Podcast
Questions and Answers
During the initial stages of root formation, which cells of the follicle differentiate into cementoblasts?
During the initial stages of root formation, which cells of the follicle differentiate into cementoblasts?
- Outermost cells
- Innermost cells (correct)
- Centrally located cells
- Fibroblasts
What is the direction of the developing fibers of the periodontal ligament initially?
What is the direction of the developing fibers of the periodontal ligament initially?
- Horizontal direction
- Coronal direction (correct)
- Oblique direction
- Apical direction
What is the name of the fibers present in the cementum and alveolar bone?
What is the name of the fibers present in the cementum and alveolar bone?
- Sharpey’s fibers (correct)
- Periodontal ligament fibers
- Principal fibers
- Dentoalveolar fibers
Which group of fibers is located near the cervical region?
Which group of fibers is located near the cervical region?
What is the function of fibroblasts in the periodontal ligament?
What is the function of fibroblasts in the periodontal ligament?
During root formation, which cells of the follicle differentiate into osteoblasts?
During root formation, which cells of the follicle differentiate into osteoblasts?
How many groups of principal fibers are there in the periodontal ligament?
How many groups of principal fibers are there in the periodontal ligament?
What is the primary function of the periodontal ligament?
What is the primary function of the periodontal ligament?
What is the characteristic of the width of the periodontal ligament with age?
What is the characteristic of the width of the periodontal ligament with age?
What is the type of cells present in the periodontal ligament?
What is the type of cells present in the periodontal ligament?
What is the function of fibroblasts in the periodontal ligament?
What is the function of fibroblasts in the periodontal ligament?
What is the thinnest portion of the periodontal ligament located?
What is the thinnest portion of the periodontal ligament located?
What is the function of the factors secreted by PDL fibroblasts?
What is the function of the factors secreted by PDL fibroblasts?
How many functions of the periodontal ligament are mentioned in the text?
How many functions of the periodontal ligament are mentioned in the text?
Which group of fibers has the greatest number of fiber bundles and performs the main support of the tooth against masticatory force?
Which group of fibers has the greatest number of fiber bundles and performs the main support of the tooth against masticatory force?
What is the direction of the fiber bundles in the Horizontal group?
What is the direction of the fiber bundles in the Horizontal group?
Which group of fibers extends from the cervical cementum of one tooth to the cervical cementum of another?
Which group of fibers extends from the cervical cementum of one tooth to the cervical cementum of another?
What is the origin of the fiber bundles in the Apical group?
What is the origin of the fiber bundles in the Apical group?
Which group of fibers attaches itself to the cervical part of the cementum and radiates from the alveolar crest?
Which group of fibers attaches itself to the cervical part of the cementum and radiates from the alveolar crest?
What is the direction of the fiber bundles in the Oblique group?
What is the direction of the fiber bundles in the Oblique group?
Which group of fibers is the most numerous and extends from the cervical cementum to the lamina propria of the gingiva?
Which group of fibers is the most numerous and extends from the cervical cementum to the lamina propria of the gingiva?
What is the primary function of the periodontal ligament?
What is the primary function of the periodontal ligament?
What is the composition of the ground substance in the periodontal ligament?
What is the composition of the ground substance in the periodontal ligament?
What type of fibers make up the majority of the periodontal ligament?
What type of fibers make up the majority of the periodontal ligament?
What is the function of the interstitial spaces in the periodontal ligament?
What is the function of the interstitial spaces in the periodontal ligament?
What is the role of fibroblasts in the periodontal ligament?
What is the role of fibroblasts in the periodontal ligament?
What is the result of aging on the periodontal ligament?
What is the result of aging on the periodontal ligament?
What type of cells are involved in the resorption of bone and cementum in the periodontal ligament?
What type of cells are involved in the resorption of bone and cementum in the periodontal ligament?
What is the role of the epithelial root sheath of Hertwig in the periodontal ligament?
What is the role of the epithelial root sheath of Hertwig in the periodontal ligament?
What is the function of the periodontal ligament in relation to the eruption of teeth?
What is the function of the periodontal ligament in relation to the eruption of teeth?
What is the composition of the proteoglycans in the ground substance of the periodontal ligament?
What is the composition of the proteoglycans in the ground substance of the periodontal ligament?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
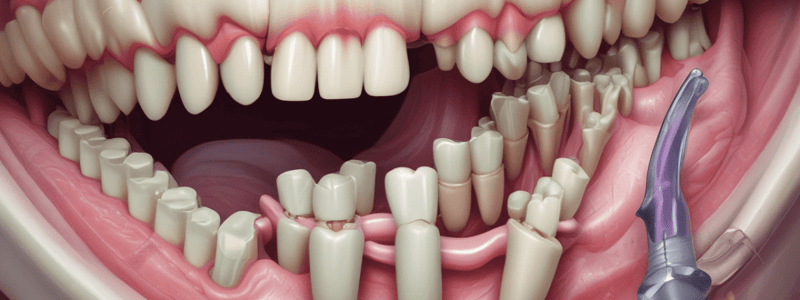
Development of PDL
- During the initial stages of root formation, follicular cells show increased proliferation.
- Innermost cells of the follicle differentiate into cementoblasts, while outermost cells differentiate into osteoblasts.
- Centrally located cells differentiate into fibroblasts, which produce periodontal ligament fibers.
- These fibers get embedded in the developing cementum and alveolar bone.
- Initially, all developing fibers of the periodontal ligament run obliquely in a coronal direction from tooth to bone.
- The part of PDL fibers present in the cementum and alveolar bone are called Sharpey's fibers.
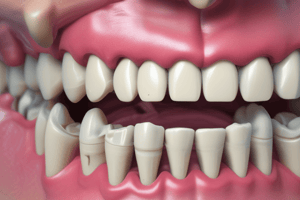
Structure of Periodontal Ligament
- The fibre bundles that exit the cementum and alveolar bone and form the periodontal ligament are called principal fibres.
- Principal fibres are grouped into:
- Alveolar crest group (near the cervical region)
- Horizontal fibre group (near the midroot)
- Oblique fibre group (immediately above apical group)
- Apical fibre group (near the apical area of the root)
- Interradicular group (between two roots)
- Gingival fibre group includes:
- Dentogingival group (extending from the cervical cementum to the lamina propria of the gingiva)
- Alveologingival group (extending from the alveolar crest to the lamina propria of the gingiva)
- Circular or Circumferential fibres (continuous around the neck of the tooth)
- Transseptal fibres (extending from the cervical cementum of one tooth to the cervical cementum of the other)
Histology of Periodontal Ligament
- The periodontal ligament consists of:
- Cells (synthetic, resorptive, progenitor, defensive, and epithelial cells)
- Fibers (collagenous, reticulin, and elastic fibers)
- Ground substance (water, glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, and glycoproteins)
- Intercellular substances (blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics)
Functions of PDL
- Formative
- Supportive
- Protective
- Sensory
- Nutritive
- Functions of PDL fibers include:
- Supportive (shock absorption and transmission of occlusal forces)
- Sensory
- Nutritive
- Homeostatic
- Eruptive
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.