Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following structures influences pain responses by modulating activity in PAG and PVG?
Which of the following structures influences pain responses by modulating activity in PAG and PVG?
- Cerebellum
- Medulla oblongata
- Limbic nuclei (correct)
- Spinal cord
Rubbing a painful area can increase pain perception.
Rubbing a painful area can increase pain perception.
False (B)
What key substances released by gray matter contribute to pain modulation?
What key substances released by gray matter contribute to pain modulation?
Endogenous opioids
The _______ is responsible for signaling information back to the gray matter to enhance pain modulation.
The _______ is responsible for signaling information back to the gray matter to enhance pain modulation.
What does the Gate Control Theory primarily explain?
What does the Gate Control Theory primarily explain?
Match the following components with their roles in pain modulation:
Match the following components with their roles in pain modulation:
Norepinephrine and serotonin are released by the spinal cord to promote pain sensation.
Norepinephrine and serotonin are released by the spinal cord to promote pain sensation.
Name one neurotransmitter released by the Locus Coeruleus.
Name one neurotransmitter released by the Locus Coeruleus.
Which of these is NOT a limbic structure associated with pain modulation?
Which of these is NOT a limbic structure associated with pain modulation?
Substance P is released by __________ fibers, indicating slow, chronic pain.
Substance P is released by __________ fibers, indicating slow, chronic pain.
Understanding pain pathways is solely important for treating acute pain.
Understanding pain pathways is solely important for treating acute pain.
What is the primary role of the anterolateral system in pain modulation?
What is the primary role of the anterolateral system in pain modulation?
Match the following pain fibers with their respective pain sensations:
Match the following pain fibers with their respective pain sensations:
Which structure is crucial for pain processing and located in Rexed Lamina II?
Which structure is crucial for pain processing and located in Rexed Lamina II?
The _______ nuclei play a critical role in the emotional and sensory aspects of pain experience.
The _______ nuclei play a critical role in the emotional and sensory aspects of pain experience.
Match the following terms with their descriptions:
Match the following terms with their descriptions:
Endogenous opioids are synthetic compounds used to relieve pain.
Endogenous opioids are synthetic compounds used to relieve pain.
What role do mechanoreceptors play in pain relief?
What role do mechanoreceptors play in pain relief?
The __________ system transmits pain to the cerebral cortex.
The __________ system transmits pain to the cerebral cortex.
Which neurotransmitter is primarily released by the Raphe Nucleus Magnus?
Which neurotransmitter is primarily released by the Raphe Nucleus Magnus?
What is the function of endogenous opioids in the body?
What is the function of endogenous opioids in the body?
Pain modulation occurs exclusively in the spinal cord.
Pain modulation occurs exclusively in the spinal cord.
Name a limbic structure that informs gray matter about emotional experiences related to pain.
Name a limbic structure that informs gray matter about emotional experiences related to pain.
The __________ system involves stimulation of descending pathways to modulate pain.
The __________ system involves stimulation of descending pathways to modulate pain.
Match the following components with their functions in pain modulation:
Match the following components with their functions in pain modulation:
Which action can dynamically adjust pain sensations according to the body's natural mechanisms?
Which action can dynamically adjust pain sensations according to the body's natural mechanisms?
Gray matter has no significant role in pain modulation.
Gray matter has no significant role in pain modulation.
What type of nerve fibers signal upward toward the brain indicating pain perception?
What type of nerve fibers signal upward toward the brain indicating pain perception?
The __________ nervous system is crucial for enhancing inhibitory actions during high pain levels.
The __________ nervous system is crucial for enhancing inhibitory actions during high pain levels.
Which of the following statements is true regarding pain pathways?
Which of the following statements is true regarding pain pathways?
What is the Gate Control Theory primarily concerned with?
What is the Gate Control Theory primarily concerned with?
Substance P is associated with fast pain sensations.
Substance P is associated with fast pain sensations.
What role do GABA-releasing interneurons play in pain perception?
What role do GABA-releasing interneurons play in pain perception?
The __________ is a critical structure involved in pain processing located in Rexed Lamina II.
