Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following bones is not part of the pelvic girdle?
Which of the following bones is not part of the pelvic girdle?
- Clavicle (correct)
- Ischium
- Ilium
- Sacrum
The pubic symphysis is located at the front of the pelvic girdle.
The pubic symphysis is located at the front of the pelvic girdle.
True (A)
What is the primary function of the acetabulum in the pelvic girdle?
What is the primary function of the acetabulum in the pelvic girdle?
It serves as the socket for the hip joint.
The ______ is a bony projection found on the iliac crest.
The ______ is a bony projection found on the iliac crest.
Match the following components of the pelvic girdle with their descriptions:
Match the following components of the pelvic girdle with their descriptions:
Which condition may result in the loss of pulsation of the dorsalis pedis artery?
Which condition may result in the loss of pulsation of the dorsalis pedis artery?
Diabetes mellitus does not affect the pulsation of the dorsalis pedis artery.
Diabetes mellitus does not affect the pulsation of the dorsalis pedis artery.
What is a potential consequence of blood vessel occlusion in the foot?
What is a potential consequence of blood vessel occlusion in the foot?
The ______ artery is located on the top of the foot.
The ______ artery is located on the top of the foot.
Match the following arteries with their locations:
Match the following arteries with their locations:
What is the common treatment for congenital dislocation of the hip?
What is the common treatment for congenital dislocation of the hip?
Most muscles in the medial compartment of the thigh are innervated by the tibial nerve.
Most muscles in the medial compartment of the thigh are innervated by the tibial nerve.
Name one muscle that is primarily an extensor of the leg at the knee.
Name one muscle that is primarily an extensor of the leg at the knee.
The ___________ is the major extensor of the thigh.
The ___________ is the major extensor of the thigh.
Match the following muscle groups with their primary functions:
Match the following muscle groups with their primary functions:
Which of the following arteries supplies blood to the medial compartment of the thigh?
Which of the following arteries supplies blood to the medial compartment of the thigh?
The sartorius muscle is involved in the extension of the thigh at the hip.
The sartorius muscle is involved in the extension of the thigh at the hip.
What is the primary function of the gluteus medius muscle?
What is the primary function of the gluteus medius muscle?
The femoral artery and vein run through the ___________ canal.
The femoral artery and vein run through the ___________ canal.
Which nerve innervates the majority of the anterior compartment muscles of the thigh?
Which nerve innervates the majority of the anterior compartment muscles of the thigh?
Which metatarsals are most commonly affected in foot injuries?
Which metatarsals are most commonly affected in foot injuries?
The flexor retinaculum is associated with dorsiflexor tendons.
The flexor retinaculum is associated with dorsiflexor tendons.
What is the primary treatment recommended for injuries affecting the metatarsals?
What is the primary treatment recommended for injuries affecting the metatarsals?
Synovial sheaths provide ______ and lubrication for muscle tendons passing from the leg to the foot.
Synovial sheaths provide ______ and lubrication for muscle tendons passing from the leg to the foot.
Match the following retinacula with their primary function:
Match the following retinacula with their primary function:
Which artery is responsible for supplying blood to the anterior compartment muscles of the leg?
Which artery is responsible for supplying blood to the anterior compartment muscles of the leg?
The popliteal fossa contains the common peroneal nerve.
The popliteal fossa contains the common peroneal nerve.
What is the primary function of the patella?
What is the primary function of the patella?
The __________ artery pierces the oblique popliteal ligament to reach inside the knee joint.
The __________ artery pierces the oblique popliteal ligament to reach inside the knee joint.
Match the following nerve with its relevant compartment of the leg:
Match the following nerve with its relevant compartment of the leg:
Which muscle group is primarily responsible for the eversion of the foot?
Which muscle group is primarily responsible for the eversion of the foot?
Name one of the muscles that form the boundaries of the popliteal fossa.
Name one of the muscles that form the boundaries of the popliteal fossa.
The medial malleolus is located on the fibula.
The medial malleolus is located on the fibula.
The __________ membrane connects the tibia and fibula along the length of the leg.
The __________ membrane connects the tibia and fibula along the length of the leg.
Which of the following arteries is not a genicular artery?
Which of the following arteries is not a genicular artery?
Which nerve is not included in the contents of the femoral sheath?
Which nerve is not included in the contents of the femoral sheath?
Femoral hernias are more common in males than females.
Femoral hernias are more common in males than females.
What structure drains the glans penis and clitoris?
What structure drains the glans penis and clitoris?
The femoral hernia is located below and lateral to the __________.
The femoral hernia is located below and lateral to the __________.
Match the following structures with their respective categories:
Match the following structures with their respective categories:
Which of the following is a structure commonly associated with the fibula?
Which of the following is a structure commonly associated with the fibula?
The pectineus is located in the medial compartment of the thigh.
