential site of disease initiation.
Key Points Summary
- The presentation summarized key anatomical and histological concepts of various periodontal components.
- Included is information on the average width of PDL, importance of different cell types and fibers for periodontal function, and clinical correlations.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.