The __________ is a critical structure involved in pain processing located in Rexed Lamina II.
Match the following neurotransmitters with their associated structures:
Match the following neurotransmitters with their associated structures:
Which neurotransmitter is primarily released by descending fibers to modulate pain perception?
Which neurotransmitter is primarily released by descending fibers to modulate pain perception?
Endogenous opioids are produced by the body to mimic the action of synthetic pain-relieving medications.
Endogenous opioids are produced by the body to mimic the action of synthetic pain-relieving medications.
What is the primary function of the Descending Analgesic System?
What is the primary function of the Descending Analgesic System?
The __________ are involved in engaging inhibitory neurons in the spinal cord to reduce pain perception.
The __________ are involved in engaging inhibitory neurons in the spinal cord to reduce pain perception.
Which of the following fibers is responsible for indicating fast pain sensations?
Which of the following fibers is responsible for indicating fast pain sensations?
What is the main function of the Gate Control Theory?
What is the main function of the Gate Control Theory?
Which neurotransmitter is released by the Locus Coeruleus in pain modulation?
Which neurotransmitter is released by the Locus Coeruleus in pain modulation?
Substance P is released by A-delta fibers indicating slow, chronic pain.
Substance P is released by A-delta fibers indicating slow, chronic pain.
Name one critical structure located in Rexed Lamina II that is involved in pain processing.
Name one critical structure located in Rexed Lamina II that is involved in pain processing.
The __________ is released by the Raphe Nucleus Magnus to help modulate pain perception.
The __________ is released by the Raphe Nucleus Magnus to help modulate pain perception.
Match the following neurotransmitters with their roles in pain modulation.
Match the following neurotransmitters with their roles in pain modulation.
What effect do mechanoreceptors have when activated during rubbing a painful area?
What effect do mechanoreceptors have when activated during rubbing a painful area?
What is the role of endogenous opioids in the body?
What is the role of endogenous opioids in the body?
Pain modulation occurs only at the peripheral level.
Pain modulation occurs only at the peripheral level.
Which of these fibers are primarily associated with fast pain sensations?
Which of these fibers are primarily associated with fast pain sensations?
What role do endogenous opioids play in the body's pain modulation system?
What role do endogenous opioids play in the body's pain modulation system?
Higher brain structures, like limbic nuclei, have no impact on pain modulation.
Higher brain structures, like limbic nuclei, have no impact on pain modulation.
Name one component of the descending pain modulation pathway.
Name one component of the descending pain modulation pathway.
The _______ is involved in releasing endogenous opioids to aid in pain modulation.
The _______ is involved in releasing endogenous opioids to aid in pain modulation.
Match the following components with their roles in pain modulation:
Match the following components with their roles in pain modulation:
Which of the following actions can help inhibit pain perception?
Which of the following actions can help inhibit pain perception?
The stimulation of descending pathways occurs exclusively through peripheral nerves.
The stimulation of descending pathways occurs exclusively through peripheral nerves.
What is the significance of understanding pain modulation?
What is the significance of understanding pain modulation?
The __________ fibers signal upward toward the brain to indicate pain perception.
The __________ fibers signal upward toward the brain to indicate pain perception.
Which structure plays a crucial role in processing pain and is found in Rexed Lamina II?
Which structure plays a crucial role in processing pain and is found in Rexed Lamina II?
Which of the following substances are released by C fibers to indicate slow, chronic pain?
Which of the following substances are released by C fibers to indicate slow, chronic pain?
The Gate Control Theory states that painful stimuli always generate pain sensations.
The Gate Control Theory states that painful stimuli always generate pain sensations.
What role do mechanoreceptors play in pain modulation?
What role do mechanoreceptors play in pain modulation?
The __________ system modulates pain at the spinal cord level through various neurotransmitters.
The __________ system modulates pain at the spinal cord level through various neurotransmitters.
Match the following pain fibers with their respective pain sensations:
Match the following pain fibers with their respective pain sensations:
Which neurotransmitter is primarily released by the Locus Coeruleus?
Which neurotransmitter is primarily released by the Locus Coeruleus?