The pectineus is located in the medial compartment of the thigh.
What are the lymph nodes found in the femoral sheath called?
What are the lymph nodes found in the femoral sheath called?
Flashcards
Iliac crest
Iliac crest
A prominent ridge on the hip bone.
Anterior superior iliac spine
Anterior superior iliac spine
A bony projection on the front of the hip bone.
Acetabulum
Acetabulum
The socket of the hip joint
Pubic Symphysis
Pubic Symphysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sacroiliac joint
Sacroiliac joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Hernia Location
Femoral Hernia Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Hernia Characteristics
Femoral Hernia Characteristics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Hernia Prevalence
Femoral Hernia Prevalence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Sheath Contents
Femoral Sheath Contents
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Canal
Femoral Canal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rosenmuller Node
Rosenmuller Node
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tibia and Fibula Fracture
Tibia and Fibula Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interosseous Membrane
Interosseous Membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dorsalis pedis artery
Dorsalis pedis artery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior tibial artery
Posterior tibial artery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Burger's disease
Burger's disease
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gangrene
Gangrene
Signup and view all the flashcards
Auto-amputation
Auto-amputation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Congenital Dislocation of the Hip
Congenital Dislocation of the Hip
Signup and view all the flashcards
Treatment for Hip Dysplasia
Treatment for Hip Dysplasia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anterior Compartment Muscles
Anterior Compartment Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
What nerve innervates the anterior compartment?
What nerve innervates the anterior compartment?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medial Compartment Muscles
Medial Compartment Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
What nerve innervates the medial compartment?
What nerve innervates the medial compartment?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hunter's Canal
Hunter's Canal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clinical Significance of Hunter's Canal
Clinical Significance of Hunter's Canal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gluteus Medius
Gluteus Medius
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hamstring Muscles
Hamstring Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metatarsal Stress Fractures
Metatarsal Stress Fractures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metatarsal Stress Fracture Treatment
Metatarsal Stress Fracture Treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tendon Sheaths
Tendon Sheaths
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flexor Retinaculum
Flexor Retinaculum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extensor Retinaculum
Extensor Retinaculum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Articular surface of medial condyle
Articular surface of medial condyle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Articular surface of lateral condyle
Articular surface of lateral condyle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibular notch
Fibular notch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medial malleolus
Medial malleolus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral malleolus
Lateral malleolus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inferior articular surface
Inferior articular surface
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patella
Patella
Signup and view all the flashcards
Popliteal fossa
Popliteal fossa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Popliteal artery
Popliteal artery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Lower Limb Anatomy
- Lower Limb Overview: The lower limb encompasses the hip, thigh, leg, and foot. It's crucial for movement and support.
Palpable Landmarks
- Anterior Superior Iliac Spine (ASIS): A prominent bony landmark.
- Inguinal Ligament: A palpable ligament in the groin.
- Greater Trochanter: A prominent bony landmark on the femur.
- Tibial Tuberosity: A bony landmark on the tibia.
- Iliac Crest: A bony landmark on the pelvis.
- Gluteal Fold: A crease in the skin at the juncture of the buttock and thigh.
- Popliteal Fossa: A depression behind the knee.
- Iliotibial Tract: A fibrous band that runs along the lateral thigh.
- Sole of Foot: The bottom surface of the foot.
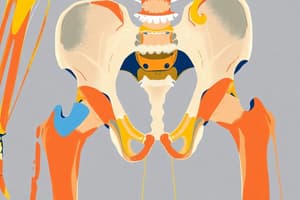
Pelvic Girdle Bones
- Coxal Bone (Hip Bone): Composed of the ilium, ischium, and pubis.
- Ilium: The largest portion of the coxal bone.
- Ischium: Posterior portion of the coxal bone.
- Pubis: Anterior portion of the coxal bone.
- Sacrum: A triangular bone forming part of the posterior pelvis.
- Coccyx: Tailbone, small triangular bone.
- Pelvic Brim: The opening boundary of the true pelvis.
- Acetabulum: The socket where the femur connects to the hip.
- Iliac Fossa: A depression on the ilium.
- Iliac Crest: The superior margin of the ilium.
- Sacroiliac Joint: Joint where the sacrum meets the ilium.
- Pubic Symphysis: Joint where the two pubic bones meet.
- Pubic Tubercle: A bony prominence on the pubis.
- Sacral Promontory: The anterior superior aspect of the sacrum.
- Anterior Superior Iliac Spine: A bony landmark on the ilium.
- Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine: Another bony landmark on the ilium.
Hip Joint
-
Iliofemoral Ligament - Anterior: Reinforces the anterior aspect of the joint capsule.
-
Pubofemoral Ligament - Anterior: Reinforces the inferior aspect of the joint capsule.
-
Ischiofemoral Ligament - Posterolateral: Reinforces the posterolateral aspect of the joint capsule.
