Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main benefit of economic value derived from biodiversity?
What is the main benefit of economic value derived from biodiversity?
- Scientific research and learning
- Essential services supporting life on Earth
- Financial benefits such as resources for jobs and products (correct)
- Cultural identity and traditions
Which of the following options best illustrates the concept of ecological life support?
Which of the following options best illustrates the concept of ecological life support?
- Cultural practices of indigenous communities
- Medicines derived from plants
- The impact of climate change on polar ice caps
- Wetlands filtering water and absorbing floods (correct)
Which example best represents the cultural value of biodiversity?
Which example best represents the cultural value of biodiversity?
- The Maasai people's reliance on local wildlife and landscapes (correct)
- Hiking in national parks
- Medicines developed from plant extracts
- Researching coral reefs to understand climate change
What is an example of negative value in biodiversity?
What is an example of negative value in biodiversity?
Which of the following is NOT considered a threat to biodiversity?
Which of the following is NOT considered a threat to biodiversity?
What term describes the role an organism plays in its environment?
What term describes the role an organism plays in its environment?
Which of the following is considered an abiotic factor in an ecosystem?
Which of the following is considered an abiotic factor in an ecosystem?
Which ecological relationship involves one organism benefiting at the expense of another?
Which ecological relationship involves one organism benefiting at the expense of another?
What does a food web represent in an ecosystem?
What does a food web represent in an ecosystem?
In a pyramid of biomass, what typically happens to biomass as you move from producers to top predators?
In a pyramid of biomass, what typically happens to biomass as you move from producers to top predators?
What type of biodiversity refers to the variety of genes within a species?
What type of biodiversity refers to the variety of genes within a species?
What method is commonly used to measure biotic factors in an ecosystem?
What method is commonly used to measure biotic factors in an ecosystem?
Which ecological relationship benefits both species involved?
Which ecological relationship benefits both species involved?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
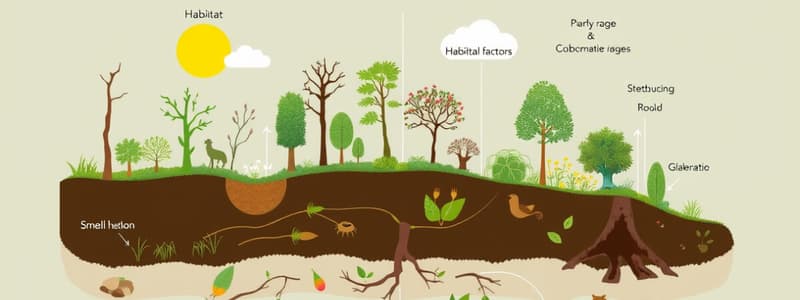
Parts of an Ecosystem
- Biotic factors encompass all living components like plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms.
- Abiotic factors include non-living elements such as water, sunlight, temperature, and soil.
- Habitat is defined as the specific environment in which an organism resides.
- Niche refers to the role of an organism, including its habitat and its interactions with other organisms.
- An ecosystem consists of a community of living organisms interacting with each other and their non-living environment.
- Community comprises all organisms in a specific location at a certain time.
- Population indicates a group of individuals of the same species residing in a defined area capable of interbreeding.
Measuring Abiotic and Biotic Factors
- Abiotic measurements utilize tools like thermometers (for temperature), rain gauges (for precipitation), and soil pH testers.
- Biotic measurements employ surveys and sampling techniques, such as quadrats or transects, to evaluate species diversity and population abundance.
Ecological Relationships
- Predation involves one organism (predator) consuming another (prey).
- Competition occurs between organisms vying for identical resources.
- Mutualism is a relationship where both species benefit, exemplified by bees and flowers.
- Commensalism results in one species benefiting while the other remains unaffected, illustrated by barnacles on whales.
- Parasitism is when one organism thrives at the expense of another, as seen with ticks on mammals.
Food Chains and Food Webs
- A food chain is a linear representation of the eating relationships in an ecosystem (e.g., grass → grasshopper → frog).
- A food web is a more intricate network illustrating various interconnected food chains and their feeding relationships.
Pyramids of Biomass
- The pyramid of biomass depicts the total living matter at each trophic level within an ecosystem.
- Generally, biomass diminishes from producers to top predators.
- Trophic levels include producers (plants), primary consumers (herbivores), secondary consumers (carnivores), and tertiary consumers.
Types and Value of Biodiversity
- Types of biodiversity:
- Genetic diversity refers to the variety of genes within a species.
- Species diversity indicates the range of different species in a habitat.
- Ecosystem diversity pertains to the variety of ecosystems present in a particular region.
- Value of biodiversity includes ecosystem services (like pollination and water purification), economic resources, and cultural significance.
Economic Value
- Economic value relates to financial benefits derived from biodiversity, including resources that generate jobs and products.
- Medicinal examples include cancer treatments developed from plants, like those derived from the rosy periwinkle.
Ecological Life Support
- This concept encapsulates vital ecosystem services necessary for supporting life on Earth.
- An example is wetlands that purify water and absorb floods.
Cultural Value
- Cultural value highlights biodiversity's role in shaping cultural identities and traditions.
- The Maasai people exemplify this by relying on local wildlife and landscapes for cultural practices.
Recreational Value
- The recreational value of biodiversity pertains to opportunities for enjoyment and activities it provides.
- Activities such as hiking and wildlife watching are particularly prominent in national parks like Yellowstone.
Scientific Value
- Scientific value indicates the importance of biodiversity in conducting research and gaining insights into natural systems.
- Studying coral reefs serves as an example to understand marine ecosystems and effects of climate change.
Negative Value
- This concept considers the detrimental impacts certain species can impose on ecosystems and human activities.
- Invasive species like zebra mussels present examples, disrupting local fisheries and waterways.
Threats to Biodiversity
- Habitat destruction results from urban development, deforestation, and pollution.
- Overexploitation refers to unsustainable hunting, fishing, and resource harvesting.
- Invasive species disrupt local ecosystems, threatening native biodiversity.
- Climate change affects habitats and species distributions, posing risks to survival.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.