Endogenous opioids produced by the body are similar to synthetic pain medications.
Endogenous opioids produced by the body are similar to synthetic pain medications.
Name one structure involved in pain processing located in Rexed Lamina II.
Name one structure involved in pain processing located in Rexed Lamina II.
During the rubbing of a painful area, interneurons release __________ to inhibit the action potentials in pain fibers.
During the rubbing of a painful area, interneurons release __________ to inhibit the action potentials in pain fibers.
Which of the following is NOT a key area in the Descending Analgesic System?
Which of the following is NOT a key area in the Descending Analgesic System?
Which structure is primarily involved in the modulation of pain by releasing endogenous opioids?
Which structure is primarily involved in the modulation of pain by releasing endogenous opioids?
Higher brain structures have no influence on pain responses.
Higher brain structures have no influence on pain responses.
What type of nerve fibers signal pain perception upwards toward the brain?
What type of nerve fibers signal pain perception upwards toward the brain?
The ________ system involves the modulation of pain through descending pathways.
The ________ system involves the modulation of pain through descending pathways.
Match the following components with their roles in pain modulation:
Match the following components with their roles in pain modulation:
Which of the following actions activates the body's natural pain relief mechanisms?
Which of the following actions activates the body's natural pain relief mechanisms?
Endogenous opioids are not involved in the body's natural pain management systems.
Endogenous opioids are not involved in the body's natural pain management systems.
Name one limbic structure that contributes to the modulation of pain.
Name one limbic structure that contributes to the modulation of pain.
Stimulation of the anterolateral system involves ________ axonal fibers.
Stimulation of the anterolateral system involves ________ axonal fibers.
Which of the following structures is involved in pain perception through modulation?
Which of the following structures is involved in pain perception through modulation?
Which of the following is primarily responsible for the release of endogenous opioids for pain modulation?
Which of the following is primarily responsible for the release of endogenous opioids for pain modulation?
The sensory cortex solely enhances pain perception without influencing pain modulation.
The sensory cortex solely enhances pain perception without influencing pain modulation.
What is the role of the limbic system in pain perception?
What is the role of the limbic system in pain perception?
The _____ fibers are responsible for signaling upward toward the brain, indicating pain perception.
The _____ fibers are responsible for signaling upward toward the brain, indicating pain perception.
Match the following terms with their descriptions:
Match the following terms with their descriptions:
Which action can activate the body's natural pain relief mechanisms?
Which action can activate the body's natural pain relief mechanisms?
Understanding pain modulation systems is essential for developing effective pain management strategies.
Understanding pain modulation systems is essential for developing effective pain management strategies.
Identify one key component of the descending pain modulation pathway.
Identify one key component of the descending pain modulation pathway.
Gray matter contributes to pain modulation by releasing _____ during higher pain levels.
Gray matter contributes to pain modulation by releasing _____ during higher pain levels.
Match the following brain structures with their roles in pain perception:
Match the following brain structures with their roles in pain perception:
Which neurotransmitter is primarily released by the Periaqueductal Gray Matter to reduce pain perception?
Which neurotransmitter is primarily released by the Periaqueductal Gray Matter to reduce pain perception?
The Gate Control Theory suggests that painful stimuli can always override non-painful stimuli.
The Gate Control Theory suggests that painful stimuli can always override non-painful stimuli.
What role do mechanoreceptors play when a painful area is rubbed?
What role do mechanoreceptors play when a painful area is rubbed?
Substance P is released by __________ fibers, indicating slow, chronic pain.
Substance P is released by __________ fibers, indicating slow, chronic pain.
Match the following neurotransmitters with their associated functions in pain modulation:
Match the following neurotransmitters with their associated functions in pain modulation:
Which structure located in Rexed Lamina II is critical for pain processing?
Which structure located in Rexed Lamina II is critical for pain processing?
Endogenous opioids such as endorphins are produced by the body.
Endogenous opioids such as endorphins are produced by the body.
What is the primary function of the Descending Analgesic System?
What is the primary function of the Descending Analgesic System?
The __________ system involves stimulation of descending pathways to modulate pain.