-
Ligament of the Head of the Femur/Ligamentum Teres: A small ligament within the hip joint.
-
Capsular Ligament: The joint capsule surrounding the hip joint.
-
Arteries of the Lower Limb and Pelvis: Diagrams show the main arterial supply branches of the aorta and pelvis to the lower limbs.
-
Veins of the Lower Limb and Pelvis: Diagrams show the main venous drainage of the lower limbs and the pelvic region.
Hip and Thigh Pathologies
-
Angle of Inclination (Coxa Vara/Normal/Coxa Valga): Abnormal angles can lead to stress on the hip joint and gait irregularities.
-
Vitamin D/Calcium Deficiency (Rickets/Osteomalacia): Bone diseases affecting children (Rickets) and adults (Osteomalacia).
-
Hip Fracture (due to Osteoporosis): Common in elderly individuals due to bone density loss.
-
Common Hip Fractures: Different types of hip fractures, including intertrochanteric, comminuted, reverse obliquity, subcapital neck, transcervical neck, displaced, and femoral head fractures.
-
Other Knee and Lower Limb Fractures: Illustrates different types and classifications of fractures of other lower limb bones and the knee joint.
-
Congenital Dislocation of the Hip: Defect common in female infants, resulting in an incomplete acetabulum or loose hip ligaments.
Lower Limb Anatomy (Nerves):
- Lumbosacral Plexus: A network of nerves that supply the lower limb.
- Nerves of the lumbar plexus: Diagrams show the different nerves branching out, with labels and anatomical locations.
- Nerves of the sacral plexus: Diagrams show the different nerves for the sacral plexus, including anatomical areas supplied.
Thigh Muscles (Anterior):
- The muscles of the anterior compartment of the thigh are primarily extensors of the leg at the knee and secondarily flexors of the thigh at the hip.
- They are innervated by the femoral nerve.
- The femoral artery supplies these muscles.
Thigh Muscles (Medial)
- The muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh are primarily adductors of the thigh.
- Most are innervated by the obturator nerve.
- The obturator and deep femoral arteries supply blood.
Muscles of the Leg (Posterior):
- These muscles consist primarily of extensors of the thigh, with medial and lateral rotation and abduction being possible.
- Gluteus medius is a common injection site.
Posterior Thigh Muscles:
- The hamstring muscles (biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus, and adductor magnus) primarily are flexors of the knee.
- They are innervated by the tibial branch of the sciatic nerve.
Special Regions:
- Hunter's Canal: A structure with the femoral artery and vein, important for procedures/injections. Clinical significance includes sensory anesthesia for procedures, and using landmarks to locate the saphenous nerve
Popliteal Fossa:
-
Posterior muscles of the lower leg (gastrocsnemius, semitendinosus etc) form the popliteal fossa.
-
Popliteal artery and vein: major vessels in this region supplying the muscles and underlying structures of the back of the knee.
-
The tibial and common fibular (peroneal) nerve's branches pass through the popliteal fossa
-
Genicular arteries and veins
-
Arteries and Veins of the Leg and Foot: Diagrams show the major arterial and venous supply to the leg and foot.
Foot Bones:
- Tarsals: A group of seven bones forming the ankle region. Details of each tarsal are specified.
- Metatarsals: A group of five bones in the mid-foot.
- Phalanges: The bones of the toes.
Ankle and Foot Joints:
- Talocrural Joint (Ankle Joint): Articulation of the tibia, fibula, and talus for dorsiflexion and plantarflexions.
- Subtalar Joint (Talocalcaneal Joint): Between the talus and calcaneus; facilitates inversion and eversion movement.
- Intertarsal Joints: Varied joints between the tarsal bones.
- Tarsometatarsal Joints (Lisfranc Joint): Joints between the tarsals and metatarsals crucial for the proper foot structure.
- Metatarsophalangeal (MTP) Joints: Joints between metatarsals and the bases of the phalanges.
- Interphalangeal (IP) Joints (toe joints): Articulations between the phalanges.
Ankle and Foot Ligaments:
- Medial (Deltoid) Ligament: Reinforces the medial side of the ankle joint.
- Lateral Ligaments: (anterior talofibular, calcaneofibular, posterior talofibular) Reinforce the lateral side of the talocrural joint.
- Syndesmotic Ligaments: Hold tibia and fibula together forming the ankle mortise.
Compartment Syndrome (Lower Leg):
- Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome (Shin Splints): Pain caused by inflammation in the tibia or surrounding structures.
- Exertional Compartment Syndrome: Pain caused by the compression of nerves and blood vessels usually by muscle swelling.
Other Musculoskeletal Injuries and Conditions
- Foot Fractures (Metatarsal stress fractures): Common injuries due to repeated stress.
- Ankle Fractures: A detailed overview of common ankle fracture patterns.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.