The __________ system involves stimulation of descending pathways to modulate pain.
Which of the following best describes the role of GABA-releasing interneurons during pain modulation?
Which of the following best describes the role of GABA-releasing interneurons during pain modulation?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
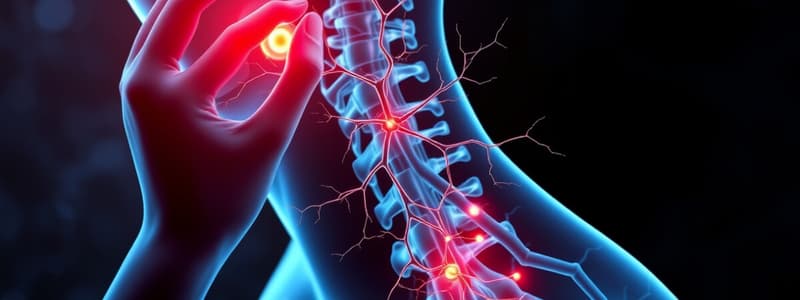
Pain Modulation Overview
- Pain modulation is as crucial as the pain pathways themselves.
- Modulation occurs endogenously, meaning the body produces chemicals to inhibit pain.
Two Analgesic Systems
-
Gate Control Theory: Explains how non-painful stimuli can inhibit pain.
- Rubbing a painful area activates touch receptors that compete with pain signals.
- Pain fibers, including A-delta and C fibers, have distinct synaptic pathways influencing pain perception.
- Substantia Gelatinosa of Rolando: A critical structure located in Rexed Lamina II involved in pain processing.
-
Descending Analgesic System: Modulates pain at the spinal cord level via cerebral structures.
- Key areas include Periaqueductal Gray Matter (PAG), Periventricular Gray Matter (PVG), Locus Coeruleus, Reticular Formation, and Raphe Nucleus Magnus.
Pain Pathway Mechanisms
- Pain is transmitted to the cerebral cortex through specific fibers (A-delta, C fibers).
- Substance P: Released by C fibers, indicating slow, chronic pain.
- Glutamate: Released by A-delta fibers, indicating fast pain sensations.
- Both substances influence the threshold for pain perception and affect neuronal excitability.
Rubbing for Pain Relief
- Mechanoreceptors activated during rubbing send signals that inhibit pain pathways:
- Interneurons release GABA, which inhibits action potentials in pain fibers, reducing pain sensation.
Descending Modulation Mechanisms
- Norepinephrine and Serotonin are critical neurotransmitters released by descending fibers.
- The Locus Coeruleus releases norepinephrine, while the Raphe Nucleus Magnus and Periaqueductal Gray matter release serotonin (5-Hydroxytryptamine).
- These neurotransmitters engage inhibitory neurons in the spinal cord, further reducing pain perception.
Opioid Analogs
- Endogenous Opioids: Produced by the body, including endorphins and dynorphins, mimic action of pain-relieving medications like morphine.
- These are key to natural pain relief mechanisms, functioning effectively alongside traditional pain pathways.
Regulation of Pain Modulation
- Pain signals from the spinal cord can stimulate descending pathways to enhance inhibitory actions during periods of high pain.
- Higher brain structures such as limbic nuclei and the sensory cortex influence the activity of PAG and PVG to modulate pain responses effectively.
Summary
- Understanding pain modulation involves exploring both the mechanisms of pain pathways and the body’s built-in systems for modulating pain.
- Rubbing the painful area activates a cascade of responses that inhibit pain perception, exemplifying the body's ability to adjust pain sensations dynamically.### Gray Matter and Pain Modulation
- Gray matter, particularly periventricular gray matter, has a role in releasing endogenous opioids which aid in pain modulation.
- Endogenous opioids are critical for the body’s natural pain management systems.
Stimulation of the Descending Pathway
- Stimulation of the descending pain modulation pathway can occur through the anterolateral system, which involves spinal axonal fibers.
- "Spinocephalic" fibers are a type of nerve fibers that can signal upward toward the brain, indicating pain perception and modulation.
- The sensory cortex contributes to pain perception by signaling information back to the gray matter to enhance pain modulation.
Role of Limbic Nuclei
- Limbic structures such as the hypothalamus, anterior insula, and cingulate gyrus play a role in informing the gray matter about emotional and sensory experiences related to pain.
- These connections form a complex and integrated system that influences pain perception and management.
Importance of Understanding Pain Modulation
- Understanding the pathways and mechanisms involved in pain modulation is essential for developing pain management strategies.
- Knowledge of these systems aids in addressing chronic pain issues and optimizing treatment approaches.
Pain Modulation Overview
- Pain modulation is essential for managing pain alongside established pain pathways.
- Endogenous modulation involves the body's natural production of chemicals to suppress pain sensations.
Two Analgesic Systems
- Gate Control Theory suggests non-painful sensory input can block pain signals.
- Rubbing an injured area activates touch receptors, competing with pain signals for processing.
- Pain fibers include A-delta (fast pain) and C fibers (slow pain), each with unique pathways affecting pain perception.
- Substantia Gelatinosa of Rolando, located in Rexed Lamina II, is central to pain processing in the spinal cord.
- Descending Analgesic System regulates pain at the spinal level, involving several brain regions including:
- Periaqueductal Gray Matter (PAG)
- Periventricular Gray Matter (PVG)
- Locus Coeruleus
- Reticular Formation
- Raphe Nucleus Magnus
Pain Pathway Mechanisms
- Pain signals are transmitted through specialized fibers:
- A-delta fibers convey rapid sharp pain.
- C fibers signal slower, dull pain.
- Substance P from C fibers indicates chronic pain, whereas Glutamate from A-delta fibers denotes acute pain.
- Both substances modify pain perception thresholds and influence neuronal activation.
Rubbing for Pain Relief
- Mechanoreceptor activation during tactile stimulation sends inhibitory signals through interneurons.
- GABA is released, inhibiting pain fiber action potentials and reducing pain intensity.
Descending Modulation Mechanisms
- Norepinephrine and Serotonin are key neurotransmitters in the descending modulation of pain.
- Norepinephrine is released by the Locus Coeruleus, while the Raphe Nucleus Magnus and PAG produce serotonin (5-HT).
- These neurotransmitters activate inhibitory spinal neurons, diminishing pain perception.
Opioid Analogs
- Endogenous opioids, such as endorphins and dynorphins, mimic opiates like morphine, providing natural pain relief.
- These compounds are vital to the body's intrinsic mechanisms for pain management.
Regulation of Pain Modulation
- Pain signaling from the spinal cord can activate descending pathways that enhance inhibition during acute pain.
- Higher brain structures, including limbic nuclei and sensory cortex, influence PAG and PVG functionality to effectively signal pain modulation.
Gray Matter and Pain Modulation
- Periventricular gray matter releases endogenous opioids, playing a pivotal role in pain modulation.
- Endogenous opioids are crucial for the body's natural ability to manage pain.
Stimulation of the Descending Pathway
- Descending pain modulation can be activated through the anterolateral system, which includes spinal axonal fibers.
- "Spinocephalic" fibers carry pain signals to the brain, facilitating perception and regulatory processes.
- The sensory cortex feeds back to the gray matter, enhancing the overall pain modulation response.
Role of Limbic Nuclei
- Limbic structures—like the hypothalamus, anterior insula, and cingulate gyrus—integrate emotional and sensory information related to pain.
- This integrated system affects both pain perception and management strategies.
Importance of Understanding Pain Modulation
- Gaining insights into pain modulation pathways and mechanisms is critical for effective pain management and treatment strategies.
- This understanding aids in tackling chronic pain challenges and refining therapeutic approaches.
Pain Modulation Overview
- Pain modulation is essential for managing pain alongside established pain pathways.
- Endogenous modulation involves the body's natural production of chemicals to suppress pain sensations.
Two Analgesic Systems
- Gate Control Theory suggests non-painful sensory input can block pain signals.
- Rubbing an injured area activates touch receptors, competing with pain signals for processing.
- Pain fibers include A-delta (fast pain) and C fibers (slow pain), each with unique pathways affecting pain perception.
- Substantia Gelatinosa of Rolando, located in Rexed Lamina II, is central to pain processing in the spinal cord.
- Descending Analgesic System regulates pain at the spinal level, involving several brain regions including:
- Periaqueductal Gray Matter (PAG)
- Periventricular Gray Matter (PVG)
- Locus Coeruleus
- Reticular Formation
- Raphe Nucleus Magnus
Pain Pathway Mechanisms
- Pain signals are transmitted through specialized fibers:
- A-delta fibers convey rapid sharp pain.
- C fibers signal slower, dull pain.
- Substance P from C fibers indicates chronic pain, whereas Glutamate from A-delta fibers denotes acute pain.
- Both substances modify pain perception thresholds and influence neuronal activation.
Rubbing for Pain Relief
- Mechanoreceptor activation during tactile stimulation sends inhibitory signals through interneurons.
- GABA is released, inhibiting pain fiber action potentials and reducing pain intensity.
Descending Modulation Mechanisms
- Norepinephrine and Serotonin are key neurotransmitters in the descending modulation of pain.
- Norepinephrine is released by the Locus Coeruleus, while the Raphe Nucleus Magnus and PAG produce serotonin (5-HT).
- These neurotransmitters activate inhibitory spinal neurons, diminishing pain perception.
Opioid Analogs
- Endogenous opioids, such as endorphins and dynorphins, mimic opiates like morphine, providing natural pain relief.
- These compounds are vital to the body's intrinsic mechanisms for pain management.
Regulation of Pain Modulation
- Pain signaling from the spinal cord can activate descending pathways that enhance inhibition during acute pain.
- Higher brain structures, including limbic nuclei and sensory cortex, influence PAG and PVG functionality to effectively signal pain modulation.
Gray Matter and Pain Modulation
- Periventricular gray matter releases endogenous opioids, playing a pivotal role in pain modulation.
- Endogenous opioids are crucial for the body's natural ability to manage pain.
Stimulation of the Descending Pathway
- Descending pain modulation can be activated through the anterolateral system, which includes spinal axonal fibers.
- "Spinocephalic" fibers carry pain signals to the brain, facilitating perception and regulatory processes.
- The sensory cortex feeds back to the gray matter, enhancing the overall pain modulation response.
Role of Limbic Nuclei
- Limbic structures—like the hypothalamus, anterior insula, and cingulate gyrus—integrate emotional and sensory information related to pain.
- This integrated system affects both pain perception and management strategies.
Importance of Understanding Pain Modulation
- Gaining insights into pain modulation pathways and mechanisms is critical for effective pain management and treatment strategies.
- This understanding aids in tackling chronic pain challenges and refining therapeutic approaches.
Pain Modulation Overview
- Pain modulation is essential for managing pain alongside established pain pathways.
- Endogenous modulation involves the body's natural production of chemicals to suppress pain sensations.
Two Analgesic Systems
- Gate Control Theory suggests non-painful sensory input can block pain signals.
- Rubbing an injured area activates touch receptors, competing with pain signals for processing.
- Pain fibers include A-delta (fast pain) and C fibers (slow pain), each with unique pathways affecting pain perception.
- Substantia Gelatinosa of Rolando, located in Rexed Lamina II, is central to pain processing in the spinal cord.
- Descending Analgesic System regulates pain at the spinal level, involving several brain regions including:
- Periaqueductal Gray Matter (PAG)
- Periventricular Gray Matter (PVG)
- Locus Coeruleus
- Reticular Formation
- Raphe Nucleus Magnus
Pain Pathway Mechanisms
- Pain signals are transmitted through specialized fibers:
- A-delta fibers convey rapid sharp pain.
- C fibers signal slower, dull pain.
- Substance P from C fibers indicates chronic pain, whereas Glutamate from A-delta fibers denotes acute pain.
- Both substances modify pain perception thresholds and influence neuronal activation.
Rubbing for Pain Relief
- Mechanoreceptor activation during tactile stimulation sends inhibitory signals through interneurons.
- GABA is released, inhibiting pain fiber action potentials and reducing pain intensity.
Descending Modulation Mechanisms
- Norepinephrine and Serotonin are key neurotransmitters in the descending modulation of pain.
- Norepinephrine is released by the Locus Coeruleus, while the Raphe Nucleus Magnus and PAG produce serotonin (5-HT).
- These neurotransmitters activate inhibitory spinal neurons, diminishing pain perception.
Opioid Analogs
- Endogenous opioids, such as endorphins and dynorphins, mimic opiates like morphine, providing natural pain relief.
- These compounds are vital to the body's intrinsic mechanisms for pain management.
Regulation of Pain Modulation
- Pain signaling from the spinal cord can activate descending pathways that enhance inhibition during acute pain.
- Higher brain structures, including limbic nuclei and sensory cortex, influence PAG and PVG functionality to effectively signal pain modulation.
Gray Matter and Pain Modulation
- Periventricular gray matter releases endogenous opioids, playing a pivotal role in pain modulation.
- Endogenous opioids are crucial for the body's natural ability to manage pain.
Stimulation of the Descending Pathway
- Descending pain modulation can be activated through the anterolateral system, which includes spinal axonal fibers.
- "Spinocephalic" fibers carry pain signals to the brain, facilitating perception and regulatory processes.
- The sensory cortex feeds back to the gray matter, enhancing the overall pain modulation response.
Role of Limbic Nuclei
- Limbic structures—like the hypothalamus, anterior insula, and cingulate gyrus—integrate emotional and sensory information related to pain.
- This integrated system affects both pain perception and management strategies.
Importance of Understanding Pain Modulation
- Gaining insights into pain modulation pathways and mechanisms is critical for effective pain management and treatment strategies.
- This understanding aids in tackling chronic pain challenges and refining therapeutic approaches.
Pain Modulation Overview
- Pain modulation is essential for managing pain alongside established pain pathways.
- Endogenous modulation involves the body's natural production of chemicals to suppress pain sensations.
Two Analgesic Systems
- Gate Control Theory suggests non-painful sensory input can block pain signals.
- Rubbing an injured area activates touch receptors, competing with pain signals for processing.
- Pain fibers include A-delta (fast pain) and C fibers (slow pain), each with unique pathways affecting pain perception.
- Substantia Gelatinosa of Rolando, located in Rexed Lamina II, is central to pain processing in the spinal cord.
- Descending Analgesic System regulates pain at the spinal level, involving several brain regions including:
- Periaqueductal Gray Matter (PAG)
- Periventricular Gray Matter (PVG)
- Locus Coeruleus
- Reticular Formation
- Raphe Nucleus Magnus
Pain Pathway Mechanisms
- Pain signals are transmitted through specialized fibers:
- A-delta fibers convey rapid sharp pain.
- C fibers signal slower, dull pain.
- Substance P from C fibers indicates chronic pain, whereas Glutamate from A-delta fibers denotes acute pain.
- Both substances modify pain perception thresholds and influence neuronal activation.
Rubbing for Pain Relief
- Mechanoreceptor activation during tactile stimulation sends inhibitory signals through interneurons.
- GABA is released, inhibiting pain fiber action potentials and reducing pain intensity.
Descending Modulation Mechanisms
- Norepinephrine and Serotonin are key neurotransmitters in the descending modulation of pain.
- Norepinephrine is released by the Locus Coeruleus, while the Raphe Nucleus Magnus and PAG produce serotonin (5-HT).
- These neurotransmitters activate inhibitory spinal neurons, diminishing pain perception.
Opioid Analogs
- Endogenous opioids, such as endorphins and dynorphins, mimic opiates like morphine, providing natural pain relief.
- These compounds are vital to the body's intrinsic mechanisms for pain management.
Regulation of Pain Modulation
- Pain signaling from the spinal cord can activate descending pathways that enhance inhibition during acute pain.
- Higher brain structures, including limbic nuclei and sensory cortex, influence PAG and PVG functionality to effectively signal pain modulation.
Gray Matter and Pain Modulation
- Periventricular gray matter releases endogenous opioids, playing a pivotal role in pain modulation.
- Endogenous opioids are crucial for the body's natural ability to manage pain.
Stimulation of the Descending Pathway
- Descending pain modulation can be activated through the anterolateral system, which includes spinal axonal fibers.
- "Spinocephalic" fibers carry pain signals to the brain, facilitating perception and regulatory processes.
- The sensory cortex feeds back to the gray matter, enhancing the overall pain modulation response.
Role of Limbic Nuclei
- Limbic structures—like the hypothalamus, anterior insula, and cingulate gyrus—integrate emotional and sensory information related to pain.
- This integrated system affects both pain perception and management strategies.
Importance of Understanding Pain Modulation
- Gaining insights into pain modulation pathways and mechanisms is critical for effective pain management and treatment strategies.
- This understanding aids in tackling chronic pain challenges and refining therapeutic approaches.
Pain Modulation Overview
- Pain modulation is essential for managing pain alongside established pain pathways.
- Endogenous modulation involves the body's natural production of chemicals to suppress pain sensations.
Two Analgesic Systems
- Gate Control Theory suggests non-painful sensory input can block pain signals.
- Rubbing an injured area activates touch receptors, competing with pain signals for processing.
- Pain fibers include A-delta (fast pain) and C fibers (slow pain), each with unique pathways affecting pain perception.
- Substantia Gelatinosa of Rolando, located in Rexed Lamina II, is central to pain processing in the spinal cord.
- Descending Analgesic System regulates pain at the spinal level, involving several brain regions including:
- Periaqueductal Gray Matter (PAG)
- Periventricular Gray Matter (PVG)
- Locus Coeruleus
- Reticular Formation
- Raphe Nucleus Magnus
Pain Pathway Mechanisms
- Pain signals are transmitted through specialized fibers:
- A-delta fibers convey rapid sharp pain.
- C fibers signal slower, dull pain.
- Substance P from C fibers indicates chronic pain, whereas Glutamate from A-delta fibers denotes acute pain.
- Both substances modify pain perception thresholds and influence neuronal activation.
Rubbing for Pain Relief
- Mechanoreceptor activation during tactile stimulation sends inhibitory signals through interneurons.
- GABA is released, inhibiting pain fiber action potentials and reducing pain intensity.
Descending Modulation Mechanisms
- Norepinephrine and Serotonin are key neurotransmitters in the descending modulation of pain.
- Norepinephrine is released by the Locus Coeruleus, while the Raphe Nucleus Magnus and PAG produce serotonin (5-HT).
- These neurotransmitters activate inhibitory spinal neurons, diminishing pain perception.
Opioid Analogs
- Endogenous opioids, such as endorphins and dynorphins, mimic opiates like morphine, providing natural pain relief.
- These compounds are vital to the body's intrinsic mechanisms for pain management.
Regulation of Pain Modulation
- Pain signaling from the spinal cord can activate descending pathways that enhance inhibition during acute pain.
- Higher brain structures, including limbic nuclei and sensory cortex, influence PAG and PVG functionality to effectively signal pain modulation.
Gray Matter and Pain Modulation
- Periventricular gray matter releases endogenous opioids, playing a pivotal role in pain modulation.
- Endogenous opioids are crucial for the body's natural ability to manage pain.
Stimulation of the Descending Pathway
- Descending pain modulation can be activated through the anterolateral system, which includes spinal axonal fibers.
- "Spinocephalic" fibers carry pain signals to the brain, facilitating perception and regulatory processes.
- The sensory cortex feeds back to the gray matter, enhancing the overall pain modulation response.
Role of Limbic Nuclei
- Limbic structures—like the hypothalamus, anterior insula, and cingulate gyrus—integrate emotional and sensory information related to pain.
- This integrated system affects both pain perception and management strategies.
Importance of Understanding Pain Modulation
- Gaining insights into pain modulation pathways and mechanisms is critical for effective pain management and treatment strategies.
- This understanding aids in tackling chronic pain challenges and refining therapeutic approaches.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.